|
Bremerhaven
Bremerhaven (, , Low German: ''Bremerhoben'') is a city at the seaport of the Free Hanseatic City of Bremen, a state of the Federal Republic of Germany. It forms a semi-enclave in the state of Lower Saxony and is located at the mouth of the River Weser on its eastern bank, opposite the town of Nordenham. Though a relatively new city, it has a long history as a trade port and today is one of the most important German ports, playing a role in Germany's trade. History in 1827, but neighboring settlements such as Lehe were in the vicinity as early as the 12th century, and Geestendorf was "mentioned in documents of the ninth century". p. 8. Fourth revised edition. Translated into English from the original German edition titled ''Bremerhaven – tätige Stadt im Noordseewind'' These tiny villages were built on small islands in the swampy estuary. In 1381, the city of Bremen established ''de facto'' rule over the lower Weser stream, including Lehe, later therefore called Bremer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
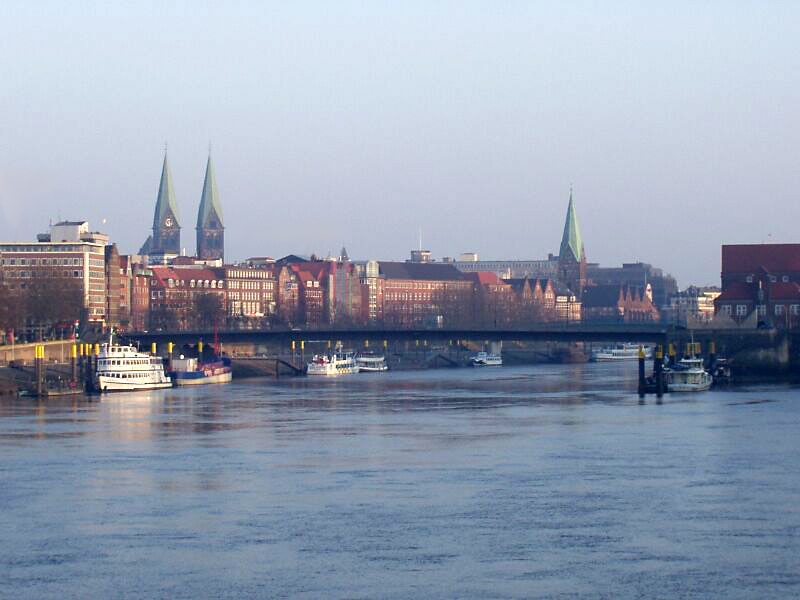
Bremen
Bremen (Low German also: ''Breem'' or ''Bräm''), officially the City Municipality of Bremen (german: Stadtgemeinde Bremen, ), is the capital of the German state Free Hanseatic City of Bremen (''Freie Hansestadt Bremen''), a two-city-state consisting of the cities of Bremen and Bremerhaven. With about 570,000 inhabitants, the Hanseatic city is the 11th largest city of Germany and the second largest city in Northern Germany after Hamburg. Bremen is the largest city on the River Weser, the longest river flowing entirely in Germany, lying some upstream from its mouth into the North Sea, and is surrounded by the state of Lower Saxony. A commercial and industrial city, Bremen is, together with Oldenburg and Bremerhaven, part of the Bremen/Oldenburg Metropolitan Region, with 2.5 million people. Bremen is contiguous with the Lower Saxon towns of Delmenhorst, Stuhr, Achim, Weyhe, Schwanewede and Lilienthal. There is an exclave of Bremen in Bremerhaven, the "Citybremian Overseas Port ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bremen (state)
Bremen (), officially the Free Hanseatic City of Bremen (german: Freie Hansestadt Bremen; nds, Free Hansestadt Bremen), is the smallest and least populous of Germany's 16 states. It is informally called ("State of Bremen"), although the term is sometimes used in official contexts. The state consists of the city of Bremen and its seaport exclave, Bremerhaven, surrounded by the larger state of Lower Saxony in northern Germany. Geography The state of Bremen consists of two non-contiguous territories. These enclaves contain Bremen, officially the 'City' (''Stadtgemeinde Bremen'') which is the state capital, and the city of Bremerhaven (''Stadt Bremerhaven''). Both are located on the River Weser; Bremerhaven ("Bremen's harbour") is further downstream on the mouth of the Weser with open access to the North Sea. Both enclaves are completely surrounded by the neighbouring State of Lower Saxony (''Niedersachsen''). The highest point in the state is in Friedehorst Park (32.5m). Hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weser
The Weser () is a river of Lower Saxony in north-west Germany. It begins at Hannoversch Münden through the confluence of the Werra and Fulda. It passes through the Hanseatic city of Bremen. Its mouth is further north against the ports of Bremerhaven and Nordenham. The latter is on the Butjadingen Peninsula. It then merges into the North Sea via two highly saline, estuarine mouths. It connects to the canal network running east-west across the North German Plain. The river, when combined with the Werra (a dialectal form of "Weser"), is long and thus, the longest river entirely situated within Germany (the Main, however, is the longest if the Weser and Werra are not combined). The Weser itself is long. The Werra rises in Thuringia, the German state south of the main projection (tongue) of Lower Saxony. Etymology "Weser" and "Werra" are the same words in different dialects. The difference reflects the old linguistic border between Central and Low German, passing through H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carlsburg, Weser
Carlsburg (also Carolus-Stadt or Carolsburg) was a 17th-century fortified town in Swedish Bremen-Verden at the confluence of the Weser and Geeste rivers, at the site of modern Bremerhaven, Germany. Planned to compete with Bremen, the settlement did not prosper. After the Thirty Years' War, the Swedish Empire gained the Lower Saxon Prince-Archbishopric of Bremen as a Swedish dominion. The status of the city of Bremen however was uncertain, and Sweden was unable to gain control of the town in two subsequent wars, 1654 and 1666. As Bremen itself was out of reach, a new town was built nearby, named Carlsburg after the Swedish king Charles XI. The town was planned by Stockholm architect Nicodemus Tessin the Elder. Tessin planned the public buildings and streets. He designated 300 to 456 building grounds for houses. Constructions began on 11 June 1672. Siege of Carlsburg Before the construction and settlement plans for Carlsburg could be realised, building work had to be interrupt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Smidt
Johann Smidt (November 5, 1773 – May 7, 1857) was an important Bremen politician, theologian, and founder of Bremerhaven. Biography Smidt was a son of the Reformed preacher Johann Smidt sen., pastor at St. Stephen Church in Bremen. Smidt jun. studied theology in Jena, and was one of the founders of the Gesellschaft der freien Männer (Community of free men). He was ordained Reformed preacher in Zürich in 1797. He then became Professor of History at the ''Gymnasium illustre'' in his hometown. He then became 'Syndikus' (company lawyer) for the Älterleute (aldermen, Bremen's merchants corporation of constitutional rank) and in 1800 'Ratsherr' (councilman), a position in which he exerted considerable influence on the governmental and commercial development of the cities of the Hanseatic League. In particular as he acted as Bremen's diplomatic representative at the Congress of Vienna and preserved the independence of the Hanseatic cities and put through their acceptance into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bremen-Verden
), which is a public-law corporation established in 1865 succeeding the estates of the Prince-Archbishopric of Bremen (established in 1397), now providing the local fire insurance in the shown area and supporting with its surplusses cultural efforts in and scientific works on the area. The ambit covers almost exactly the former Duchies of Bremen and Verden except of some of Bremen's northern quarters, incorporated in 1939, which prior belonged to the Landschaft's ambit too. , capital = Stade , common_languages = Low Saxon, German , title_leader = Monarch , leader1 = Christina , year_leader1 = 1648–1654 , leader2 = Charles I Gustav , year_leader2 = 1654–1660 , leader3 = Charles IICharles III , year_leader3 = 1660–1697•1697–1712 , leader4 = George I Louis , year_leader4 = 1715–1727 , leader5 = George II Augustus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nordenham
Nordenham () is a town in the Wesermarsch district, in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is located at the mouth (on the west bank) of the Weser river on the Butjadingen peninsula on the coast of the North Sea. The seaport city of Bremerhaven is located on the other side (east bank) of the river. The Midgard-seaport in Nordenham is the largest private-owned harbor in Germany. Geography Geographical location Nordenham is located on the West Bank of the Weser River across from Bremerhaven along the river's mouth at the North Sea, north of the cities of Bremen and Oldenburg. The local environment is mainly marshland, specifically ''Marsch oder Schwemmland''. Boroughs Nordenham is composed of 35 districts, each with a long history as a separate community: Abbehausen, Abbehauser Groden, Abbehauser Hörne, Abbehauserwisch, Atens, Atenserfeld, Blexen, Blexersande, Blexerwurp, Bulterweg, Butterburg, Einswarden, Ellwürden, Enjebuhr, Esenshamm, Esenshammer Altendeich, Esenshammer Oberdeich, Es ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony (german: Niedersachsen ; nds, Neddersassen; stq, Läichsaksen) is a German state (') in northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with , and fourth-largest in population (8 million in 2021) among the 16 ' federated as the Federal Republic of Germany. In rural areas, Northern Low Saxon and Saterland Frisian are still spoken, albeit in declining numbers. Lower Saxony borders on (from north and clockwise) the North Sea, the states of Schleswig-Holstein, Hamburg, , Brandenburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia, Hesse and North Rhine-Westphalia, and the Netherlands. Furthermore, the state of Bremen forms two enclaves within Lower Saxony, one being the city of Bremen, the other its seaport, Bremerhaven (which is a semi-enclave, as it has a coastline). Lower Saxony thus borders more neighbours than any other single '. The state's largest cities are state capital Hanover, Braunschweig (Brunswick), Lüneburg, Osnabrück, Oldenburg, Hildesheim, Salzgitt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Province Of Hanover
The Province of Hanover (german: Provinz Hannover) was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia and the Free State of Prussia from 1868 to 1946. During the Austro-Prussian War, the Kingdom of Hanover had attempted to maintain a neutral position, along with some other member states of the German Confederation. After Hanover voted in favour of mobilising confederation troops against Prussia on 14 June 1866, Prussia saw this as a just cause for declaring war; the Kingdom of Hanover was soon dissolved and annexed by Prussia. The private wealth of the dethroned House of Hanover was then used by Otto von Bismarck to finance his continuing efforts against Ludwig II of Bavaria. In 1946, the British military administration recreated the State of Hanover based on the former Kingdom of Hanover; but within the year, at the instigation of the German leadership, it was merged into the new state () of Lower Saxony—along with the states of Oldenburg, Brunswick, and Schaumburg-Lippe—with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Bremian War
The Swedish wars on Bremen were fought between the Swedish Empire and the Hanseatic town of Bremen in 1654 and 1666. Bremen claimed to be subject to the Holy Roman Emperor, maintaining Imperial immediacy, while Sweden claimed Bremen to be a mediatised part of her dominions of Bremen-Verden, themselves territories immediately beneath the emperor. Sweden was able to gain some territory, but despite forcing a formal oath of allegiance on Bremen, did not gain control of the town. Background When in 1648 the Peace of Westphalia ended the Thirty Years' War, the parties agreed that the prince-bishoprics of Bremen and Verden were to become dominions of Sweden. The peace treaty had been prepared at a congress throughout the final years of the war.Postler (1998), p.529 During the negotiations, several mostly Hanseatic cities requested that they become Imperial cities, with only Bremen being successful: Ferdinand III, Holy Roman Emperor accepted Bremen as a Free imperial city in 1646. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Rudolf Brommy
Rear Admiral Karl Rudolf Brommy (changed his name to reflect the English pronunciation of his original name, Bromme) (10 September 1804 – 9 January 1860) was a German naval officer who helped establish the first unified German fleet, the Reichsflotte, during the First Schleswig War which broke out just before the Revolutions of 1848 in the German states. A skilled sea commander, Brommy also made significant contributions to German naval education and shore infrastructure. Early life and career Born Karl Rudolf ''Bromme'' in Anger (now part of Leipzig), in the Electorate of Saxony, he was the fifth child of Johann Simon Bromme and his wife, Louise; he was orphaned while still a child. In 1818, the youth received permission from his guardian to become a sailor; he studied at the navigational school in Hamburg and made his first sea voyage on the brig ''Heinrich''. Eventually, he served on various United States sailing vessels. During this time, the young man altered the spellin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles XI Of Sweden
Charles XI or Carl ( sv, Karl XI; ) was King of Sweden from 1660 until his death, in a period of Swedish history known as the Swedish Empire (1611–1721). He was the only son of King Charles X Gustav of Sweden and Hedwig Eleonora of Holstein-Gottorp. His father died when he was four years old, so Charles was educated by his governors until his coronation at the age of seventeen. Soon afterward, he was forced out on military expeditions to secure the recently acquired dominions from Danish troops in the Scanian War. Having successfully fought off the Danes, he returned to Stockholm and engaged in correcting the country's neglected political, financial, and economic situation. He managed to sustain peace during the remaining 20 years of his reign. Changes in finance, commerce, national maritime and land armaments, judicial procedure, church government, and education emerged during this period. Charles XI was succeeded by his only son Charles XII, who made use of the well-tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)


.jpg)





_en2.png)