|
Bognor Regis
Bognor Regis (), also known as Bognor, is a town and seaside resort in West Sussex on the south coast of England, south-west of London, west of Brighton, south-east of Chichester and east of Portsmouth. Other nearby towns include Littlehampton east-north-east and Selsey to the south-west. The nearby villages of Felpham, and Aldwick are now suburbs of Bognor Regis, along with those of North Bersted, North and South Bersted. The population of the Bognor Regis built-up area, including Felpham and Aldwick, was 63,855 at the 2011 census. A seaside resort was developed by Sir Richard Hotham in the late 18th century on what was a sand and gravel, undeveloped coastline. It has been claimed that Hotham and his new resort are portrayed in Jane Austen's unfinished novel ''Sanditon''. The resort grew slowly in the first half of the 19th century but grew rapidly following the coming of the railway in 1864. In 1929 King George V spent three months in the area recuperating, and later that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bognor Regis And Littlehampton
Bognor Regis and Littlehampton () is a Constituencies of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, constituency in West Sussex represented in the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, UK Parliament since 2024 United Kingdom general election, 2024 by Alison Griffiths (politician), Alison Griffiths, a Conservative Party (UK), Conservative. Boundaries The constituency is elongated along the south coast of England. It includes the towns of Bognor Regis and Littlehampton. 1997–2010: The District of Arun wards of Aldwick East, Aldwick West, Bersted, Felpham East, Felpham West, Hotham, Littlehampton Beach, Littlehampton Central, Littlehampton Ham, Littlehampton River, Littlehampton Wick, Marine, Middleton on Sea, Orchard, Pagham, and Pevensey. 2010–2024: The District of Arun wards of Aldwick East, Aldwick West, Beach, Bersted, Brookfield, Felpham East, Felpham West, Ham, Hotham, Marine, Middleton-on-Sea, Orchard, Pagham and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King George V
George V (George Frederick Ernest Albert; 3 June 1865 – 20 January 1936) was King of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions, and Emperor of India, from 6 May 1910 until his death in 1936. George was born during the reign of his paternal grandmother, Queen Victoria, as the second son of the Prince and Princess of Wales (later King Edward VII and Queen Alexandra). He was third in the line of succession to the British throne behind his father and his elder brother, Prince Albert Victor. From 1877 to 1892, George served in the Royal Navy, until his elder brother's unexpected death in January 1892 put him directly in line for the throne. The next year George married his brother's former fiancée, Princess Victoria Mary of Teck, and they had six children. When Queen Victoria died in 1901, George's father ascended the throne as Edward VII, and George was created Prince of Wales. He became king-emperor on his father's death in 1910. George's reign saw the rise of soc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Du Cros
Sir Arthur Philip Du Cros, 1st Baronet (26 January 1871 – 28 October 1955) was a British industrialist and politician. Early life and education Du Cros was born in Dublin on 26 January 1871, the third of seven sons of Harvey du Cros and his wife Annie Jane Roy. In his childhood, his father was only a bookkeeper with an income of £170 a year and Arthur grew up in modest circumstances. He attended a National school (Ireland), national school in Dublin and entered the civil service at the lowest-paid grade. Business career In 1892 he joined his father and brothers in Dublin's Pneumatic Tyre and Booth's Cycle Agency. This business had been set up in 1889 by Harvey du Cros and J B Dunlop to exploit Dunlop's pneumatic tyre. Arthur was made general manager. His brothers had been or were later sent to Europe and America to develop their family's pneumatic tyre interests there. After J B Dunlop retired in 1895. Ernest Terah Hooley, Terah Hooley bought the business, now named Pneumati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Craigweil House
Craigweil House was a coastal mansion at Aldwick near Bognor Regis in southern England. King George V stayed there for three months in 1929. Craigweil House was built for Barbara Kemp, Countess of Newburgh, who died in 1797. She called it 'The Pavilion’. In 1828, The Pavilion belonged to the Reverend Henry Raikes, and later to Sir Alexander Dixie, a captain in the Royal Navy who served with distinction at the Battle of Trafalgar. From 1850 it was occupied by Colonel Austen, at which time it was still known as The Pavilion. It was purchased by Dr Alonzo Stocker, the proprietor of mental illness institutions in London, and used as a seaside retreat for his patients from the 1870s until 1910, whilst he and his family lived in the house's lodge. Craigweil House was sold to industrialist and Member of Parliament Sir Arthur du Cros Sir Arthur Philip Du Cros, 1st Baronet (26 January 1871 – 28 October 1955) was a British industrialist and politician. Early life and education ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
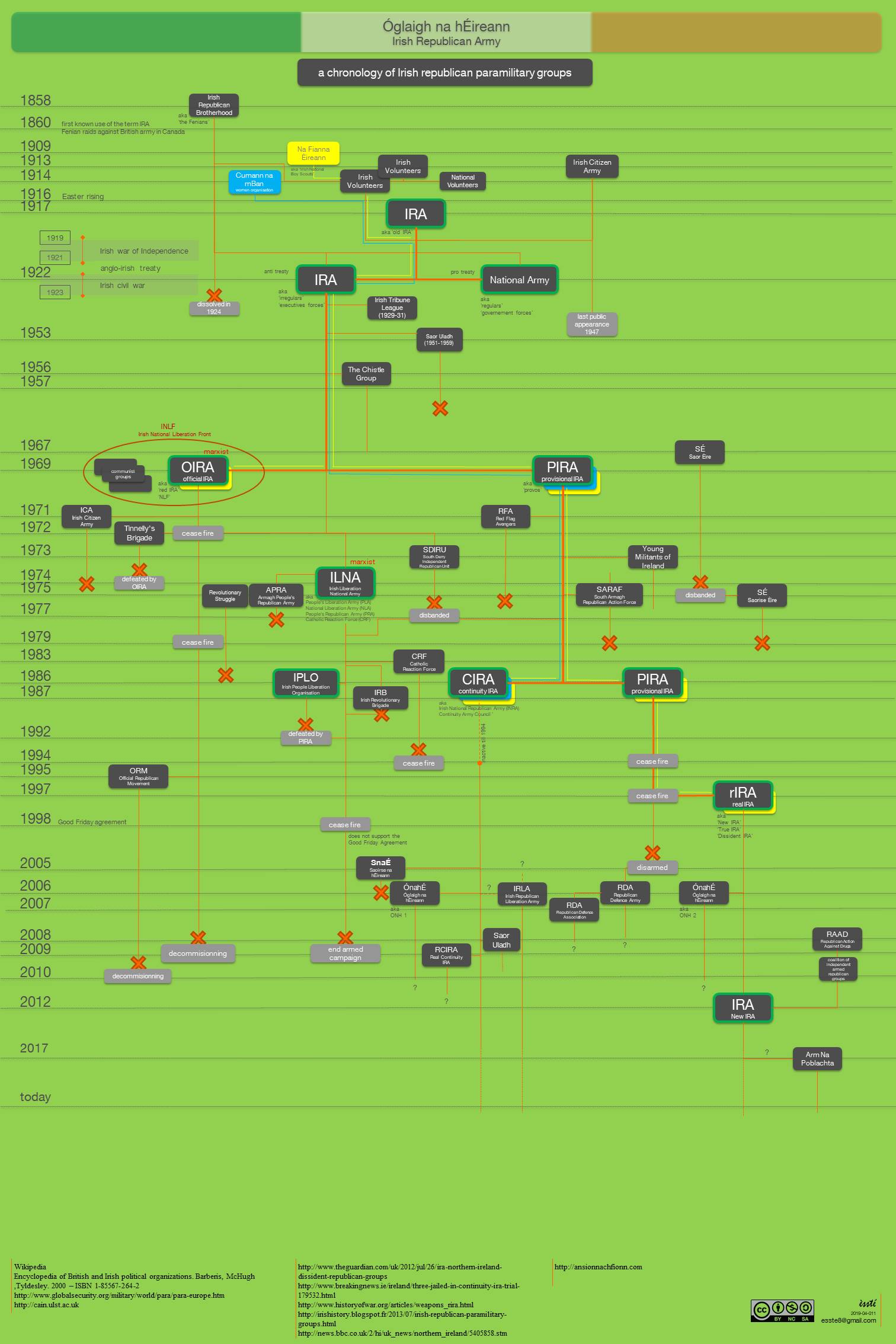
Irish Republican Army
The Irish Republican Army (IRA) is a name used by various Resistance movement, resistance organisations in Ireland throughout the 20th and 21st centuries. Organisations by this name have been dominantly Catholic and dedicated to anti-imperialism through Irish republicanism, the belief that all of Ireland should be an independent republic free from British colonial rule. The original Irish Republican Army (1919–1922), often now referred to as the "old IRA", was raised in 1917 from members of the Irish Volunteers and the Irish Citizen Army later reinforced by Irishmen formerly in the British Army in World War I, who returned to Ireland to fight against Britain in the Irish War of Independence. In Irish law, this IRA was the army of the revolutionary republic, revolutionary Irish Republic as declared by its parliament, Dáil Éireann (Irish Republic), Dáil Éireann, in 1919. In the century that followed, the original IRA was reorganised, changed and split on multiple occasions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metz
Metz ( , , , then ) is a city in northeast France located at the confluence of the Moselle (river), Moselle and the Seille (Moselle), Seille rivers. Metz is the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Moselle (department), Moselle Departments of France, department and the seat of the parliament of the Grand Est Regions of France, region. Located near the Tri-border area, tripoint along the junction of France, Germany and Luxembourg,Says J.M. (2010) La Moselle, une rivière européenne. Eds. Serpenoise. the city forms a central part of the European Greater Region and the SaarLorLux euroregion. Metz has a rich 3,000-year history,Bour R. (2007) Histoire de Metz, nouvelle édition. Eds. Serpenoise. having variously been a Celts, Celtic ''oppidum'', an important Gallo-Roman city,Vigneron B. (1986) Metz antique: Divodurum Mediomatricorum. Eds. Maisonneuve. the Merovingian capital of Austrasia,Huguenin A. (2011) Histoire du royaume mérovingien d'Austrasie. Eds. des Paraiges. p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Channel
The English Channel, also known as the Channel, is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that separates Southern England from northern France. It links to the southern part of the North Sea by the Strait of Dover at its northeastern end. It is the busiest Sea lane, shipping area in the world. It is about long and varies in width from at its widest to at its narrowest in the Strait of Dover."English Channel". ''The Columbia Encyclopedia'', 2004. It is the smallest of the shallow seas around the continental shelf of Europe, covering an area of some . The Channel aided the United Kingdom in becoming a naval superpower, serving as a natural defence against invasions, such as in the Napoleonic Wars and in the World War II, Second World War. The northern, English coast of the Channel is more populous than the southern, French coast. The major languages spoken in this region are English language, English and French language, French. Names Roman historiography, Roman sources as (or , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
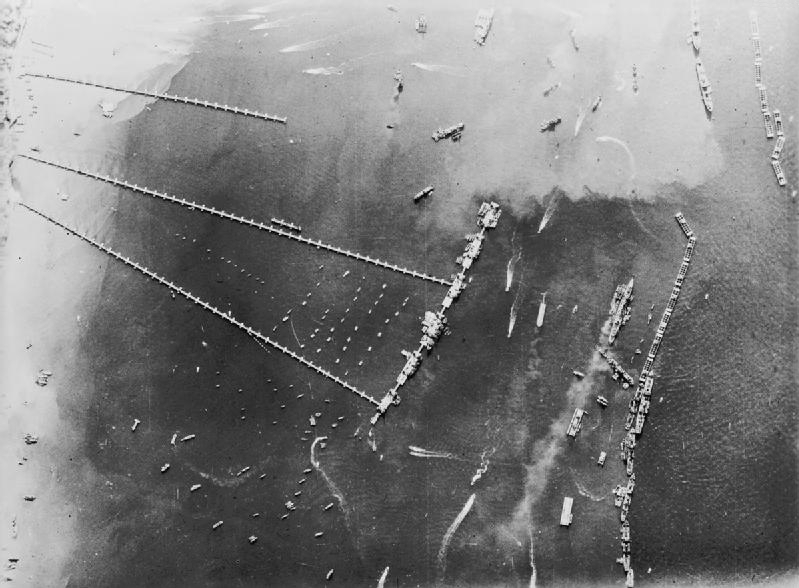
Mulberry Harbour
The Mulberry harbours were two temporary portable harbours developed by the Admiralty (United Kingdom), British Admiralty and War Office during the Second World War to facilitate the rapid offloading of cargo onto beaches during the Allies of World War II, Allied invasion of Normandy in June 1944. They were designed in 1942 then built in under a year in great secrecy; within hours of the Allies creating beachheads after D-Day, sections of the two prefabricated harbours were towed across the English Channel from southern England and placed in position off Omaha Beach (Mulberry "A") and Gold Beach (Mulberry "B"), along with old ships to be sunk as breakwater (structure), breakwaters. The Mulberry harbours solved the problem of needing deepwater jetties and a harbour to provide the invasion force with the necessary reinforcements and supplies, and were to be used until major French ports could be captured and brought back into use after repair of the inevitable sabotage by German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phoenix Breakwaters
The Phoenix breakwaters were a set of reinforced concrete caissons built as part of the artificial Mulberry harbours that were assembled as part of the preparations for the Normandy landings during World War II. A total of 213 were built, with 212 floated or side-launched. They were constructed by civil engineering contractors around the coast of Britain. They were collected at Dungeness and Selsey, and then towed by tugboats across the English Channel and sunk to form the Mulberry harbour breakwaters replacing the initial " Gooseberry" block ships. Caissons were added in the autumn of 1944 to reinforce the existing structure to cope with the harbour continuing in use longer than planned. Several Phoenix breakwaters still exist in Britain: two are part of the harbour off Castletown at Portland Harbour in Dorset, and two can be dived in less than 10 metres of water off Pagham in West Sussex. There is also a smaller Phoenix Caisson (type C) in Langstone Harbour in Hampshire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Hotham
Sir Richard Hotham (5 October 1722 – 13 March 1799) was an East India merchant, property developer and politician who sat in the House of Commons from 1780 to 1784. He is especially noted for his development of the Sussex village of Bognor Regis, Bognor into a seaside resort. He was also sometimes called Hotham the Hatter, to mark his original trade. Early life Hotham was born the youngest of five children in York in October 1722, but otherwise very little is known about his childhood. Having moved to London to become a hatter's apprentice, in 1743, at the age of 21 he married Frances Atkinson, the daughter of his employer, in the chapel of the Royal Hospital, Chelsea. By 1746 he was trading as a hatter in his own right from premises in Serle Street, Lincoln's Inn, a few years later moving to new premises in Strand, London, The Strand. Hotham's wife Frances died in 1760, and the next year, at the age of 39 he remarried, to Barbara Huddart. At this time he became involved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smuggling
Smuggling is the illegal transportation of objects, substances, information or people, such as out of a house or buildings, into a prison, or across an international border, in violation of applicable laws or other regulations. More broadly, social scientists define smuggling as the purposeful movement across a border in contravention to the relevant legal frameworks. There are various motivations to smuggle. These include the participation in illegal trade, such as in the drug trade, illegal weapons trade, prostitution, human trafficking, kidnapping, heists, chop shops, illegal immigration or illegal emigration, tax evasion, import restrictions, export restrictions, providing contraband to prison inmates, or the theft of the items being smuggled. Smuggling is a common theme in literature, from Bizet's opera ''Carmen'' to the James Bond spy books (and later films) '' Diamonds Are Forever'' and '' Goldfinger''. Etymology The verb ''smuggle'', from Low German ''smuggeln'' o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |