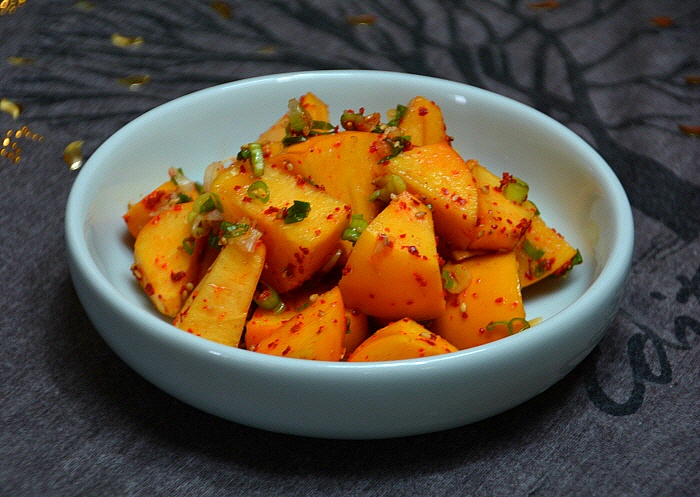|
Banchan
''Banchan'' (, from Korean: ) or bansang are small side dishes served along with cooked rice in Korean cuisine. As the Korean language does not distinguish between singular and plural grammatically, the word is used for both one such dish or all of them combined. The basic table setting for a meal called ''bansang'' (반상) usually consists of ''bap'' (밥, cooked rice), ''guk'' or ''tang'' (soup), ''gochujang'' or ''ganjang'', ''jjigae'', and ''kimchi''. According to the number of ''banchan'' added, the table setting is called ''3 cheop'' (삼첩), ''5 cheop'' (오첩), ''7 cheop'' (칠첩), ''9 cheop'' (구첩), ''12 cheop'' (십이첩) ''bansang'', with the ''12 cheop'' used in Korean royal cuisine. ''Banchan'' are set in the middle of the table to be shared. At the center of the table is the secondary main course, such as ''galbi'' or ''bulgogi'', and a shared pot of ''jjigae''. Bowls of cooked rice and ''guk'' (soup) are set individually. ''Banchan'' are served in sma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korean Cuisine
Korean cuisine has evolved through centuries of social and political change. Originating from ancient agricultural and nomadic traditions in Korea and southern Manchuria, Korean cuisine reflects a complex interaction of the natural environment and different cultural trends. Korean cuisine is largely based on rice, vegetables, seafood and (at least in South Korea) meats. Dairy is largely absent from the traditional Korean diet. Traditional Korean meals are named for the number of side dishes (반찬; 飯饌; ''banchan'') that accompany steam-cooked short-grain rice. Kimchi is served at nearly every meal. Commonly used ingredients include sesame oil, ''doenjang'' (fermented bean paste), soy sauce, salt, garlic, ginger, ''gochugaru'' (pepper flakes), '' gochujang'' (fermented red chili paste) and napa cabbage. Ingredients and dishes vary by province. Many regional dishes have become national, and dishes that were once regional have proliferated in different variations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kimchi
''Kimchi'' (; ko, 김치, gimchi, ), is a traditional Korean side dish of salted and fermented vegetables, such as napa cabbage and Korean radish. A wide selection of seasonings are used, including ''gochugaru'' (Korean chili powder), spring onions, garlic, ginger, and ''jeotgal'' (salted seafood), etc. Kimchi is also used in a variety of soups and stews. As a staple food in Korean cuisine, it is eaten as a side dish with almost every Korean meal. There are hundreds of different types of kimchi made with different vegetables as the main ingredients. Traditionally, winter kimchi, called kimjang, was stored in large earthenware fermentation vessels, called ''onggi'', in the ground to prevent freezing during the winter months and to keep it cool enough to slow down the fermentation process during summer months. The vessels are also kept outdoors in special terraces called jangdokdae. In contemporary times, household kimchi refrigerators are more commonly used. Etymology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bap (food)
''Bap'' ( ko, 밥) is a Korean name for cooked rice prepared by boiling rice or other grains, such as black rice, barley, sorghum, various millets, and beans, until the water has cooked away. Special ingredients such as vegetables, seafood, and meat can also be added to create different kinds of ''bap''. In the past, except for the socially wealthy class, people used to eat mixed grain rice together with beans and barley rather than only rice. In Korea, grain food centered on rice has been the most commonly used since ancient times and has established itself as a staple food in everyday diets. In Korean, the honorific terms for ''bap'' (meal) include ''jinji'' () for an elderly person, ''sura'' () for a monarch, and ''me'' () for the deceased (in the ancestral rites). Preparation Traditionally, ''bap'' was made using ''gamasot'' (a cast iron cauldron) for a large family; however, in modern times, an electronic rice cooker is usually used to cook rice. A regular heavy-bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galbi
''Galbi'' * (), ''galbi-gui'' (), or grilled ribs, is a type of ''gui'' (grilled dish) in Korean cuisine. "''Galbi''" is the Korean word for "rib", and the dish is usually made with beef short ribs. When pork spare ribs or another meat is used instead, the dish is named accordingly. ''Galbi'' is served raw, then cooked on tabletop grills usually by the diners themselves. The dish may be marinated in a sweet and savory sauce usually containing soy sauce, garlic, and sugar. Both non-marinated and marinated ''galbi'' are often featured in Korean barbecue. This and many other dishes in Korean barbecue influenced Yakiniku as seen in the use of galbi (coined as karubi). Preparation Cuts and marination Traditionally, ''galbi'' is cut to expose one smooth bone along the short edge with the meat uniformly filleted in flat layers. An alternative cut, "LA ''galbi''", also known as a flanken cut, features cut bones peeking out along the long edge. The method was developed by Korean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kkakdugi
''Kkakdugi'' (깍두기) or diced radish kimchi is a variety of kimchi in Korean cuisine. Usually, Korean radish (called ''mu'', 무 in Korean) is used, but other vegetables or fruits can also be used. ''Kkakduk-kkakduk'' is an ideophone related to dicing/cubing. Kimchi made with radish that are not diced into cubes are not called ''kkakdugi''. ''Kkakdugi'' is a popular banchan (side dish) enjoyed by Koreans and others. Origin and history The origin of ''kkakdugi'' is mentioned in a cookbook named ''Joseon yorihak'' (조선요리학 朝鮮料理學, literally "Korean Gastronomy") written by Hong Seon-pyo (홍선표) in 1940. According to the book, ''kkakdugi'' was created by Princess Sukseon (숙선옹주 淑善翁主), a daughter of King Jeongjo (r. 1776–1800) and the wife of Hong Hyeon-ju (홍현주 洪 顯周), a high-ranking government officer titled as ''Yeongmyeongwi'' (영명위 永明慰). When a matter for congratulation happened to the royal court, members of the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dongchimi
''Dongchimi'' is a variety of kimchi consisting of Korean radish, napa cabbage, scallions, jangajji, pickled green chili pepper, chilli, ginger, Pyrus pyrifolia, Korean pear and watery brine in Korean cuisine. As the name ''dong'' (hangul: 동; hanja: wikt:冬, 冬; literally "winter") and ''chimi'' (hangul: 치미, an ancient term for kimchi), suggests, this kimchi is traditionally consumed during the winter season. Dongchimi is fermented like other varieties of kimchi, but its maturing period is relatively short (2–3 days). Although it can be made at any time of the year, it is usually made during the ''gimjang'' season. The northern regions consisting of Hamgyeong-do and Pyeongan-do in North Korea are particularly famous for their dongchimi. The clear and clean taste of the watery dongchimi is used as a soup for making ''dongchimi guksu'' (동치미국수 cold noodle soup made with ''dongchimi'') and ''naengmyeon'', or served with ''tteok'' or steamed sweet potatoes to bal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nabak-kimchi
''Nabak-kimchi'' * () is a watery kimchi, similar to ''dongchimi'', in Korean cuisine. It is made of Korean radish and napa cabbage (called ''baechu'', hangul 배추, in Korean) as main ingredients, thinly sliced into rectangular shapes, salted and mixed with vegetables and spices such as cucumber, scallion, Java water dropwort (called ''"minari"'', 미나리 in Korean), garlic, ginger, red chilies, chili pepper powder, sugar, salt, and water. ''Nabak gimchi'' looks similar to ''dongchimi'' in form but is commonly consumed during spring and summer, whereas ''dongchimi'' is most commonly eaten in winter. Chili pepper powder is added to make ''nabak kimchi'', resulting in a rose pink color as opposed to the white-colored ''dongchimi''. The term ''nabak'' originated from ''nabaknabak'' (나박나박) which is a Korean adverb for "making flattened" or "slicing thinly". See also * Korean radish References External links Brief information and recipe about ''nabak kimc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korean Radish
''Mu'' or Korean radish is a variety of white radish with a firm crunchy texture. Although ''mu'' () is also a generic term for radishes in Korean, the word is usually used in its narrow sense, referring to the white radish, or more specifically Korean radish (, ''Joseon-mu''). Korean radishes are generally short, stout, and sturdy, and have a pale green shade halfway down from the top. They also have a strong flavour, dense flesh and soft leaves. The greens of Korean radishes are called ''mucheong'' () and are used as a vegetable in various dishes. Description Korean radishes, like other radishes, are an annual or biennial crop grown for the taproots. The rotund cylindrical roots weigh about , being approximately long with their diameter around . The flesh of Korean radishes harvested timely is crisp, peppery and sweet. The upper part of the roots are subterranean stems, from which the long ovate leaves grow. The pinnate leaves with enlarged terminal lobe and smaller later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongol Invasions Of Korea
A series of campaigns were conducted between 1231 and 1270 by the Mongol Empire against the Goryeo dynasty of Korea. There were seven major campaigns at tremendous cost to civilian lives, the last campaign made Goryeo a vassal state of the Yuan dynasty for approximately 80 years. The Yuan dynasty would exact wealth and tributes from the Goryeo kings. Despite submission to the Yuan dynasty, internal struggles among Goryeo royalty and rebellions against Yuan rule would continue, the most famous being the Sambyeolcho Rebellion. A greater amount of "stubborn resistance" was put up by Korea and Song Dynasty towards the Mongol invasions than many others in Eurasia who were swiftly crushed by the Mongols at a lightning pace. The initial campaigns Fleeing from the Mongols, in 1216 the Khitans invaded Goryeo and defeated the Korean armies multiple times, even reaching the gates of the capital and raiding deep into the south, but were defeated by Korean General Kim Chwi-ryeo who pushe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brassica Juncea
''Brassica juncea'', commonly brown mustard, Chinese mustard, Indian mustard, leaf mustard, Oriental mustard and vegetable mustard, is a species of mustard plant. Cultivar ''Brassica juncea'' cultivars can be divided into four major subgroups: integrifolia, juncea, napiformis, and tsatsai. Integrifolia Juncea Napiformis Tsatsai Uses Nutrition In a reference serving, cooked mustard greens provide of food energy and are a rich source (20% or more of the Daily Value) of vitamins A, C, and K—K being especially high as a multiple of its Daily Value. Mustard greens are a moderate source of vitamin E and calcium. Greens are 92% water, 4.5% carbohydrates, 2.6% protein and 0.5% fat (table). Cuisine The leaves, seeds, and stems of this mustard variety are edible. The plant appears in some form in African, Bangladeshi, Chinese, Filipino, Italian, Indian, Japanese, Nepali, Pakistani, Korean, Southern and African-American (soul food) cuisines. Culti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scallion
Scallions (also known as spring onions or green onions) are vegetables derived from various species in the genus ''Allium''. Scallions generally have a milder taste than most onions and their close relatives include garlic, shallot, leek, chive, and Chinese onions. Although the bulbs of many ''Allium'' species are used as food, the defining characteristic of scallion species is that they lack a fully developed bulb. Instead the ''Allium'' species referred to as scallions make use of the hollow, tubular green leaves growing directly from the bulb. These leaves are used as a vegetable and can be eaten either raw or cooked. Often the leaves are chopped into other dishes and used as garnishes. Etymology and names The words ''scallion'' and ''shallot'' are related and can be traced back to the Ancient Greek () as described by the Greek writer Theophrastus. This name, in turn, is believed to originate from the name of the ancient Canaanite city of Ashkelon. Various other nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nabak Kimchi
''Nabak-kimchi'' * () is a watery kimchi, similar to ''dongchimi'', in Korean cuisine. It is made of Korean radish and napa cabbage (called ''baechu'', hangul 배추, in Korean) as main ingredients, thinly sliced into rectangular shapes, salted and mixed with vegetables and spices such as cucumber, scallion, Java water dropwort (called ''"minari"'', 미나리 in Korean), garlic, ginger, red chilies, chili pepper powder, sugar, salt, and water. ''Nabak gimchi'' looks similar to ''dongchimi'' in form but is commonly consumed during spring and summer, whereas ''dongchimi'' is most commonly eaten in winter. Chili pepper powder is added to make ''nabak kimchi'', resulting in a rose pink color as opposed to the white-colored ''dongchimi''. The term ''nabak'' originated from ''nabaknabak'' (나박나박) which is a Korean adverb for "making flattened" or "slicing thinly". See also * Korean radish References External links Brief information and recipe about ''nabak kimchi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)