|
1871
Events January–March * January 3 – Franco-Prussian War – Battle of Bapaume: Prussians win a strategic victory. * January 18 – Proclamation of the German Empire: The member states of the North German Confederation and the south German states, aside from Austria, unite into a single nation state, known as the German Empire. The King of Prussia is declared the first German Emperor as Wilhelm I of Germany, in the Hall of Mirrors at the Palace of Versailles. Constitution of the German Confederation comes into effect. It abolishes all restrictions on Jewish marriage, choice of occupation, place of residence, and property ownership, but exclusion from government employment and discrimination in social relations remain in effect. * January 21 – Giuseppe Garibaldi's group of French and Italian volunteer troops, in support of the French Third Republic, win a battle against the Prussians in the Battle of Dijon. * February 8 – 1871 French legislative election elects t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Empire
The German Empire (),Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditary empire led by an emperor, although has been used in German to denote the Roman Empire because it had a weak hereditary tradition. In the case of the German Empire, the official name was , which is properly translated as "German Empire" because the official position of head of state in the constitution of the German Empire was officially a "presidency" of a confederation of German states led by the King of Prussia who would assume "the title of German Emperor" as referring to the German people, but was not emperor of Germany as in an emperor of a state. –The German Empire" ''Harper's New Monthly Magazine''. vol. 63, issue 376, pp. 591–603; here p. 593. also referred to as Imperial Germany, the Second Reich, as well as simply Germany, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Third Republic
The French Third Republic (french: Troisième République, sometimes written as ) was the system of government adopted in France from 4 September 1870, when the Second French Empire collapsed during the Franco-Prussian War, until 10 July 1940, after the Fall of France during World War II led to the formation of the Vichy government. The early days of the Third Republic were dominated by political disruptions caused by the Franco-Prussian War of 1870–1871, which the Republic continued to wage after the fall of Emperor Napoleon III in 1870. Harsh reparations exacted by the Prussians after the war resulted in the loss of the French regions of Alsace (keeping the Territoire de Belfort) and Lorraine (the northeastern part, i.e. present-day department of Moselle), social upheaval, and the establishment of the Paris Commune. The early governments of the Third Republic considered re-establishing the monarchy, but disagreement as to the nature of that monarchy and the rightful occ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North German Confederation
The North German Confederation (german: Norddeutscher Bund) was initially a German military alliance established in August 1866 under the leadership of the Kingdom of Prussia, which was transformed in the subsequent year into a confederated state (a ''de facto'' federal state) that existed from July 1867 to December 1870. A milestone of the German Unification, it was the earliest continual legal predecessor of the modern German nation-state known today as the Federal Republic of Germany. The Confederation came into existence following the Prussian victory in the Austro-Prussian War of 1866 over the lordship of two small Danish duchies (Schleswig-Holstein) resulting in the Peace of Prague, where Prussia pressured Austria and its allies into accepting the dissolution of the existing German Confederation (an association of German states under the leadership of the Austrian Empire), thus paving the way for the Lesser German version of German unification in the form of a federal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proclamation Of The German Empire
The proclamation of the German Empire, also known as the ''Deutsche Reichsgründung'', took place in January 1871 after the joint victory of the German states in the Franco-Prussian War. As a result of the November Treaties of 1870, the southern German states of Baden, Hesse-Darmstadt, with their territories south of the Main line, Württemberg and Bavaria, joined the Prussian-dominated "German Confederation" on 1 January 1871. On the same day, the new Constitution of the German Confederation came into force, thereby significantly extending the federal German lands to the newly created German Empire. Karl Kroeschell: ''Deutsche Rechtsgeschichte'', Bd. 3: ''Seit 1650'', 5. Aufl., Böhlau/UTB, Köln/Weimar/Wien 2008, S. 235.Michael Kotulla: ''Deutsche Verfassungsgeschichte: Vom Alten Reich bis Weimar (1495–1934)'', 2008, Rn. 2042. Klaus Stern: ''Das Staatsrecht der Bundesrepublik Deutschland. Band V: Die geschichtlichen Grundlagen des deutschen Staatsrechts. Die Verfassungsentw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constitution Of The German Confederation (1871)
The Constitution of the German Confederation (german: Verfassung des Deutschen Bundes) or November Constitution (''Novemberverfassung'') was the constitution of the German federal state at the beginning of the year 1871. It was enacted on January 1, 1871. This is a slightly changed version of the Constitution of the North German Confederation; it is not to be confused with the constitutional laws of the German Confederation of 1815. The Constitution of the German Confederation of 1871 incorporated agreements between the North German Confederation and some the South German states that joined the Confederation: with Baden and Hesse-Darmstadt, but not Bavaria and Württemberg. The new constitution appeared on 31 December 1870 in the ''Bundesgesetzblatt des Norddeutschen Bundes'' (North German Federal Law Gazette) and came into effect the following day. New elections to the Reichstag, the parliament, took place on 3 March. They included for the first time the South German states, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Dijon (1870)
The Battles of Dijon were a series of battles that took place in 1870 and 1871, as part of the Franco-Prussian War, on the current territory of the French commune of Dijon between the French Third Republic, French Republic and the German states of Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia and Grand Duchy of Baden, Baden and later, the German Empire. Background The Franco-Prussian War, which started on July 19, 1870, begins with a rapid succession of French defeats: the evacuation of northern Alsace with defeats at Battle of Wissembourg (1870), Wissembourg and Battle of Wörth, Wörth), the capitulation of Marshal Bazaine in Metz at the Battle of Gravelotte, the defeat and capture of Emperor Napoleon III at the Battle of Sedan, his capitulation on September 2. The Germanic armies invaded all of eastern France and opened up the road to Paris. The Republic is proclaimed on September 4 and the provisional government decides, under the impetus of Léon Gambetta, in charge of the new Government of Nat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm I Of Germany
William I or Wilhelm I (german: Wilhelm Friedrich Ludwig; 22 March 1797 – 9 March 1888) was King of Prussia from 2 January 1861 and German Emperor from 18 January 1871 until his death in 1888. A member of the House of Hohenzollern, he was the first head of state of a united Germany. He was de facto head of state of Prussia from 1858, when he became regent for his brother Frederick William IV, whose death three years later would make him king. Under the leadership of William and his minister president Otto von Bismarck, Prussia achieved the unification of Germany and the establishment of the German Empire. Despite his long support of Bismarck as Minister President, William held strong reservations about some of Bismarck's more reactionary policies, including his anti-Catholicism and tough handling of subordinates. In contrast to the domineering Bismarck, William was described as polite, gentlemanly and, while staunchly conservative, more open to certain classical liberal ideas th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1871 French Legislative Election
Legislative elections were held in France on 8 February 1871 to elect the first legislature of the French Third Republic, the unicameral National Assembly. The elections were held during a situation of crisis in the country, as following the Franco-Prussian War, 43 departments were occupied by Prussian forces. As a result, all public meetings were outlawed and Paris was the only city where an election campaign took place. The electoral law allowed candidates to run in more than one seat at a time. As a result, several candidates were elected in more than one seat, with Adolphe Thiers elected in 86 constituencies. A series of by-elections were subsequently held on 2 July to elect representatives for the 114 vacant seats. This election saw the victory of monarchists (Legitimists and Orleanists), favourable to peace with the German Empire, with a large majority. Results , - style="background-color:#E9E9E9; text-align:center;" , - , colspan="6" , , - ! colspan="3" style="text ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
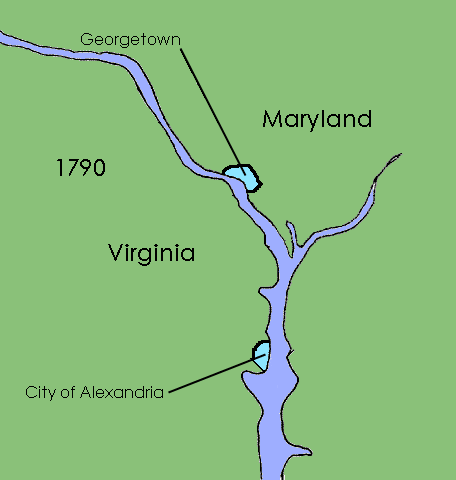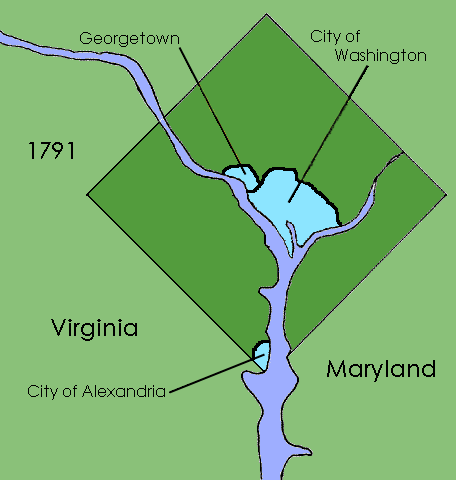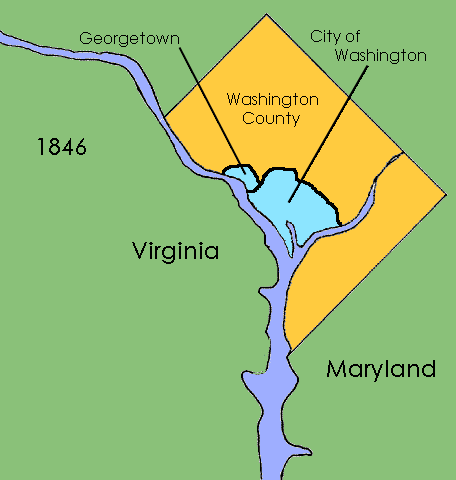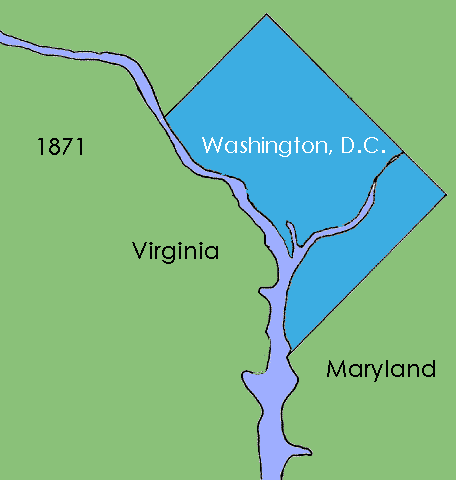
District Of Columbia Organic Act Of 1871
The District of Columbia Organic Act of 1871 is an Act of Congress that repealed the individual charters of the cities of Washington and Georgetown and established a new territorial government for the whole District of Columbia. Though Congress repealed the territorial government in 1874, the legislation was the first to create a single municipal government for the federal district. History The passage of the Residence Act in 1790 created a new federal district that would become the capital of the United States. Formed from land donated by the states of Maryland and Virginia, the capital territory already included two large settlements at its creation: the port of Georgetown, Maryland and the town of Alexandria, Virginia. A new capital city named in honor of President George Washington was founded to the east of Georgetown in 1791. Shortly after establishing operations in the new capital, Congress passed the Organic Act of 1801, which organized the federal territory. The ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Emperor
The German Emperor (german: Deutscher Kaiser, ) was the official title of the head of state and hereditary ruler of the German Empire. A specifically chosen term, it was introduced with the 1 January 1871 constitution and lasted until the official abdication of Wilhelm II on 9 November 1918. The Holy Roman Emperor is sometimes also called "German Emperor" when the historical context is clear, as derived from the Holy Roman Empire's official name of "Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation" from 1512. Following the revolution of 1918, the head of state was the president of the Reich (german: Reichspräsident), beginning with Friedrich Ebert. German Empire (1848–49) In the wake of the revolutions of 1848 and during the German Empire (1848–49), King Frederick Wilhelm IV of Prussia was offered the title "Emperor of the Germans" (german: Kaiser der Deutschen) by the Frankfurt Parliament in 1849, but declined it as "not the Parliament's to give". Frederick Wilhelm believed tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Bapaume (1871)
The Battle of Bapaume was a battle during the Franco-Prussian War, brought about by French attempts to relieve the besieged city of Péronne, Somme. The battle was fought on 3 January 1871 near the town of Bapaume. The Prussian 1st Army had reached Bapaume at the end of December while at the same time the French Army of the North under Faidherbe moved out to break the German siege of Péronne. Both sides encountered each other near Bapaume. Although Faidherbe's green troops held their own against the outnumbered but experienced Prussians, they did not follow up their advantage. As a consequence, Péronne surrendered on 10 January. Soon the Prussians would be reinforced and two weeks later they would meet Faidherbe in battle again at Saint Quentin Saint Quentin ( la, Quintinus; died 287 AD) also known as Quentin of Amiens, was an early Christian saint. Hagiography Martyrdom The legend of his life has him as a Roman citizen who was martyred in Gaul. He is said to have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legitimists
The Legitimists (french: Légitimistes) are royalists who adhere to the rights of dynastic succession to the French crown of the descendants of the eldest branch of the Bourbon dynasty, which was overthrown in the 1830 July Revolution. They reject the claim of the July Monarchy of 1830–1848 which placed Louis Philippe, Duke of Orléans, head of the Orléans cadet branch of the Bourbon dynasty, on the throne until he too was dethroned and driven with his family into exile. Following the movement of Ultra-royalists during the Bourbon Restoration of 1814, Legitimists came to form one of the three main right-wing factions in France, which was principally characterized by its counter-revolutionary views. According to historian René Rémond, the other two right-wing factions were the Orléanists and the Bonapartists. Legitimists believe that the traditional rules of succession, based on the Salic law, determine the rightful King of France. The last ruling king whom legitimists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_(LOC)_-_Flickr_-_The_Library_of_Congress.jpg)