|
Bürgi–Dunitz Angle
The Bürgi–Dunitz angle (BD angle) is one of two angles that fully define the geometry of "attack" (approach via collision) of a nucleophile on a trigonal unsaturated center in a molecule, originally the carbonyl center in an organic ketone, but now extending to aldehyde, ester, and amide carbonyls, and to alkenes (olefins) as well.Fleming, I. (2010) ''Molecular Orbitals and Organic Chemical Reactions: Reference Edition'', John Wiley & Sons, pp. 214–215.Cieplak, A.S. (2008) Organic addition and elimination reactions: Transformation paths of carbonyl derivatives ''In'' Structure Correlation, Vol. 1 (H.-B. Bürgi & J. D. Dunitz, eds.), New York:John Wiley & Sons, pp. 205–302, esp. 216-218. oi:10.1002/9783527616091.ch06; /ref> The angle was named after crystallographers Hans-Beat Bürgi and Jack D. Dunitz, its first senior investigators. Practically speaking, the Bürgi–Dunitz and Flippin–Lodge angles were central to the development of understanding of chiral chemi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
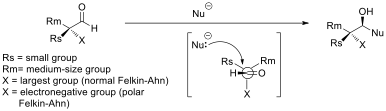
Cram-Felkin-Anh
In stereochemistry, asymmetric induction (also enantioinduction) describes the preferential formation in a chemical reaction of one enantiomer or diastereoisomer over the other as a result of the influence of a chiral feature present in the substrate, reagent, catalyst or environment. Asymmetric induction is a key element in asymmetric synthesis. Asymmetric induction was introduced by Hermann Emil Fischer based on his work on carbohydrates. Several types of induction exist. Internal asymmetric induction makes use of a chiral center bound to the reactive center through a covalent bond and remains so during the reaction. The starting material is often derived from chiral pool synthesis. In relayed asymmetric induction the chiral information is introduced in a separate step and removed again in a separate chemical reaction. Special synthons are called chiral auxiliaries. In external asymmetric induction chiral information is introduced in the transition state through a catalyst of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahedron
In geometry, a tetrahedron (plural: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, six straight edges, and four vertex corners. The tetrahedron is the simplest of all the ordinary convex polyhedra and the only one that has fewer than 5 faces. The tetrahedron is the three-dimensional case of the more general concept of a Euclidean simplex, and may thus also be called a 3-simplex. The tetrahedron is one kind of pyramid, which is a polyhedron with a flat polygon base and triangular faces connecting the base to a common point. In the case of a tetrahedron the base is a triangle (any of the four faces can be considered the base), so a tetrahedron is also known as a "triangular pyramid". Like all convex polyhedra, a tetrahedron can be folded from a single sheet of paper. It has two such nets. For any tetrahedron there exists a sphere (called the circumsphere) on which all four vertices lie, and another sphere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahedral Angle
In geometry, a tetrahedron (plural: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, six straight edges, and four vertex corners. The tetrahedron is the simplest of all the ordinary convex polyhedra and the only one that has fewer than 5 faces. The tetrahedron is the three-dimensional case of the more general concept of a Euclidean simplex, and may thus also be called a 3-simplex. The tetrahedron is one kind of pyramid, which is a polyhedron with a flat polygon base and triangular faces connecting the base to a common point. In the case of a tetrahedron the base is a triangle (any of the four faces can be considered the base), so a tetrahedron is also known as a "triangular pyramid". Like all convex polyhedra, a tetrahedron can be folded from a single sheet of paper. It has two such nets. For any tetrahedron there exists a sphere (called the circumsphere) on which all four vertices lie, and another sph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LCAO
A linear combination of atomic orbitals or LCAO is a quantum superposition of atomic orbitals and a technique for calculating molecular orbitals in quantum chemistry. In quantum mechanics, electron configurations of atoms are described as wavefunctions. In a mathematical sense, these wave functions are the basis set of functions, the basis functions, which describe the electrons of a given atom. In chemical reactions, orbital wavefunctions are modified, i.e. the electron cloud shape is changed, according to the type of atoms participating in the chemical bond. It was introduced in 1929 by Sir John Lennard-Jones with the description of bonding in the diatomic molecules of the first main row of the periodic table, but had been used earlier by Linus Pauling for H2+. Mathematical description An initial assumption is that the number of molecular orbitals is equal to the number of atomic orbitals included in the linear expansion. In a sense, ''n'' atomic orbitals combine to for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Orbital Theory
In chemistry, molecular orbital theory (MO theory or MOT) is a method for describing the electronic structure of molecules using quantum mechanics. It was proposed early in the 20th century. In molecular orbital theory, electrons in a molecule are not assigned to individual chemical bonds between atoms, but are treated as moving under the influence of the atomic nuclei in the whole molecule. Quantum mechanics describes the spatial and energetic properties of electrons as molecular orbitals that surround two or more atoms in a molecule and contain valence electrons between atoms. Molecular orbital theory revolutionized the study of chemical bonding by approximating the states of bonded electrons—the molecular orbitals—as linear combinations of atomic orbitals (LCAO). These approximations are made by applying the density functional theory (DFT) or Hartree–Fock (HF) models to the Schrödinger equation. Molecular orbital theory and valence bond theory are the foundational ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protopine
Protopine is an alkaloid occurring in opium poppy, ''Corydalis'' tubers and other plants of the family papaveraceae, like ''Fumaria officinalis''. Protopine is metabolically derived from the benzylisoquinoline alkaloid ''(S)''-Reticuline through a progressive series of five enzymatic transformations: 1) berberine bridge enzyme to ''(S)''-Scoulerine; 2) ''(S)-''cheilanthifoline synthase/CYP719A25 to ''(S)-''Cheilanthifoline; 3) ''(S)-''stylopine synthase/CYP719A20 to ''(S)''-Stylopine; 4) ''(S)''-tetrahydroprotoberberine ''N''-methyltransferase to ''(S)''-''cis''-''N''-Methylstylopine; and ultimately, 5) ''N''-methylstylopine hydroxylase to protopine. It has been found to inhibit histamine H1 receptors and platelet aggregation, and acts as an analgesic. See also * Protopine 6-monooxygenase * Cryptopine Cryptopine is an opium alkaloid. It is found in plants in the family Papaveraceae, including ''Argemone mexicana''. See also * Protopine * Allocryptopine References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methadone
Methadone, sold under the brand names Dolophine and Methadose among others, is a synthetic opioid agonist used for chronic pain and also for opioid dependence. It is used to treat chronic pain, and it is also used to treat addiction to heroin or other opioids. Prescribed for daily use, the medicine relieves cravings and removes withdrawal symptoms. Detoxification using methadone can be accomplished in less than a month, or it may be done gradually over as long as six months. While a single dose has a rapid effect, maximum effect can take up to five days of use. The pain-relieving effects last about six hours after a single dose. After long-term use, in people with normal liver function, effects last 8 to 36 hours. Methadone is usually taken by mouth and rarely by injection into a muscle or vein. Side effects are similar to those of other opioids. These frequently include dizziness, sleepiness, vomiting, and sweating. Serious risks include opioid abuse and respiratory depre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group (these may respectively be called alkylamines and arylamines; amines in which both types of substituent are attached to one nitrogen atom may be called alkylarylamines). Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines, trimethylamine, and aniline; Inorganic derivatives of ammonia are also called amines, such as monochloramine (). The substituent is called an amino group. Compounds with a nitrogen atom attached to a carbonyl group, thus having the structure , are called amides and have different chemical properties from amines. Classification of amines Amines can be classified according to the nature and number of substituents on nitrogen. Aliphatic amines contain only H and alkyl substituents. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formaldehyde
Formaldehyde ( , ) (systematic name methanal) is a naturally occurring organic compound with the formula and structure . The pure compound is a pungent, colourless gas that polymerises spontaneously into paraformaldehyde (refer to section Forms below), hence it is stored as an aqueous solution (formalin), which is also used to store animal specimens. It is the simplest of the aldehydes (). The common name of this substance comes from its similarity and relation to formic acid. Formaldehyde is an important precursor to many other materials and chemical compounds. In 1996, the installed capacity for the production of formaldehyde was estimated at 8.7 million tons per year. It is mainly used in the production of industrial resins, e.g., for particle board and coatings. Forms Formaldehyde is more complicated than many simple carbon compounds in that it adopts several diverse forms. These compounds can often be used interchangeably and can be interconverted. *Molecular formald ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clayton Heathcock
Clayton Heathcock is an organic chemist, Professor of Chemistry, and Dean of the College of Chemistry at the University of California, Berkeley. Professor Heathcock is well known for his accomplishments in the synthesis of complex polycyclic natural products and for his contributions to the chemistry community. In 1995 he became a member of the National Academy of Sciences. Clayton Heathcock received his B.Sc. in chemistry in 1958 from Abilene Christian University and a Ph.D in organic chemistry in 1963 from the University of Colorado. His graduate work was carried out under the direction of Alfred Hassner and dealt with the synthesis of steroidal heterocycles. He then completed a postdoctoral fellowship with Gilbert Stork at Columbia University. In 1964, he joined the faculty at UC Berkeley where he is currently Professor in the Graduate School and Dean of the College of Chemistry. Heathcock is known for tackling the chemical synthesis of complex, polycyclic natural pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flippin–Lodge Angle
The Flippin–Lodge angle is one of two angles used by organic and biological chemists studying the relationship between a molecule's chemical structure and ways that it reacts, for reactions involving "attack" of an electron-rich reacting species, the nucleophile, on an electron-poor reacting species, the electrophile. Specifically, the angles—the Bürgi–Dunitz, \alpha_, and the Flippin–Lodge, \alpha_—describe the "trajectory" or "angle of attack" of the nucleophile as it approaches the electrophile, in particular when the latter is planar in shape. This is called a nucleophilic addition reaction and it plays a central role in the biological chemistry taking place in many biosyntheses in nature, and is a central "tool" in the reaction toolkit of modern organic chemistry, e.g., to construct new molecules such as pharmaceuticals. Theory and use of these angles falls into the areas of synthetic and physical organic chemistry, which deals with chemical structure and rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)