|
C. C. Kingston
Charles Cameron Kingston (22 October 1850 – 11 May 1908) was an Australian politician. From 1893 to 1899 he was a radical liberal Premier of South Australia, occupying this office with the support of Labor, which in the House of Assembly was led by John McPherson from 1893, and by Lee Batchelor upon McPherson's death in 1897. Kingston won the 1893, 1896 and 1899 colonial elections against the conservatives. During his time as Premier, Kingston was responsible for such measures as electoral reform including the first law to give votes to women in Australia (and second in the world only to New Zealand), a legitimation Act, the first conciliation and arbitration act in Australia, establishment of a state bank, a high protective tariff, regulation of factories, a progressive system of land, and income taxation, a public works program, and more extensive workers' compensation. A leading advocate of federation, Kingston contributed extensively at a practical level to bringing it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Right Honourable
''The Right Honourable'' ( abbreviation: ''Rt Hon.'' or variations) is an honorific style traditionally applied to certain persons and collective bodies in the United Kingdom, the former British Empire and the Commonwealth of Nations. The term is predominantly used today as a style associated with the holding of certain senior public offices in the United Kingdom, Canada, New Zealand, and to a lesser extent, Australia. ''Right'' in this context is an adverb meaning 'very' or 'fully'. Grammatically, ''The Right Honourable'' is an adjectival phrase which gives information about a person. As such, it is not considered correct to apply it in direct address, nor to use it on its own as a title in place of a name; but rather it is used in the third person along with a name or noun to be modified. ''Right'' may be abbreviated to ''Rt'', and ''Honourable'' to ''Hon.'', or both. ''The'' is sometimes dropped in written abbreviated form, but is always pronounced. Countries with common or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lee Batchelor
Egerton Lee Batchelor (10 April 1865 – 8 October 1911) was an Australian politician and trade unionist. He was a pioneer of the Australian Labor Party (ALP) in South Australia, which at the time was known as the United Labor Party (ULP). He was a member of the South Australian House of Assembly (1893–1901), leading the ULP from 1898 until his resignation in 1899 to accept a ministerial post in a non-Labor government, with the party's approval. Batchelor entered federal politics in 1901 and held cabinet posts in the first three ALP governments. He was Minister for Home Affairs (1904) under Chris Watson, and then served two terms as Minister for External Affairs (1908–1909, 1910–1911) under Andrew Fisher. He suffered a fatal heart attack at the age of 46 while climbing Mount Donna Buang. Early life Lee Batchelor was born in Adelaide, South Australia in 1865 and after the early death of his photographer father, he and his two brothers were raised by his mother. Batchelor wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Division Of Adelaide
The Division of Adelaide is an Australian electoral division in South Australia and is named for the city of Adelaide, South Australia's capital. At the 2016 federal election, the electorate covered 76 km², is centred on the Adelaide city centre and spanning from Grand Junction Road in the north to Cross Road in the south and from Portrush Road in the east to Marion and Holbrooks Road in the west, taking in suburbs including Ashford, Enfield, Goodwood, Kent Town, Keswick, Kilburn, Mansfield Park, Maylands, Northgate, Norwood, Parkside, Prospect, Rose Park, St Peters, Toorak Gardens, Torrensville, Thebarton, Unley and Walkerville. Geography Since 1984, federal electoral division boundaries in Australia have been determined at redistributions by a redistribution committee appointed by the Australian Electoral Commission. Redistributions occur for the boundaries of divisions in a particular state, and they occur every seven years, or sooner if a state's repr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1901 Australian Federal Election
The 1901 Australian federal election for the inaugural Parliament of Australia was held in Australia on Friday 29 March and Saturday 30 March 1901. The elections followed Federation and the establishment of the Commonwealth of Australia on 1 January 1901. All 75 seats in the Australian House of Representatives, six of which were uncontested, as well as all 36 seats in the Australian Senate, were up for election. After the initial confusion of the Hopetoun Blunder, the first Prime Minister of Australia, Edmund Barton, went into the inaugural 1901 federal election as the appointed head of a Protectionist Party caretaker government. While the Protectionists came first on votes and seats, they fell short of a majority. The incumbent government remained in office with the parliamentary support of the Labour Party, who held the balance of power, while the Free Trade Party formed the opposition. A few months prior to the 1903 election, Barton resigned to become a founding membe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
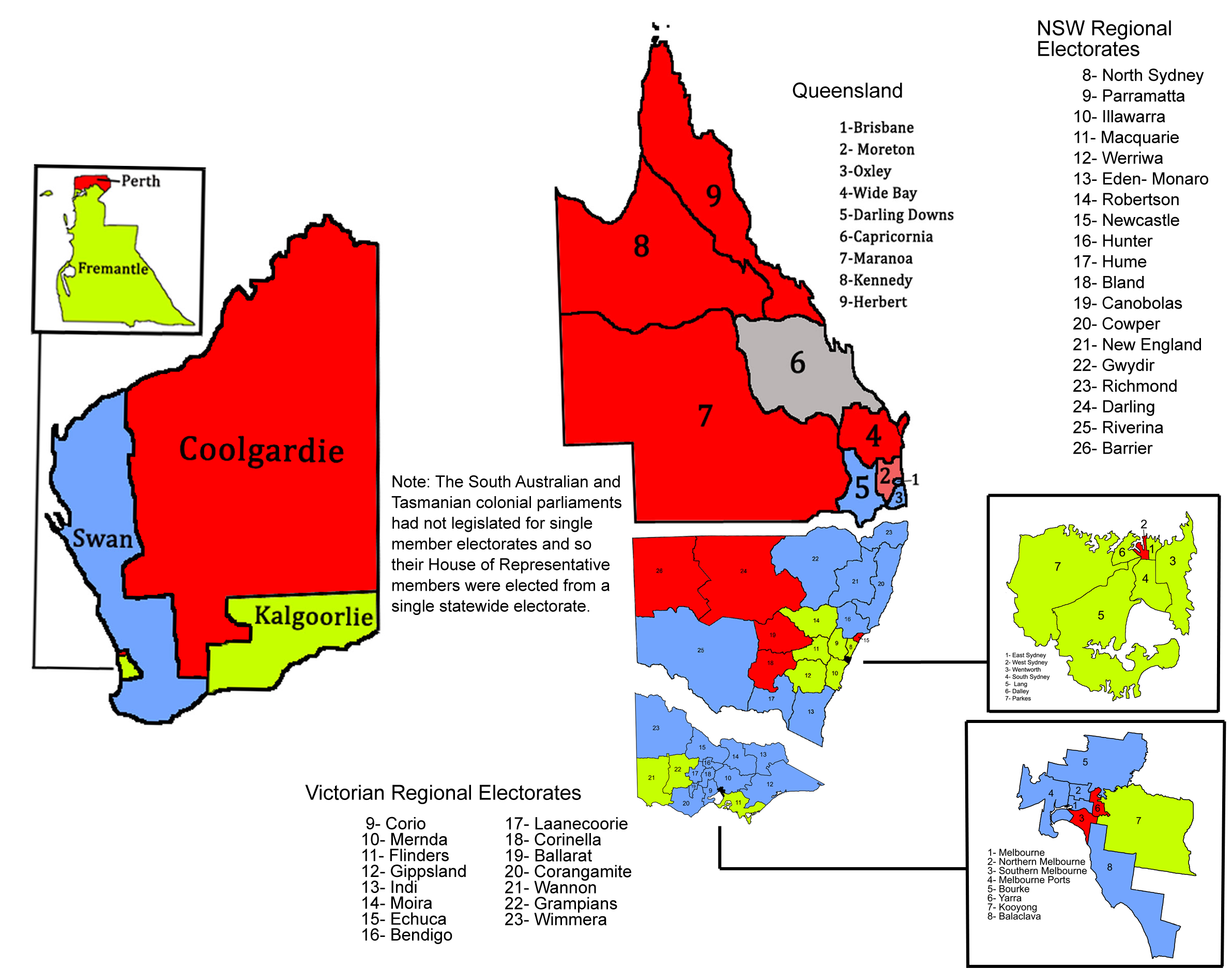
Division Of South Australia
The Division of South Australia was an Divisions of the Australian House of Representatives, Australian electoral division covering South Australia.The Northern Territory was part of South Australia until 1911. Its area was covered by the Division of Grey from 1903 to 1910 Australian federal election, 1910. The seven-member statewide seat existed from the inaugural 1901 Australian federal election, 1901 election until the 1903 Australian federal election, 1903 election. Each elector cast seven votes. Unlike most of the other states, South Australia had not been split into individual single-member electorates. The other exception was the five-member Division of Tasmania. The statewide seats were abolished at a redistribution conducted two months prior to the 1903 election and were subsequently replaced with single-member divisions, one per displaced member, with each elector now casting a single vote. Members ''Sorted in order of votes received'' The Division was split into s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian House Of Representatives
The House of Representatives is the lower house of the bicameral Parliament of Australia, the upper house being the Senate. Its composition and powers are established in Chapter I of the Constitution of Australia. The term of members of the House of Representatives is a maximum of three years from the date of the first sitting of the House, but on only one occasion since Federation has the maximum term been reached. The House is almost always dissolved earlier, usually alone but sometimes in a double dissolution of both Houses. Elections for members of the House of Representatives are often held in conjunction with those for the Senate. A member of the House may be referred to as a "Member of Parliament" ("MP" or "Member"), while a member of the Senate is usually referred to as a "Senator". The government of the day and by extension the Prime Minister must achieve and maintain the confidence of this House in order to gain and remain in power. The House of Representatives c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federation Of Australia
The Federation of Australia was the process by which the six separate British self-governing colonies of Queensland, New South Wales, Victoria, Tasmania, South Australia (which also governed what is now the Northern Territory), and Western Australia agreed to unite and form the Commonwealth of Australia, establishing a system of federalism in Australia. The colonies of Fiji and New Zealand were originally part of this process, but they decided not to join the federation. Following federation, the six colonies that united to form the Commonwealth of Australia as states kept the systems of government (and the bicameral legislatures) that they had developed as separate colonies, but they also agreed to have a federal government that was responsible for matters concerning the whole nation. When the Constitution of Australia came into force, on 1 January 1901, the colonies collectively became states of the Commonwealth of Australia. The efforts to bring about federation in the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tariff
A tariff is a tax imposed by the government of a country or by a supranational union on imports or exports of goods. Besides being a source of revenue for the government, import duties can also be a form of regulation of foreign trade and policy that taxes foreign products to encourage or safeguard domestic industry. ''Protective tariffs'' are among the most widely used instruments of protectionism, along with import quotas and export quotas and other non-tariff barriers to trade. Tariffs can be fixed (a constant sum per unit of imported goods or a percentage of the price) or variable (the amount varies according to the price). Taxing imports means people are less likely to buy them as they become more expensive. The intention is that they buy local products instead, boosting their country's economy. Tariffs therefore provide an incentive to develop production and replace imports with domestic products. Tariffs are meant to reduce pressure from foreign competition and reduce th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arbitration
Arbitration is a form of alternative dispute resolution (ADR) that resolves disputes outside the judiciary courts. The dispute will be decided by one or more persons (the 'arbitrators', 'arbiters' or 'arbitral tribunal'), which renders the 'arbitration award'. An arbitration decision or award is legally binding on both sides and enforceable in the courts, unless all parties stipulate that the arbitration process and decision are non-binding. Arbitration is often used for the resolution of commercial disputes, particularly in the context of international commercial transactions. In certain countries such as the United States, arbitration is also frequently employed in consumer and employment matters, where arbitration may be mandated by the terms of employment or commercial contracts and may include a waiver of the right to bring a class action claim. Mandatory consumer and employment arbitration should be distinguished from consensual arbitration, particularly commercial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conciliation
Conciliation is an alternative dispute resolution (ADR) process whereby the parties to a dispute use a conciliator, who meets with the parties both separately and together in an attempt to resolve their differences. They do this by lowering tensions, improving communications, interpreting issues, encouraging parties to explore potential solutions and assisting parties in finding a mutually acceptable outcome. Conciliation differs from arbitration in that the conciliation process, in and of itself, has no legal standing, and the conciliator usually has no authority to seek evidence or call witnesses, usually writes no decision, and makes no award. Conciliation techniques There is a form of "conciliation" that is more akin to negotiation. A "conciliator" assists each of the parties to independently develop a list of all of their objectives (the outcomes which they desire to obtain from the conciliation). The conciliator then has each of the parties separately prioritize their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legitimation
Legitimation or legitimisation is the act of providing legitimacy. Legitimation in the social sciences refers to the process whereby an act, process, or ideology becomes legitimate by its attachment to norms and values within a given society. It is the process of making something acceptable and normative to a group or audience. Legitimate power is the right to exercise control over others by virtue of the authority of one's superior organization position or status. Power and influence For example, the legitimation of power can be understood using Max Weber's traditional bases of power. In a bureaucracy, people gain legitimate use of power by their positions in which it is widely agreed that the specified person hold authority. There is no inherent right to wield power. For example, a president can exercise power and authority because the position is fully legitimated by society as a whole. In another example, if an individual attempts to convince others that something is "ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electoral Reform
Electoral reform is a change in electoral systems which alters how public desires are expressed in election results. That can include reforms of: * Voting systems, such as proportional representation, a two-round system (runoff voting), instant-runoff voting (alternative voting, ranked-choice voting, or preferential voting), Instant Round Robin Voting called Condorcet Voting, range voting, approval voting, citizen initiatives and referendums and recall elections. * Vote-counting procedures * Rules about political parties, typically changes to election laws * Eligibility to vote * How candidates and political parties are able to stand (nomination rules) and how they are able to get their names onto ballots (ballot access) * Electoral constituencies and election district borders * Ballot design and voting equipment * Scrutineering (election monitoring by candidates, political parties, etc.) * Safety of voters and election workers * Measures against bribery, coercion, and conflicts of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_(cropped).jpg)
.jpg)




.png)

