|
Burnley Coalfield
The Burnley Coalfield is the most northerly portion of the Lancashire Coalfield. Surrounding Burnley, Nelson, Blackburn and Accrington, it is separated from the larger southern part by an area of Millstone Grit that forms the Rossendale anticline. Occupying a syncline, it stretches from Blackburn past Colne to the Yorkshire border where its eastern flank is the Pennine anticline. Geography and geology The Burnley Coalfield which surrounds Burnley, Nelson, Blackburn and Accrington is the most northerly portion of the Lancashire Coalfield. The Rossendale anticline, an area of Millstone Grit, separates it from the larger southern part of the coalfield. Occupying a syncline bounded by the Pendle monocline to the north, the coalfield stretches from Blackburn, eastwards past Colne to the Pennine anticline on the border with Yorkshire. The coalfield's seams are the Westphalian Coal Measures of the Carboniferous period, laid down from the vegetation of tropical swampy forests mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
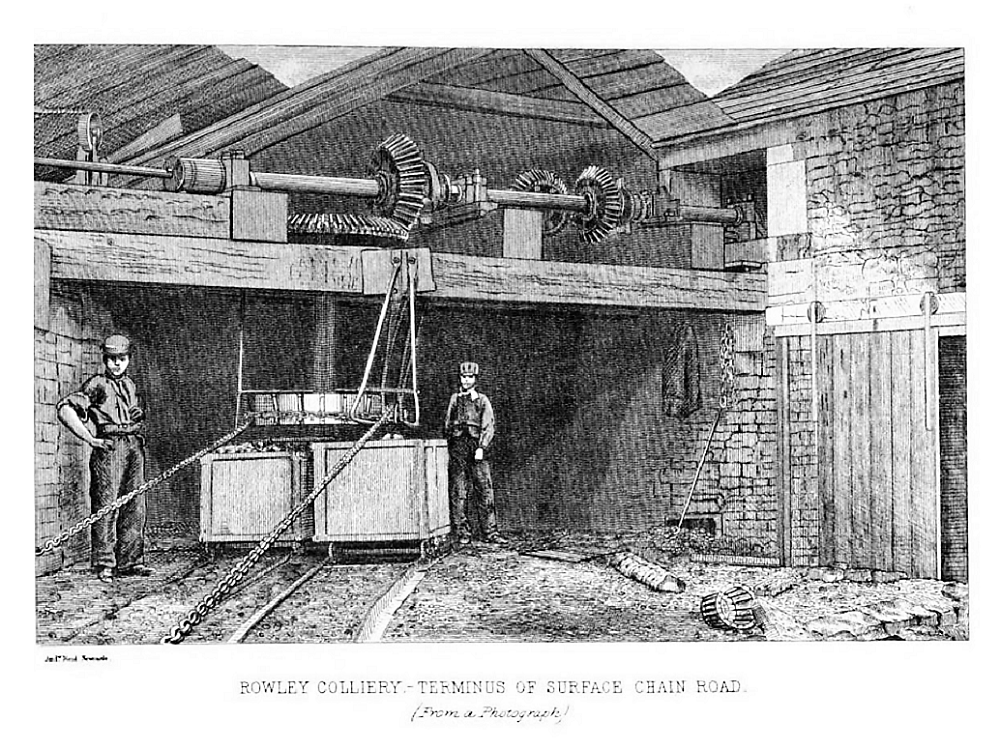
Rowley Ginny Track Terminus
Rowley may refer to: Places Canada * Rowley, Alberta * Rowley Island, Nunavut United Kingdom * Rowley, County Durham, a hamlet * Rowley, East Riding of Yorkshire, England * Rowley, Shropshire, a location in Shropshire, England * Rowley Regis, a historic parish in the West Midlands, England United States * Rowley, Iowa * Rowley, Massachusetts ** Rowley (CDP), Massachusetts * Rowley, Utah * Rowley Creek, a stream in Wisconsin People Surname * Alec Rowley (1892–1958), English composer * Alex Rowley (born 1963), Scottish politician * Arthur Rowley (footballer born 1870), English footballer with Stoke and Port Vale * Arthur Rowley (1926–2002), English footballer with Fulham, Leicester City and Shrewsbury * Bartholomew Rowley (1764–1811), British naval officer * Beth Rowley, English singer-songwriter * Sir Charles Rowley, 1st Baronet (1770–1845), British naval officer * Chris Rowley, American baseball pitcher * Christopher Rowley (born 1948), American writer * Coleen Rowl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huncoat
Huncoat is a village in Lancashire, England; situated in the North West. It is located to the east of Accrington. It is a ward of Hyndburn where the population taken at the 2011 census was 4,418. Huncoat railway station is on the East Lancashire Line. History The name is of Anglo-Saxon origin where Hun, or Hunna was a family name and Cotte is an Old English name for a shelter for animals. The brief details of the Blackburnshire hundred in the Domesday survey, mention Huncoat with King Edward holding two carucates of land here. Huncoat Colliery on the Burnley Coalfield was sunk by George Hargreaves and Company between 1890 and 1893. Before 1930, the company had linked its Calder and Scaitcliffe Collieries to Huncoat underground and it wound the coal from all three pits. The colliery was nationalised in 1947 and closed after its coal was exhausted in 1968. The coal-fired Huncoat Power Station was located at the eastern end of the village, off Altham Lane and operated from 1952 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lancashire And Yorkshire Railway
The Lancashire and Yorkshire Railway (L&YR) was a major British railway company before the 1923 Grouping. It was incorporated in 1847 from an amalgamation of several existing railways. It was the third-largest railway system based in northern England (after the Midland and North Eastern Railways). The intensity of its service was reflected in the 1,650 locomotives it owned – it was by far the most densely-trafficked system in the British Isles with more locomotives per mile than any other company – and that one third of its 738 signal boxes controlled junctions averaging one every . No two adjacent stations were more than apart and its 1,904 passenger services occupied 57 pages in '' Bradshaw'', a number exceeded only by the Great Western Railway, the London and North Western Railway, and the Midland Railway. It was the first mainline railway to introduce electrification of some of its lines, and it also ran steamboat services across the Irish Sea an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leeds And Liverpool Canal
The Leeds and Liverpool Canal is a canal in Northern England, linking the cities of Leeds and Liverpool. Over a distance of , crossing the Pennines, and including 91 locks on the main line. The Leeds and Liverpool Canal has several small branches, and in the early 21st century a new link was constructed into the Liverpool docks system. History Background In the mid-18th century the growing towns of Yorkshire, including Leeds, Wakefield and Bradford, were trading increasingly. While the Aire and Calder Navigation improved links to the east for Leeds, links to the west were limited. Bradford merchants wanted to increase the supply of limestone to make lime for mortar and agriculture using coal from Bradford's collieries and to transport textiles to the Port of Liverpool. On the west coast, traders in the busy port of Liverpool wanted a cheap supply of coal for their shipping and manufacturing businesses and to tap the output from the industrial regions of Lancashire. Inspired by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adit
An adit (from Latin ''aditus'', entrance) is an entrance to an underground mine which is horizontal or nearly horizontal, by which the mine can be entered, drained of water, ventilated, and minerals extracted at the lowest convenient level. Adits are also used to explore for mineral veins. Construction Adits are driven into the side of a hill or mountain, and are often used when an ore body is located inside the mountain but above the adjacent valley floor or coastal plain. In cases where the mineral vein outcrops at the surface, the adit may follow the lode or vein until it is worked out, in which case the adit is rarely straight. The use of adits for the extraction of ore is generally called drift mining. Adits can only be driven into a mine where the local topography permits. There will be no opportunity to drive an adit to a mine situated on a large flat plain, for instance. Also if the ground is weak, the cost of shoring up a long adit may outweigh its possible advantage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outcrop
An outcrop or rocky outcrop is a visible exposure of bedrock or ancient superficial deposits on the surface of the Earth. Features Outcrops do not cover the majority of the Earth's land surface because in most places the bedrock or superficial deposits are covered by soil and vegetation and cannot be seen or examined closely. However, in places where the overlying cover is removed through erosion or tectonic uplift, the rock may be exposed, or ''crop out''. Such exposure will happen most frequently in areas where erosion is rapid and exceeds the weathering rate such as on steep hillsides, mountain ridges and tops, river banks, and tectonically active areas. In Finland, glacial erosion during the last glacial maximum (ca. 11000 BC), followed by scouring by sea waves, followed by isostatic uplift has produced many smooth coastal and littoral outcrops. Bedrock and superficial deposits may also be exposed at the Earth's surface due to human excavations such as quarrying and build ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cliviger
Cliviger is a civil parish in the Borough of Burnley, in Lancashire, England. It is situated to the southeast of Burnley, and northwest of Todmorden. According to the 2011 census, the parish has a population of 2,238. Although the whole parish lies within the Borough of Burnley it is actually split between three post towns, with a few farms lying in either the Todmorden or Bacup postal areas. Nowadays, it is mainly a dormitory area for people working in Burnley and other towns in East Lancashire and West Yorkshire. Contrary to popular (and in some cases mistaken local) belief there is no village of "Cliviger". The principal settlements within the parish are Walk Mill, Southward Bottom, Overtown, Mereclough and Holme Chapel. Toponymy There is some lack of certainty as to the origin of the name Cliviger. The Rev. Dr. Thomas Dunham Whitaker, historian, theologian and curate of Holme Chapel and later also vicar of the parishes of Whalley and Blackburn (until 1821), conjectured tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trawden
Trawden is a village in the Trawden Forest parish of Pendle, at the foot of Boulsworth Hill, in Lancashire, England. The village co-operatively owns and runs its library, shop, community centre and pub. Activities As a way of encouraging people to visit Trawden and the surrounding area, a small group of village residents organise and mobilise other villagers in order to hold the annual Trawden Garden Festival and Scarecrow Trail. This takes place over the first weekend in July. Trawden also holds an annual agricultural show on the 2nd Sunday in August, which many farmers, riders and people from around Lancashire enjoy and take part in. Trawden F.C. were champions of the Pendle Charity League Second Division in the 2006–07 season. Trawden Athletic Club is a running club consisting of around 400 members (as of January 2017) who compete in local and regional road, fell, trail and cross country races. The Trawden Forest Community Centre is in the heart of the village. The Ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castercliff Camp Hillfort - Geograph
Castercliff is an Iron Age multivallate hillfort situated close to the towns of Nelson and Colne in Lancashire, Northern England. __TOC__ It is located on a hilltop overlooking the valley system of the River Calder and its tributaries, on the western edge of the South Pennines. On the upper part of the hill, triple rubble ramparts up to high, separated by ditches of similar depth, surround the site on all sides except the north. On this side the defences consist mainly of a single rampart and ditch, but some short lengths of triple rampart and ditch are also found here. The inner rampart may have been timber-laced and revetted with stone and enclosed an oval area measuring approximately . The summit of the hill is above sea level and the surrounding ground falls rapidly on all sides except the south east. Here a neck of land, dropping from the summit, connects it to similarly high ground about away. Streams spring from either side of the ridge and the deep valleys which t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coal Ball
A coal ball is a type of concretion, varying in shape from an imperfect sphere to a flat-lying, irregular slab. Coal balls were formed in Carboniferous Period swamps and mires, when peat was prevented from being turned into coal by the high amount of calcite surrounding the peat; the calcite caused it to be turned into stone instead. As such, despite not actually being made of coal, the coal ball owes its name to its similar origins as well as its similar shape with actual coal. Coal balls often preserve a remarkable record of the microscopic tissue structure of Carboniferous swamp and mire plants, which would otherwise have been completely destroyed. Their unique preservation of Carboniferous plants makes them valuable to scientists, who cut and peel the coal balls to research the geological past. In 1855, two English scientists, Joseph Dalton Hooker and Edward William Binney, made the first scientific description of coal balls in England, and the initial research on coal b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coke (fuel)
Coke is a grey, hard, and porous coal-based fuel with a high carbon content and few impurities, made by heating coal or oil in the absence of air—a destructive distillation process. It is an important industrial product, used mainly in iron ore smelting, but also as a fuel in stoves and forges when air pollution is a concern. The unqualified term "coke" usually refers to the product derived from low-ash and low-sulphur bituminous coal by a process called coking. A similar product called petroleum coke, or pet coke, is obtained from crude oil in oil refineries. Coke may also be formed naturally by geologic processes.B. Kwiecińska and H. I. Petersen (2004): "Graphite, semi-graphite, natural coke, and natural char classification — ICCP system". ''International Journal of Coal Geology'', volume 57, issue 2, pages 99-116. History China Historical sources dating to the 4th century describe the production of coke in ancient China. The Chinese first used coke for heating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metallurgical
Metallurgy is a domain of materials science and engineering that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their inter-metallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are known as alloys. Metallurgy encompasses both the science and the technology of metals; that is, the way in which science is applied to the production of metals, and the engineering of metal components used in products for both consumers and manufacturers. Metallurgy is distinct from the craft of metalworking. Metalworking relies on metallurgy in a similar manner to how medicine relies on medical science for technical advancement. A specialist practitioner of metallurgy is known as a metallurgist. The science of metallurgy is further subdivided into two broad categories: chemical metallurgy and physical metallurgy. Chemical metallurgy is chiefly concerned with the reduction and oxidation of metals, and the chemical performance of metals. Subjects of study in chemical metallurgy include mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)




