|
1864 In Science
The year 1864 in science and technology included many events, some of which are listed here. Astronomy * May 14 – The Orgueil meteorite, composed of carbonaceous chondrite, falls in southwestern France. * August 29 – William Huggins is the first to take the spectrum of a planetary nebula when he analyzes NGC 6543. Botany * English botanist Richard Spruce completes a 15-year expedition to the Andes and Amazon Basin during which he has collected more than 30,000 plant specimens. Chemistry * August 20 – John Alexander Reina Newlands produces the first periodic table of the elements. * November 27 – Barbituric acid is first synthesized, by German chemist Adolf von Baeyer. * Lothar Meyer develops an early version of the periodic table, with 28 elements organized by valence. * Cato Maximilian Guldberg and Peter Waage, building on Claude Louis Berthollet's ideas, propose the law of mass action. Conservation * June 30 – The Yosemite Grant is created in the United St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
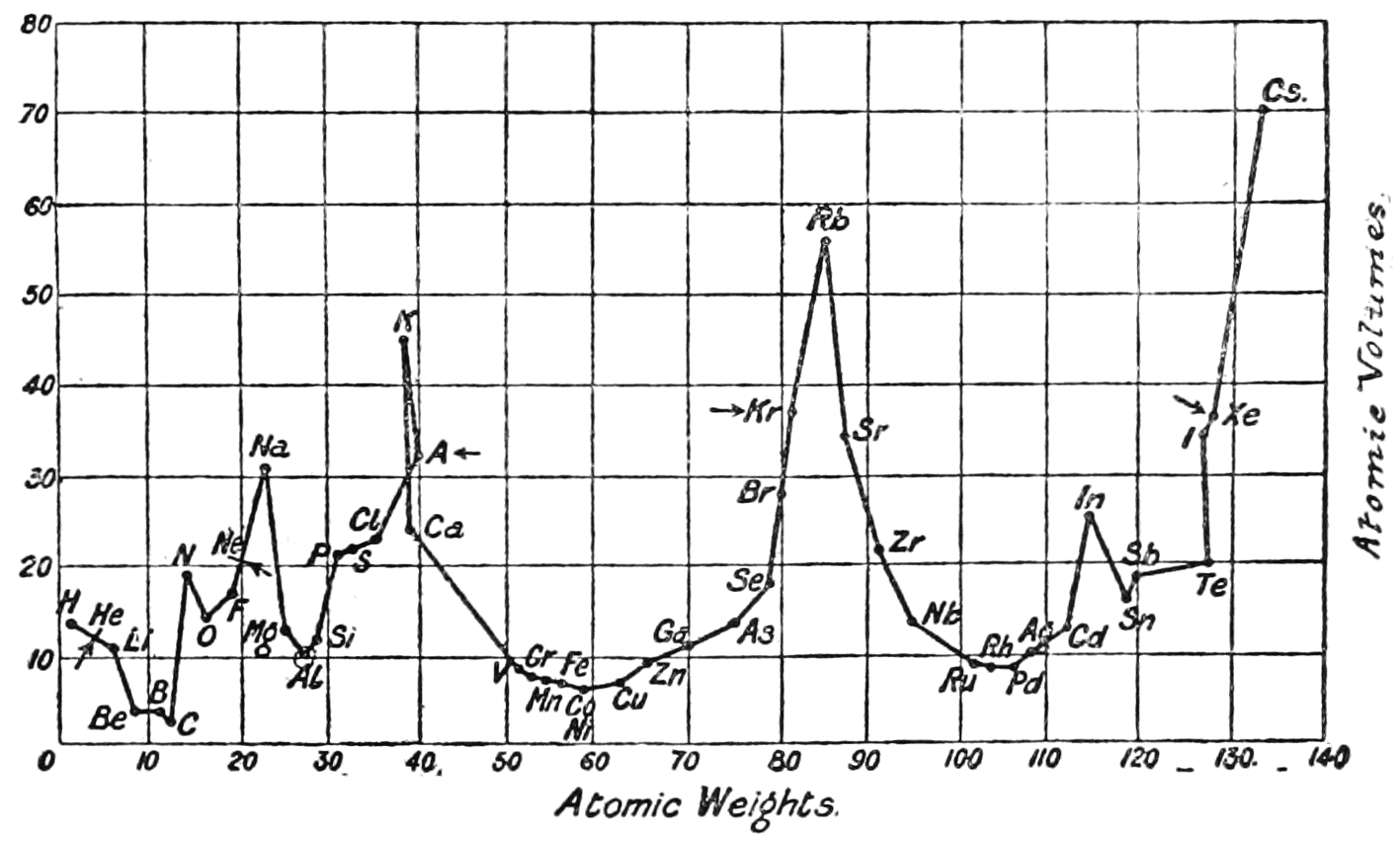
Lothar Meyer
Julius Lothar Meyer (19 August 1830 – 11 April 1895) was a German chemist. He was one of the pioneers in developing the earliest versions of the periodic table of the chemical elements. The Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev (his chief rival) and he both had worked with Robert Bunsen. Meyer never used his first given name and was simply known as Lothar Meyer throughout his life. Career Meyer was born in Varel, Germany (then part of the Duchy of Oldenburg). He was the son of Friedrich August Meyer, a physician, and Anna Biermann. After attending the Altes Gymnasium in Oldenburg, he studied medicine at the University of Zurich in 1851. Two years later, he studied pathology at the University of Würzburg as a student of Rudolf Virchow. At Zurich, he had studied under Carl Ludwig, which had prompted him to devote his attention to physiological chemistry. After graduating as a Doctor of Medicine from Würzburg in 1854, he went to Heidelberg University, where Robert Bunsen held the ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Dynamical Theory Of The Electromagnetic Field
"A Dynamical Theory of the Electromagnetic Field" is a paper by James Clerk Maxwell on electromagnetism, published in 1865. ''(Paper read at a meeting of the Royal Society on 8 December 1864).'' Physicist Freeman Dyson called the publishing of the paper the "most important event of the nineteenth century in the history of the physical sciences". The paper was key in establishing the classical theory of electromagnetism. Maxwell derives an electromagnetic wave equation with a velocity for light in close agreement with measurements made by experiment, and also deduces that light is an electromagnetic wave. Publication Following standard procedure for the time, the paper was first read to the Royal Society on 8 December 1864, having been sent by Maxwell to the society on 27 October. It then underwent peer review, being sent to William Thomson (later Lord Kelvin) on 24 December 1864. It was then sent to George Gabriel Stokes, the Society's physical sciences secretary, on 23 March 186 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Clerk Maxwell
James Clerk Maxwell (13 June 1831 – 5 November 1879) was a Scottish physicist and mathematician who was responsible for the classical theory of electromagnetic radiation, which was the first theory to describe electricity, magnetism and light as different manifestations of the same phenomenon. Maxwell's equations for electromagnetism achieved the Unification (physics)#Unification of magnetism, electricity, light and related radiation, second great unification in physics, where Unification (physics)#Unification of gravity and astronomy, the first one had been realised by Isaac Newton. Maxwell was also key in the creation of statistical mechanics. With the publication of "A Dynamical Theory of the Electromagnetic Field" in 1865, Maxwell demonstrated that electric force, electric and magnetic fields travel through space as waves moving at the speed of light. He proposed that light is an undulation in the same medium that is the cause of electric and magnetic phenomena. (Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minimal Surface
In mathematics, a minimal surface is a surface that locally minimizes its area. This is equivalent to having zero mean curvature (see definitions below). The term "minimal surface" is used because these surfaces originally arose as surfaces that minimized total surface area subject to some constraint. Physical models of area-minimizing minimal surfaces can be made by dipping a wire frame into a soap solution, forming a soap film, which is a minimal surface whose boundary is the wire frame. However, the term is used for more general surfaces that may self-intersect or do not have constraints. For a given constraint there may also exist several minimal surfaces with different areas (for example, see minimal surface of revolution): the standard definitions only relate to a local optimum, not a global optimum. Definitions Minimal surfaces can be defined in several equivalent ways in \R^3. The fact that they are equivalent serves to demonstrate how minimal surface theory lies at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enneper Surface
In differential geometry and algebraic geometry, the Enneper surface is a self-intersecting surface that can be described parametrically by: \begin x &= \tfrac u \left(1 - \tfracu^2 + v^2\right), \\ y &= \tfrac v \left(1 - \tfracv^2 + u^2\right), \\ z & = \tfrac \left(u^2 - v^2\right). \end It was introduced by Alfred Enneper in 1864 in connection with minimal surface theory.Ulrich Dierkes, Stefan Hildebrandt, Friedrich Sauvigny (2010). Minimal Surfaces. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer. . The Weierstrass–Enneper parameterization is very simple, f(z)=1, g(z)=z, and the real parametric form can easily be calculated from it. The surface is conjugate to itself. Implicitization methods of algebraic geometry can be used to find out that the points in the Enneper surface given above satisfy the degree-9 polynomial equation \begin & 64 z^9 - 128 z^7 + 64 z^5 - 702 x^2 y^2 z^3 - 18 x^2 y^2 z + 144 (y^2 z^6 - x^2 z^6)\\ & + 162 (y^4 z^2 - x^4 z^2) + 27 (y^6 - x^6) + 9 (x^4 z + y^4 z) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parametrization (geometry)
In mathematics, and more specifically in geometry, parametrization (or parameterization; also parameterisation, parametrisation) is the process of finding parametric equations of a curve, a surface, or, more generally, a manifold or a variety, defined by an implicit equation. The inverse process is called implicitization. "To parameterize" by itself means "to express in terms of parameters". Parametrization is a mathematical process consisting of expressing the state of a system, process or model as a function of some independent quantities called parameters. The state of the system is generally determined by a finite set of coordinates, and the parametrization thus consists of one function of several real variables for each coordinate. The number of parameters is the number of degrees of freedom of the system. For example, the position of a point that moves on a curve in three-dimensional space is determined by the time needed to reach the point when starting from a fixed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred Enneper
Alfred Enneper (June 14, 1830, Barmen – March 24, 1885 Hanover) was a German mathematician. Enneper earned his PhD from the Georg-August-Universität Göttingen in 1856, under the supervision of Peter Gustav Lejeune Dirichlet, for his dissertation about functions with complex arguments.. After his habilitation in 1859 in Göttingen, he was from 1870 on Professor (Extraordinarius) at Göttingen. He studied minimal surfaces and parametrized Enneper's minimal surfaces in 1864. A contemporary of Karl Weierstrass Karl Theodor Wilhelm Weierstrass (; ; 31 October 1815 – 19 February 1897) was a German mathematician often cited as the " father of modern analysis". Despite leaving university without a degree, he studied mathematics and trained as a school t ..., the two created a whole class of parameterizations, the Enneper–Weierstrass parameterization.. References External links * 19th-century German mathematicians 1830 births 1885 deaths University of Göttingen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 contiguous states border Canada to the north and Mexico to the south, with the semi-exclave of Alaska in the northwest and the archipelago of Hawaii in the Pacific Ocean. The United States asserts sovereignty over five Territories of the United States, major island territories and United States Minor Outlying Islands, various uninhabited islands in Oceania and the Caribbean. It is a megadiverse country, with the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, third-largest land area and List of countries and dependencies by population, third-largest population, exceeding 340 million. Its three Metropolitan statistical areas by population, largest metropolitan areas are New York metropolitan area, New York, Greater Los Angeles, Los Angel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yosemite National Park
Yosemite National Park ( ) is a List of national parks of the United States, national park of the United States in California. It is bordered on the southeast by Sierra National Forest and on the northwest by Stanislaus National Forest. The park is managed by the National Park Service and covers in four County, countiescentered in Tuolumne County, California, Tuolumne and Mariposa County, California, Mariposa, extending north and east to Mono County, California, Mono and south to Madera County, California, Madera. Designated a World Heritage Site in 1984, Yosemite is internationally recognized for its granite cliffs, waterfalls, clear streams, groves of Sequoiadendron giganteum, giant sequoia, lakes, mountains, meadows, glaciers, and Biodiversity, biological diversity. Almost 95 percent of the park is designated National Wilderness Preservation System, wilderness. Yosemite is one of the largest and least fragmented habitat blocks in the Sierra Nevada. Its geology of the Yosem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Law Of Mass Action
In chemistry, the law of mass action is the proposition that the rate of a chemical reaction is directly proportional to the product of the activities or concentrations of the reactants. It explains and predicts behaviors of solutions in dynamic equilibrium. Specifically, it implies that for a chemical reaction mixture that is in equilibrium, the ratio between the concentration of reactants and products is constant. Two aspects are involved in the initial formulation of the law: 1) the equilibrium aspect, concerning the composition of a reaction mixture at equilibrium and 2) the kinetic aspect concerning the rate equations for elementary reactions. Both aspects stem from the research performed by Cato M. Guldberg and Peter Waage between 1864 and 1879 in which equilibrium constants were derived by using kinetic data and the rate equation which they had proposed. Guldberg and Waage also recognized that chemical equilibrium is a dynamic process in which rates of reaction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claude Louis Berthollet
Claude Louis Berthollet (, 9 December 1748 – 6 November 1822) was a Savoyard-French chemist who became vice president of the French Senate in 1804. He is known for his scientific contributions to the theory of chemical equilibria via the mechanism of reverse chemical reactions, and for his contribution to modern chemical nomenclature. On a practical basis, Berthollet was the first to demonstrate the bleaching action of chlorine gas, and was first to develop a solution of sodium hypochlorite as a modern bleaching agent. Biography Claude Louis Berthollet was born in Talloires, near Annecy, then part of the Duchy of Savoy, in 1749. He started his studies at Chambéry and then in Turin where he graduated in medicine. Berthollet's great new developments in works regarding chemistry made him, in a short period of time, an active participant of the Academy of Science in 1780. Berthollet, along with Antoine Lavoisier and others, devised a chemical nomenclature, or a system of na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |