|
1822 In China ...
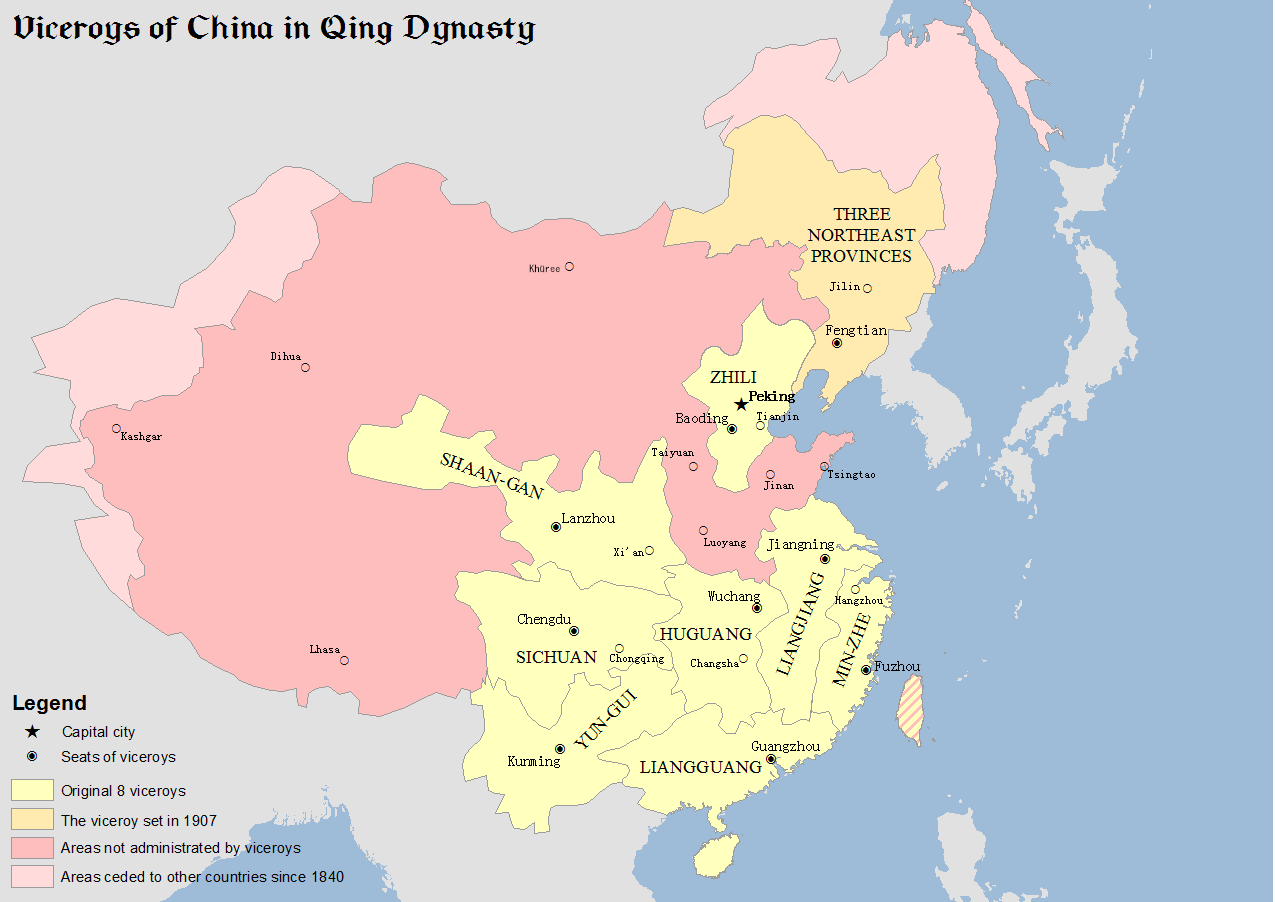
Events from the year 1822 in China. Incumbents * Daoguang Emperor (2nd year) Viceroys * Viceroy of Zhili — Fang Shouchou then Yan Jian * Viceroy of Min-Zhe — Qingbao then Zhao Shenzhen * Viceroy of Huguang — Chen Ruolin then Li Hongbin * Viceroy of Shaan-Gan — Nayancheng * Viceroy of Liangguang — Li Hongbin * Viceroy of Yun-Gui — Shi Zhiguang * Viceroy of Sichuan — Jiang Youxian * Viceroy of Liangjiang — Sun Yuting Events * the teaching and practice of acupuncture and moxibustion were banned from the Imperial Medical Academy (Taiyuyuan) References {{China-stub China China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and borders fourteen countries by land, the most of any country in the world, tied with Russia. Covering an area of approximately , it is the world's third largest country by total land area. The country consists of 22 provinces, five autonomous regions, four municipalities, and two Special Administrative Regions (Hong Kong and Macau). The national capital is Beijing, and the most populous city and financial center is Shanghai. Modern Chinese trace their origins to a cradle of civilization in the fertile basin of the Yellow River in the North China Plain. The semi-legendary Xia dynasty in the 21st century BCE and the well-attested Shang and Zhou dynasties developed a bureaucratic political system to serve hereditary monarchies, or dyna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viceroy Of Liangguang
The Viceroy of Liangguang or Viceroy of the Two Guangs, was one of eight regional Viceroys during the Ming and Qing dynasties. The two ''Guang'' referred to Guangdong and Guangxi provinces. The areas under the Viceroy's jurisdiction included present-day Guangdong and Guangxi provinces, as well as Hainan Province. Name Its full name in Chinese is Governor-General, Commander and Quartermaster, Supervisor of Waterways, and Inspector-General of the Two Expanses and Surrounding Areas. History Ming dynasty The office of the Viceroy of Liangguang originated in 1452 during the Ming dynasty. The Jingtai Emperor accepted Yu Qian's proposal to create the office and appointed Wang Ao (王翱) as the first viceroy. In 1465, the Chenghua Emperor appointed Han Yong (韓雍) as Left Censor-in-Chief and Viceroy of Liangguang. The office was formalised in 1469, with the administrative headquarters fixed in Wuzhou, Guangxi. In 1536, during the reign of the Jiajing Emperor, the viceroy Qia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UBC Press
The University of British Columbia Press (UBC Press) is a university press that is part of the University of British Columbia. It was established in 1971. The press is based in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, and has editorial offices in Kelowna, British Columbia, and Toronto, Ontario. UBC Press is primarily a social sciences publisher. It publishes books of original scholarship that draws on and reflects current research. Each year UBC Press publishes seventy new titles in a number of fields, including Aboriginal studies, Asian studies, Canadian history, environmental studies, gender and women's studies, health and food studies, geography, law, media and communications, military and security studies, planning and urban studies, and political science. The press is a member of the Canadian Association of University Presses (CAUP), the Association of American University Presses (AAUP), the Association of Canadian Publishers (ACP), the International Association of Scholarly Publi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Medical Academy (China)
The Imperial Military School of Medicine,Strauss, Johann. "Twenty Years in the Ottoman Capital: The Memoirs of Dr. Hristo Tanev Stambolski of Kazanlik (1843-1932) from an Ottoman Point of View." In: Herzog, Christoph and Richard Wittmann (editors). ''Istanbul - Kushta - Constantinople: Narratives of Identity in the Ottoman Capital, 1830-1930''. Routledge, 10 October 2018. , 9781351805223. Google Books P263(actually circa p. 267) or the Imperial School of Medicine (''Mekteb-i Tıbbiye-i Şahane'') was a school of medicine in Ottoman Constantinople. The school has changed locations several times. The well-known building in the Üsküdar district of Istanbul is a collaboration by Levantine architect Alexandre Vallaury and Raimondo D'Aronco in the Ottoman Revivalist architectural style, incorporating Ottoman and Seljuk design features. It was built between 1893 and 1903. It currently houses the University of Health Sciences campus at Haydarpaşa. Originally commissioned by Sultan Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moxibustion
Moxibustion () is a traditional Chinese medicine therapy which consists of burning dried mugwort ('' wikt:moxa'') on particular points on the body. It plays an important role in the traditional medical systems of China, Japan, Korea, Vietnam, and Mongolia. Suppliers usually age the mugwort and grind it up to a fluff; practitioners burn the fluff or process it further into a cigar-shaped stick. They can use it indirectly, with acupuncture needles, or burn it on the patient's skin. Moxibustion is promoted as a treatment for a wide variety of conditions, but its use is not backed by good evidence and it carries a risk of adverse effects. Terminology The first Western remarks on moxibustion can be found in letters and reports written by Portuguese missionaries in 16th-century Japan. They called it ''botão de fogo'' ("fire button"), a term originally used for round-headed Western cautery irons. Hermann Buschoff, who published the first Western book on this matter in 1674 (Engli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acupuncture
Acupuncture is a form of alternative medicine and a component of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) in which thin needles are inserted into the body. Acupuncture is a pseudoscience; the theories and practices of TCM are not based on scientific knowledge, and it has been characterized as quackery. There is a range of acupuncture variants which originated in different philosophies, and techniques vary depending on the country in which it is performed, but can be divided into two main foundational philosophical applications and approaches, the first being the modern standardized form called eight principles TCM and the second an older system that is based on the ancient Daoist '' wuxing'', better known as the five elements or phases in the West. Acupuncture is most often used to attempt pain relief, though acupuncturists say that it can also be used for a wide range of other conditions. Acupuncture is generally used only in combination with other forms of treatment. The global ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sun Yuting
Sun Yuting (1752–1834), courtesy name Jiashu and pseudonym Jipu, was a Chinese official of the Qing dynasty. He served as the Provincial Governor of Jiangxi, Jiangsu, and Anhui provinces, Viceroy of Huguang and Liangjiang, and as a member of the Grand Council. Life Sun Yuting was from Jining, Shandong Province. He sat for the palace-level imperial examination in 1775 and obtained the position of a ''tong jinshi chushen'' (third class graduate). He was admitted to the Hanlin Academy, where he served as a shujishi (). In August 1802, he was promoted from ''buzhengshi'' (布政使; Lieutenant-Governor) of Hubei Province to Provincial Governor of Guangxi Province. On 29 October 1803, he was reassigned to serve as the Provincial Governor of Guangdong Province. Around December 1804, he was transferred back to Guangxi, but was relocated back to Guangdong on 4 July 1805 until 1808. In 1810, Sun Yuting was appointed as the Provincial Governor of Yunnan Province before he was late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viceroy Of Liangjiang
The Viceroy of Liangjiang or Viceroy of the Two Jiangs, fully referred to in Chinese as the Governor-General of the Two Yangtze Provinces and Surrounding Areas Overseeing Military Affairs, Provisions and Funds, Manager of Waterways, Director of Civil Affairs, was one of eight regional Viceroys in China proper during the Qing dynasty. The Viceroy of Liangjiang had jurisdiction over Jiangsu, Jiangxi and Anhui provinces. Because Jiangsu and Anhui were previously part of a single province, Jiangnan ("south of the Yangtze"), they were thus known, along with Jiangxi ("west of the Yangtze"), as the two ''jiang''s, hence the name "Liangjiang" ("two Jiangs"). History The office of Viceroy of Liangjiang originated in 1647 during the reign of the Shunzhi Emperor. It was called "Viceroy of the Three Provinces of Jiangdong, Jiangxi and Henan" (江東江西河南三省總督) and headquartered in Jiangning (江寧; present-day Nanjing, Jiangsu). In 1652, the office was renamed "Viceroy of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jiang Youxian
Jiang may refer to: * ''Jiang'' (rank), rank held by general officers in the military of China *Jiang (surname), several Chinese surnames **Jiang Zemin (1926–2022), as general secretary of the Chinese Communist Party *Jiang River The Jiang River (, p ''Jiāng Shuǐ'') is the ancient name of a river in China. According to Sima Qian's ''Records of the Grand Historian'', the river gave its name to Shennong's family. According to the '' Guoyu'', it was the birthplace of the ..., an ancient river of China * Jiang County, in Shanxi, China {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viceroy Of Sichuan
The Viceroy of Sichuan, fully referred to in Chinese as the Governor-General of Sichuan Province and the Surrounding Areas Overseeing Military Affairs and Food Production, Director of Civil Affairs, was one of eight regional viceroys in China proper during the Qing dynasty. As its name suggests, the Viceroy of Sichuan had control over Sichuan (Szechuan) Province, as well as modern Chongqing Municipality, which was split off in 1997. History The origins of the Viceroy of Sichuan trace back to 1644, during the reign of the Shunzhi Emperor, with the creation of the office of the Provincial Governor of Sichuan (四川巡撫). Its headquarters were in Chengdu. In 1645, the Qing government created the Viceroy of Huguang-Sichuan with Luo Xiujin (羅繡錦) as the first Viceroy overseeing both Huguang (present-day Hubei and Hunan) and Sichuan provinces. In 1653, Sichuan was placed under the jurisdiction of the Viceroy of the Three Borders in Shaanxi, which was subsequently renamed " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shi Zhiguang
Shi or SHI may refer to: Language * ''Shi'', a Japanese title commonly used as a pronoun * ''Shi'', proposed gender-neutral pronoun * Shi (kana), a kana in Japanese syllabaries * Shi language * ''Shī'', transliteration of Chinese Radical 44 * Tachelhit or the Shilha language (ISO 639 code) Art * Shi, a piece in Chinese chess * ''Shi'' (comics), a comic book series created by William Tucci * Shi (poetry), the Chinese conception of poetry * ''Poetry'' (film) or ''Shi'', a 2010 South Korean film directed by Lee Chang-dong People * Shi (class) (), the low aristocratic class of Shang/Zhou China, later the scholar-gentry class of imperial China * Shi (rank) (), rank group for non-commissioned officers * Shi (personator) (), a ceremonial "corpse" involved in early forms of ancestor worship in China Names * ''Shì'' (氏), a Chinese clan name previously distinguished from ancestral or family names; see Origin of Chinese surnames * Shī (surname), the romanization of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viceroy Of Yun-Gui
The Viceroy of Yun-Gui, fully referred to in Chinese as the Governor-General of Yunnan and Guizhou Provinces and the Surrounding Areas Overseeing Military Affairs and Food Production, Director of Civil Affairs, was one of eight regional viceroys in China proper during the Qing dynasty. The Viceroy controlled Yunnan and Guizhou (Kweichow) provinces. History The Viceroy of Yun-Gui was created in 1659, during the reign of the Shunzhi Emperor, as a ''jinglue'' (經略; military governor) office before it was converted to a Viceroy. In 1662, during the reign of the Kangxi Emperor, the Viceroy of Yun-Gui split into the Viceroy of Yunnan and Viceroy of Guizhou, which were respectively headquartered in Qujing and Anshun. Two years later, the two viceroys were merged and the headquarters shifted to Guiyang. In 1673, the Kangxi Emperor restored the Viceroy of Yunnan, with its headquarters in Qujing. Between 1673 and 1681, the Revolt of the Three Feudatories broke out in Yunnan, Guangdong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |