|
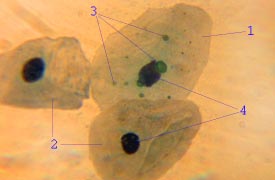
C. Trachomatis
''Chlamydia trachomatis'' (), commonly known as chlamydia, is a bacterium that causes chlamydia, which can manifest in various ways, including: trachoma, lymphogranuloma venereum, nongonococcal urethritis, cervicitis, salpingitis, pelvic inflammatory disease. ''C. trachomatis'' is the most common infectious cause of blindness and the most common sexually transmitted bacterium. Different types of ''C. trachomatis'' cause different diseases. The most common strains cause disease in the genital tract, while other strains cause disease in the eye or lymph nodes. Like other ''Chlamydia'' species, the ''C. trachomatis'' life cycle consists of two morphologically distinct life stages: elementary bodies and reticulate bodies. Elementary bodies are spore-like and infectious, whereas reticulate bodies are in the replicative stage and are seen only within host cells. Description ''Chlamydia trachomatis'' is a gram-negative bacterium that can replicate only within a host cell. Over the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlamydia Infection
Chlamydia, or more specifically a chlamydia infection, is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium ''Chlamydia trachomatis''. Most people who are infected have no symptoms. When symptoms do appear they may occur only several weeks after infection; the incubation period between exposure and being able to infect others is thought to be on the order of two to six weeks. Symptoms in women may include vaginal discharge or burning with urination. Symptoms in men may include discharge from the penis, burning with urination, or pain and swelling of one or both testicles. The infection can spread to the upper genital tract in women, causing pelvic inflammatory disease, which may result in future infertility or ectopic pregnancy. Chlamydia infections can occur in other areas besides the genitals, including the anus, eyes, throat, and lymph nodes. Repeated chlamydia infections of the eyes that go without treatment can result in trachoma, a common cause of blindness i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlamydia Suis
''Chlamydia suis'' is a member of the genus ''Chlamydia''. ''C. suis'' has only been isolated from swine, in which it may be endemic. Glycogen has been detected in ''Chlamydia suis'' inclusions in infected swine tissues and in cell culture. ''C. suis'' is associated with conjunctivitis, enteritis and pneumonia in swine. Some strains have enhanced resistance to sulfadiazine and tetracycline. Several strains of ''C. suis'' are known to have an extrachromosomal plasmid, pCS. ''C. suis'' strains are somewhat more diverse than are other chlamydial species. The deduced ompA gene products of various ''Chlamydia suis'' strains contain vs4 epitopes TLNPTIAG(A.K.T)G(D.K.N.T), TWNPTIAGAGS or TLNPTISGKGQ. These epitopes are identical or nearly identical to the ''Chlamydia'' MOMP core epitopes NPTI, TLNPTI, LNPTIA or LNPTI, which are recognized by ''Chlamydia trachomatis ''Chlamydia trachomatis'' (), commonly known as chlamydia, is a bacterium that causes chlamydia, which can manifes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlamydophila Pecorum
''Chlamydia pecorum'', also known as Chlamydophila pecorum is a species of Chlamydiaceae that originated from ruminants, such as cattle, sheep and goats. It has also infected koalas and swine. ''C. pecorum'' strains are serologically and pathogenically diverse. In the koalas, ''C. pecorum'' causes infections in the reproductive systems and urinary tract, as well as pneumonia, infertility, and death. It is considered one of the most important infectious diseases that currently plagues koalas. C.pecorum is the most common chlamydial species to infect koalas and is the most pathogenic. In other animals, ''C. pecorum'' has been associated with abortion, conjunctivitis, encephalomyelitis, enteritis, arthritis, and polyarthritis Polyarthritis is any type of arthritis that involves 5 or more joints simultaneously. It is usually associated with autoimmune conditions and may be experienced at any age and is not sex specific. Causes Polyarthritis is most often caused by an au .... S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlamydophila Pneumoniae
''Chlamydia pneumoniae'' is a species of ''Chlamydia (genus), Chlamydia'', an Obligate intracellular parasite, obligate intracellular bacterium that infects humans and is a major cause of pneumonia. It was known as the Taiwan acute respiratory agent (TWAR) from the names of the two original isolates – Taiwan (TW-183) and an acute respiratory isolate designated AR-39. Briefly, it was known as ''Chlamydophila pneumoniae,'' and that name is used as an alternate in some sources. In some cases, to avoid confusion, both names are given. ''Chlamydia pneumoniae'' has a complex life cycle and must infect another cell to reproduction, reproduce; thus, it is classified as an Obligate intracellular parasite, obligate intracellular pathogen. The full genome sequence for ''C. pneumoniae'' was published in 1999. It also infects and causes disease in koalas, emerald tree boas (''Corallus caninus''), iguanas, chameleons, frogs, and turtles. The first known case of infection with ''C. pneu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlamydia Muridarum
''Chlamydia muridarum'' is an intracellular bacterial species that at one time belonged to ''Chlamydia trachomatis''. However, ''C. trachomatis'' naturally only infects humans and ''C. muridarum'' naturally infects only members of the family Muridae (includes both mice and hamsters, Alderton, 1996). Two strains of ''Chlamydia muridarum'', MoPn (originally named Nigg) and SFPD, have been isolated from mice and hamsters. Glycogen production by both strains has been demonstrated. The chromosome and extrachromosomal plasmid of MoPn have been sequenced. ''Chlamydia muridarum'' MoPn binds mAbs recognizing ''Chlamydia trachomatis'' MOMP vs4 core epitope (T) LNPT (IA). DNA sequence analysis indicates that these mAbs should recognize SFPD and that ''Chlamydia trachomatis'' B-serogroup mAbs specific for the vs4 epitope IAGAG should recognize SFPD. MoPn was isolated in 1942 from the lungs of asymptomatic albino Swiss mice and was subsequently shown to be capable of producing disease in mic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ectopic Pregnancies
Ectopic pregnancy is a complication of pregnancy in which the embryo attaches outside the uterus. Signs and symptoms classically include abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding, but fewer than 50 percent of affected women have both of these symptoms. The pain may be described as sharp, dull, or crampy. Pain may also spread to the shoulder if bleeding into the abdomen has occurred. Severe bleeding may result in a fast heart rate, fainting, or shock. With very rare exceptions the fetus is unable to survive. Overall, ectopic pregnancies are very rare, annually affecting less than 2% of pregnancies worldwide. Risk factors for ectopic pregnancy include pelvic inflammatory disease, often due to chlamydia infection; tobacco smoking; prior tubal surgery; a history of infertility; and the use of assisted reproductive technology. Those who have previously had an ectopic pregnancy are at much higher risk of having another one. Most ectopic pregnancies (90%) occur in the fallopian tube, whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response. The term ''antigen'' originally referred to a substance that is an antibody generator. Antigens can be proteins, peptides (amino acid chains), polysaccharides (chains of monosaccharides/simple sugars), lipids, or nucleic acids. Antigens are recognized by antigen receptors, including antibodies and T-cell receptors. Diverse antigen receptors are made by cells of the immune system so that each cell has a specificity for a single antigen. Upon exposure to an antigen, only the lymphocytes that recognize that antigen are activated and expanded, a process known as clonal selection. In most cases, an antibody can only react to and bind one specific antigen; in some instances, however, antibodies may cross-react and bind more than one antigen. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serovar
A serotype or serovar is a distinct variation within a species of bacteria or virus or among immune cells of different individuals. These microorganisms, viruses, or cells are classified together based on their surface antigens, allowing the epidemiologic classification of organisms to the subspecies level. A group of serovars with common antigens is called a serogroup or sometimes ''serocomplex''. Serotyping often plays an essential role in determining species and subspecies. The ''Salmonella'' genus of bacteria, for example, has been determined to have over 2600 serotypes. ''Vibrio cholerae'', the species of bacteria that causes cholera, has over 200 serotypes, based on cell antigens. Only two of them have been observed to produce the potent enterotoxin that results in cholera: O1 and O139. Serotypes were discovered by the American microbiologist Rebecca Lancefield in 1933. Role in organ transplantation The immune system is capable of discerning a cell as being 'self' or 'n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biovar
A biovar is a variant prokaryotic strain that differs physiologically or biochemically from other strains in a particular species. Morphovars (or morphotypes) are those strains that differ morphologically. Serovars (or serotypes) are those strains that have antigenic properties that differ from other strains. __FORCETOC__ List of biovars This is a list of biovars and strains of biovars listed at the NCBI Taxonomy database:Schoch CL, et al. NCBI Taxonomy: a comprehensive update on curation, resources and tools. Database (Oxford). 2020: baaa062. PubMed: 32761142 PMC: PMC7408187 * ''Acinetobacter calcoaceticus'' biovar ''anitratus'', a homotypic synonym for ''Acinetobacter calcoaceticus'' subsp. ''anitratus'' * ''Actinobacillus anseriformium'' biovar 1 * ''Actinobacillus anseriformium'' biovar 2 * ''Aeromonas veronii'' bv. ''sobria'' * ''Aeromonas veronii'' bv. ''veronii'' * ''Agrobacterium'' biovar 1, a synonym for ''Agrobacterium tumefaciens'' complex * ''Agrobacterium'' biovar 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryote
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacteria and Archaea (both prokaryotes) make up the other two domains. The eukaryotes are usually now regarded as having emerged in the Archaea or as a sister of the Asgard archaea. This implies that there are only two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but, due to their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass is estimated to be about equal to that of prokaryotes. Eukaryotes emerged approximately 2.3–1.8 billion years ago, during the Proterozoic eon, likely as flagellated phagotrophs. Their name comes from the Greek εὖ (''eu'', "well" or "good") and κάρυον (''karyon'', "nut" or "kernel"). Euka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlamydia
Chlamydia, or more specifically a chlamydia infection, is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium ''Chlamydia trachomatis''. Most people who are infected have no symptoms. When symptoms do appear they may occur only several weeks after infection; the incubation period between exposure and being able to infect others is thought to be on the order of two to six weeks. Symptoms in women may include vaginal discharge or burning with urination. Symptoms in men may include discharge from the penis, burning with urination, or pain and swelling of one or both testicles. The infection can spread to the upper genital tract in women, causing pelvic inflammatory disease, which may result in future infertility or ectopic pregnancy. Chlamydia infections can occur in other areas besides the genitals, including the anus, eyes, throat, and lymph nodes. Repeated chlamydia infections of the eyes that go without treatment can result in trachoma, a common cause of blindness in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |