|
C.E.K. Mees Observatory
C. E. K. Mees Observatory is an astronomical observatory in Bristol, New York, owned and operated by the University of Rochester. The observatory is named after C. E. Kenneth Mees, "in honor of his pioneering work in the development of sensitive photographic emulsions for use in astronomy." The site possesses a 24 in (61 cm) Cassegrain telescope on an English-style telescope mount in a two-story dome in addition to a 12 in (31 cm) Orion SkyQuest Dobsonian, an inoperative 6 in (15 cm) Newtonian reflector on a German equatorial mount, and a 6 in refractor A refracting telescope (also called a refractor) is a type of optical telescope that uses a lens (optics), lens as its objective (optics), objective to form an image (also referred to a dioptrics, dioptric telescope). The refracting telescope d ... used as a guide telescope. The observatory is notable as a premier location for astronomical observation in Ontario county due to the low levels of light pollut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies astronomical object, celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and chronology of the Universe, evolution. Objects of interest include planets, natural satellite, moons, stars, nebulae, galaxy, galaxies, and comets. Relevant phenomena include supernova explosions, gamma ray bursts, quasars, blazars, pulsars, and cosmic microwave background radiation. More generally, astronomy studies everything that originates beyond atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere. Cosmology is a branch of astronomy that studies the universe as a whole. Astronomy is one of the oldest natural sciences. The early civilizations in recorded history made methodical observations of the night sky. These include the Babylonian astronomy, Babylonians, Greek astronomy, Greeks, Indian astronomy, Indians, Egyptian astronomy, Egyptians, Chinese astronomy, Chinese, Maya civilization, Maya, and many anc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Observatory
An observatory is a location used for observing terrestrial, marine, or celestial events. Astronomy, climatology/meteorology, geophysical, oceanography and volcanology are examples of disciplines for which observatories have been constructed. Historically, observatories were as simple as containing an astronomical sextant (for measuring the distance between stars) or Stonehenge (which has some alignments on astronomical phenomena). Astronomical observatories Astronomical observatories are mainly divided into four categories: space-based, airborne, ground-based, and underground-based. Ground-based observatories Ground-based observatories, located on the surface of Earth, are used to make observations in the radio and visible light portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. Most optical telescopes are housed within a dome or similar structure, to protect the delicate instruments from the elements. Telescope domes have a slit or other opening in the roof that can be opened during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bristol, New York
Bristol is a town in Ontario County, New York, United States. The population was 2,298 at the 2020 census. Bristol was named after Bristol County, Massachusetts, by settlers from New England. The town of Bristol is in the western half of the county, southwest of the city of Canandaigua. History The region was visited by the explorers Robert de La Salle and René de Bréhant de Galinée in 1669 in order to observe a burning spring known to the area's indigenous members of the Seneca tribe. Such "burning springs" occur in places where the water appears to support a flame caused by escaping natural gas. The Sullivan Expedition destroyed native villages as it passed through Bristol in 1779. Some of the soldiers were impressed with the area and later returned to buy land. The town area was first settled around 1788. The town of Bristol was formed in 1789, but the first town meeting was not held until 1797. In 1838 part of the town was used to form the town of South Bristol. Geog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York State
New York, officially the State of New York, is a state in the Northeastern United States. It is often called New York State to distinguish it from its largest city, New York City. With a total area of , New York is the 27th-largest U.S. state by area. With 20.2 million people, it is the fourth-most-populous state in the United States as of 2021, with approximately 44% living in New York City, including 25% of the state's population within Brooklyn and Queens, and another 15% on the remainder of Long Island, the most populous island in the United States. The state is bordered by New Jersey and Pennsylvania to the south, and Connecticut, Massachusetts, and Vermont to the east; it has a maritime border with Rhode Island, east of Long Island, as well as an international border with the Canadian provinces of Quebec to the north and Ontario to the northwest. New York City (NYC) is the most populous city in the United States, and around two-thirds of the state's population liv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Rochester
The University of Rochester (U of R, UR, or U of Rochester) is a private research university in Rochester, New York. The university grants undergraduate and graduate degrees, including doctoral and professional degrees. The University of Rochester enrolls approximately 6,800 undergraduates and 5,000 graduate students. Its 158 buildings house over 200 academic majors. According to the National Science Foundation, Rochester spent more than $397 million on research and development in 2020, ranking it 66th in the nation. With approximately 28,000 full-time employees, the university is the largest private employer in Upstate New York and the 7th largest in all of New York State. The College of Arts, Sciences, and Engineering is home to departments and divisions of note. The Institute of Optics was founded in 1929 through a grant from Eastman Kodak and Bausch and Lomb as the first educational program in the US devoted exclusively to optics, awards approximately half ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kenneth Mees
Charles Edward Kenneth Mees FRS (26 May 1882 – 15 August 1960) was a British scientist and photographic researcher. Early life and education Mees was born in Wellingborough, England, the son of a Wesleyan minister. He attended the University of London. In 1906 he was awarded his D.Sc. with a dissertation on photographic theory. Career From 1906 until 1912, Mees worked for Wratten and Wainwright, Ltd., assisting Frederick Wratten in developing the first panchromatic photographic plates, as well as light filters and safelights for the darkroom. In 1912, Eastman Kodak Company acquired Wratten and Wainwright because they were interested in the skills Mees provided. George Eastman convinced Mees to move to Rochester, New York, United States, where Mees created the Kodak Research Laboratories, becoming its first director. Mees helped the US military in World War I in its instruction of photography. After the attack on Pearl Harbor, Mees became an American citizen so that h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
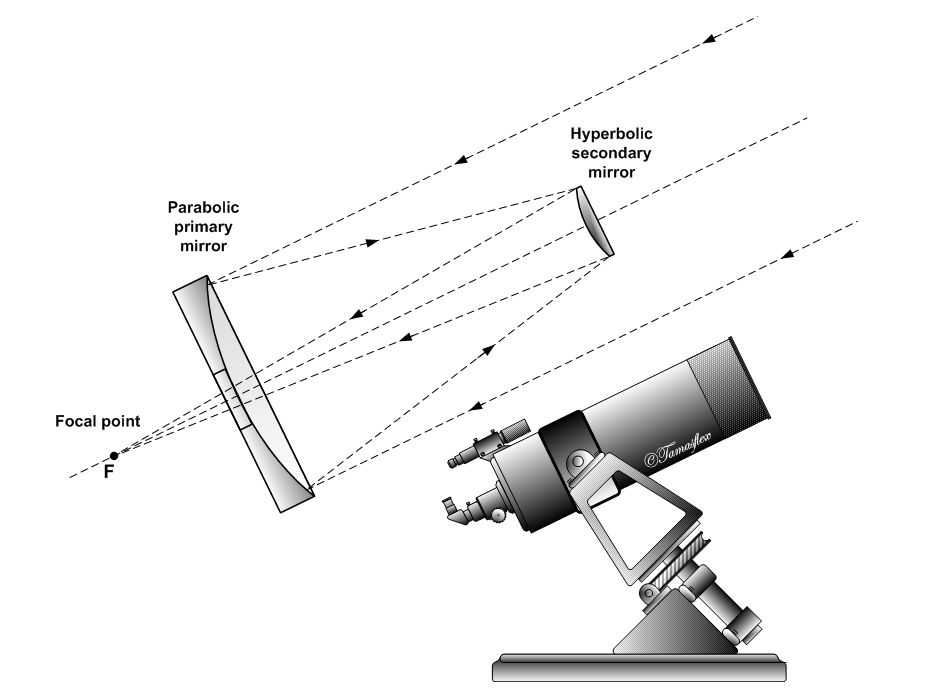
Cassegrain Telescope
The Cassegrain reflector is a combination of a primary concave mirror and a secondary convex mirror, often used in optical telescopes and radio antennas, the main characteristic being that the optical path folds back onto itself, relative to the optical system's primary mirror entrance aperture. This design puts the focal point at a convenient location behind the primary mirror and the convex secondary adds a telephoto effect creating a much longer focal length in a mechanically short system. In a symmetrical Cassegrain both mirrors are aligned about the optical axis, and the primary mirror usually contains a hole in the center, thus permitting the light to reach an eyepiece, a camera, or an image sensor. Alternatively, as in many radio telescopes, the final focus may be in front of the primary. In an asymmetrical Cassegrain, the mirror(s) may be tilted to avoid obscuration of the primary or to avoid the need for a hole in the primary mirror (or both). The classic Cassegrain co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telescope Mount
A telescope mount is a mechanical structure which supports a telescope. Telescope mounts are designed to support the mass of the telescope and allow for accurate pointing of the instrument. Many sorts of mounts have been developed over the years, with the majority of effort being put into systems that can track the motion of the fixed stars as the Earth rotates. Fixed mounts Fixed telescope mounts are entirely fixed in one position, such as Zenith telescopes that point only straight up and the National Radio Astronomy Observatory's Green Bank fixed radio 'horn' built to observe Cassiopeia A. Fixed altitude mounts Fixed-altitude mounts usually have the primary optics fixed at an altitude angle while rotating horizontally (in azimuth). They can cover the whole sky but only observe objects for the short time when that object passes a specific altitude and azimuth. Transit mounts Transit mounts are single axis mounts fixed in azimuth while rotating in altitude, usually orient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dobsonian
A Dobsonian telescope is an altazimuth-mounted Newtonian telescope design popularized by John Dobson in 1965 and credited with vastly increasing the size of telescopes available to amateur astronomers. Dobson's telescopes featured a simplified mechanical design that was easy to manufacture from readily available components to create a large, portable, low-cost telescope. The design is optimized for observing faint, deep-sky objects such as nebulae and galaxies. This type of observation requires a large objective diameter (i.e. light-gathering power) of relatively short focal length and portability for travel to less light-polluted locations. Dobsonians are intended to be what is commonly called a "light bucket" operating at low magnification, and therefore the design omits features found in other amateur telescopes such as equatorial tracking. Dobsonians are popular in the amateur telescope making community, where the design was pioneered and continues to evolve. A number of c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newtonian Reflector
The Newtonian telescope, also called the Newtonian reflector or just a Newtonian, is a type of reflecting telescope invented by the English scientist Sir Isaac Newton, using a concave primary mirror and a flat diagonal secondary mirror. Newton's first reflecting telescope was completed in 1668 and is the earliest known functional reflecting telescope. The Newtonian telescope's simple design has made it very popular with amateur telescope makers. Description [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equatorial Mount
An equatorial mount is a mount for instruments that compensates for Earth's rotation by having one rotational axis, the polar axis, parallel to the Earth's axis of rotation. This type of mount is used for astronomical telescopes and cameras. The advantage of an equatorial mount lies in its ability to allow the instrument attached to it to stay fixed on any celestial object with diurnal motion by driving one axis at a constant speed. Such an arrangement is called a sidereal or clock drive. Equatorial mounts achieve this by aligning their rotational axis with the Earth, a process known as polar alignment. Astronomical telescope mounts In astronomical telescope mounts, the equatorial axis (the '' right ascension'') is paired with a second perpendicular axis of motion (known as the '' declination''). The equatorial axis of the mount is often equipped with a motorized "''clock drive''", that rotates that axis one revolution every 23 hours and 56 minutes in exact sync with the appar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refractor
A refracting telescope (also called a refractor) is a type of optical telescope that uses a lens (optics), lens as its objective (optics), objective to form an image (also referred to a dioptrics, dioptric telescope). The refracting telescope design was originally used in spyglasses and astronomy, astronomical telescopes but is also used for long-focus lens, long-focus camera lenses. Although large refracting telescopes were very popular in the second half of the 19th century, for most research purposes, the refracting telescope has been superseded by the reflecting telescope, which allows larger apertures. A refractor's magnification is calculated by dividing the focal length of the objective lens by that of the eyepiece. Refracting telescopes typically have a lens at the front, then a optical train, long tube, then an eyepiece or instrumentation at the rear, where the telescope view comes to focus. Originally, telescopes had an objective of one element, but a century later, tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |