|
Bun Sruth
Bun Sruth is a small loch about in length at the southeast extremity of the island of South Uist in the Outer Hebrides of Scotland. It is surrounded by hills and is connected to the sea by a narrow passage between cliffs of sheer rock, from which its name, meaning "Bottom of the stream", is derived. Access The only access to Bun Sruth is on foot or by boat. From the sea the narrow tidal gorge is difficult to find, and difficulties in negotiating the channel can arise from the fast tidal flow and from seaweed which prevents the use of a propeller. At low tide the water level in the loch is higher than sea level, and drains over a rock shelf in the entrance, making entrance by boat impossible until the tide has risen at least seven feet. Exit by boat is thus best undertaken just after high tide. Wildlife The valley contains some ruins of croft houses, but the area is now inhabited only by sheep and wildlife. Pollock may be found in the loch, and both sea trout and salmon Sal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Uist
South Uist ( gd, Uibhist a Deas, ; sco, Sooth Uist) is the second-largest island of the Outer Hebrides in Scotland. At the 2011 census, it had a usually resident population of 1,754: a decrease of 64 since 2001. The island, in common with the rest of the Hebrides, is one of the last remaining strongholds of the Gaelic language in Scotland. South Uist's inhabitants are known in Gaelic as ''Deasaich'' (Southerners). The population is about 90% Roman Catholic. The island is home to a nature reserve and a number of sites of archaeological interest, including the only location in the British Isles where prehistoric mummies have been found. In the northwest, there is a missile testing range. In 2006 South Uist, together with neighbouring Benbecula and Eriskay, was involved in Scotland's biggest-ever community land buyout by Stòras Uibhist. The group also owns the "biggest community wind farm in Scotland", Lochcarnan, on South Uist which opened in 2013. Geology In common with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, the North Sea to the northeast and east, and the Irish Sea to the south. It also contains more than 790 islands, principally in the archipelagos of the Hebrides and the Northern Isles. Most of the population, including the capital Edinburgh, is concentrated in the Central Belt—the plain between the Scottish Highlands and the Southern Uplands—in the Scottish Lowlands. Scotland is divided into 32 administrative subdivisions or local authorities, known as council areas. Glasgow City is the largest council area in terms of population, with Highland being the largest in terms of area. Limited self-governing power, covering matters such as education, social services and roads and transportation, is devolved from the Scott ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loch
''Loch'' () is the Scottish Gaelic, Scots language, Scots and Irish language, Irish word for a lake or sea inlet. It is Cognate, cognate with the Manx language, Manx lough, Cornish language, Cornish logh, and one of the Welsh language, Welsh words for lake, llwch. In English English and Hiberno-English, the Anglicisation, anglicised spelling lough is commonly found in place names; in Lowland Scots and Scottish English, the spelling "loch" is always used. Many loughs are connected to stories of lake-bursts, signifying their mythical origin. Sea-inlet lochs are often called sea lochs or sea loughs. Some such bodies of water could also be called firths, fjords, estuary, estuaries, straits or bays. Background This name for a body of water is Insular Celtic languages, Insular CelticThe current form has currency in the following languages: Scottish Gaelic, Irish language, Irish, Manx language, Manx, and has been borrowed into Scots language, Lowland Scots, Scottish English, Iri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outer Hebrides
The Outer Hebrides () or Western Isles ( gd, Na h-Eileanan Siar or or ("islands of the strangers"); sco, Waster Isles), sometimes known as the Long Isle/Long Island ( gd, An t-Eilean Fada, links=no), is an island chain off the west coast of mainland Scotland. The islands are geographically coextensive with , one of the 32 unitary council areas of Scotland. They form part of the archipelago of the Hebrides, separated from the Scottish mainland and from the Inner Hebrides by the waters of the Minch, the Little Minch, and the Sea of the Hebrides. Scottish Gaelic is the predominant spoken language, although in a few areas English speakers form a majority. Most of the islands have a bedrock formed from ancient metamorphic rocks, and the climate is mild and oceanic. The 15 inhabited islands have a total population of and there are more than 50 substantial uninhabited islands. The distance from Barra Head to the Butt of Lewis is roughly . There are various important prehisto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tide
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravity, gravitational forces exerted by the Moon (and to a much lesser extent, the Sun) and are also caused by the Earth and Moon orbiting one another. Tide tables can be used for any given locale to find the predicted times and amplitude (or "tidal range"). The predictions are influenced by many factors including the alignment of the Sun and Moon, the #Phase and amplitude, phase and amplitude of the tide (pattern of tides in the deep ocean), the amphidromic systems of the oceans, and the shape of the coastline and near-shore bathymetry (see ''#Timing, Timing''). They are however only predictions, the actual time and height of the tide is affected by wind and atmospheric pressure. Many shorelines experience semi-diurnal tides—two nearly equal high and low tides each day. Other locations have a diurnal cycle, diurnal tide—one high and low tide each day. A "mixed tide"—two uneven magnitude ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seaweed
Seaweed, or macroalgae, refers to thousands of species of macroscopic, multicellular, marine algae. The term includes some types of '' Rhodophyta'' (red), ''Phaeophyta'' (brown) and ''Chlorophyta'' (green) macroalgae. Seaweed species such as kelps provide essential nursery habitat for fisheries and other marine species and thus protect food sources; other species, such as planktonic algae, play a vital role in capturing carbon, producing at least 50% of Earth's oxygen. Natural seaweed ecosystems are sometimes under threat from human activity. For example, mechanical dredging of kelp destroys the resource and dependent fisheries. Other forces also threaten some seaweed ecosystems; a wasting disease in predators of purple urchins has led to a urchin population surge which destroyed large kelp forest regions off the coast of California. Humans have a long history of cultivating seaweeds for their uses. In recent years, seaweed farming has become a global agricultural practic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Croft (land)
A croft is a fenced or enclosed area of land, usually small and arable, and usually, but not always, with a crofter's dwelling thereon. A crofter is one who has tenure and use of the land, typically as a tenant farmer, especially in rural areas. Etymology The word ''croft'' is West Germanic in etymology and is now most familiar in Scotland, most crofts being in the Highlands and Islands area. Elsewhere the expression is generally archaic. In Scottish Gaelic, it is rendered (, plural ). Legislation in Scotland The Scottish croft is a small agricultural landholding of a type that has been subject to special legislation applying to the Scottish Highlands since 1886. The legislation was largely a response to the complaints and demands of tenant families who were victims of the Highland Clearances. The modern crofters or tenants appear very little in evidence before the beginning of the 18th century. They were tenants at will underneath the tacksman and wadsetters, but practi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
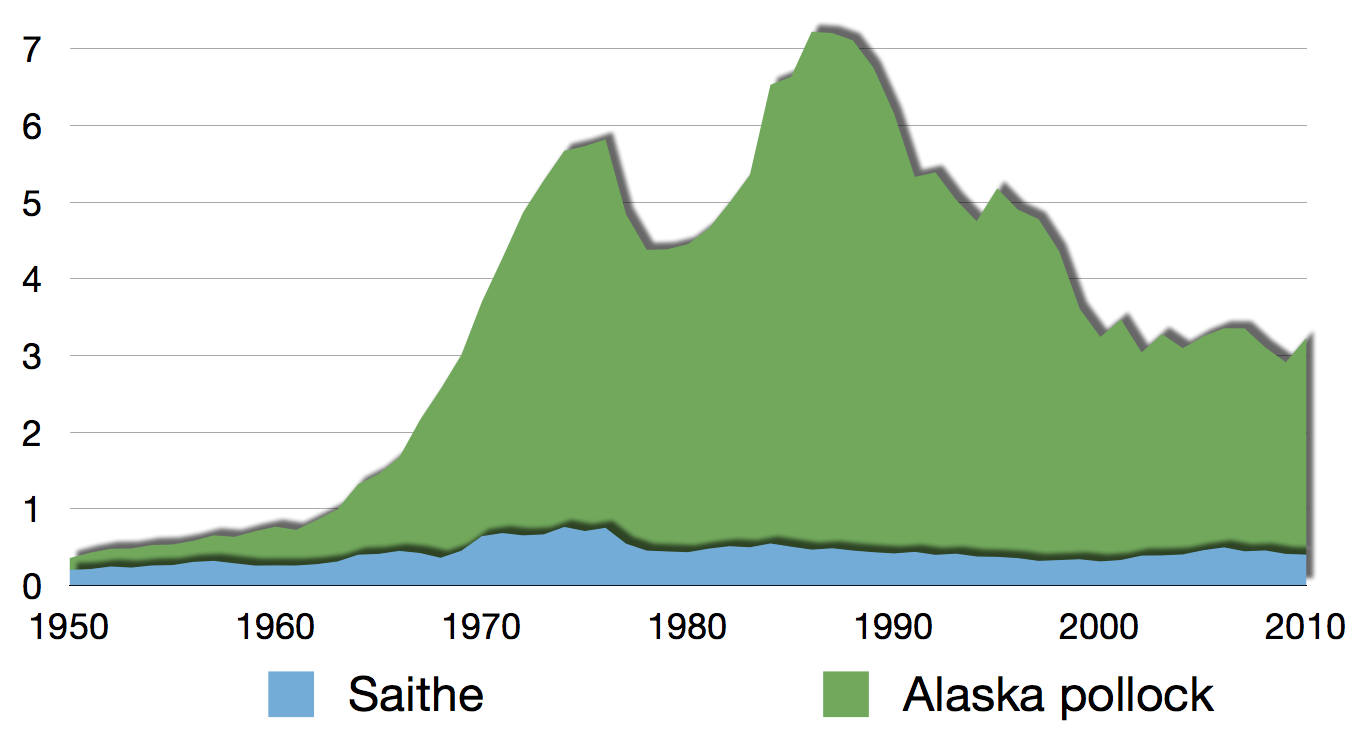
Pollock
Pollock or pollack (pronounced ) is the common name used for either of the two species of North Atlantic marine fish in the genus ''Pollachius''. ''Pollachius pollachius'' is referred to as pollock in North America, Ireland and the United Kingdom, while ''Pollachius virens'' is usually known as saithe or coley in Great Britain and Ireland (derived from the older name coalfish). Other names for ''P. pollachius'' include the Atlantic pollock, European pollock, ''lieu jaune'', and lythe; while ''P. virens'' is also known as Boston blue (distinct from bluefish), silver bill, or saithe. Species The recognized species in this genus are: * ''Pollachius pollachius'' (Linnaeus, 1758) (pollack) * ''Pollachius virens'' (Linnaeus, 1758) (coalfish) Description Both species can grow to and can weigh up to . ''P. virens'' has a strongly defined, silvery lateral line running down the sides. Above the lateral line, the colour is a greenish black. The belly is white, while '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brown Trout
The brown trout (''Salmo trutta'') is a European species of salmonid fish that has been widely introduced into suitable environments globally. It includes purely freshwater populations, referred to as the riverine ecotype, ''Salmo trutta'' morpha ''fario'', a lacustrine ecotype, ''S. trutta'' morpha ''lacustris'', also called the lake trout, and anadromous forms known as the sea trout, ''S. trutta'' morpha ''trutta''. The latter migrates to the oceans for much of its life and returns to fresh water only to spawn. Sea trout in Ireland and Britain have many regional names: sewin in Wales, finnock in Scotland, peal in the West Country, mort in North West England, and white trout in Ireland. The lacustrine morph of brown trout is most usually potamodromous, migrating from lakes into rivers or streams to spawn, although evidence indicates some stocks spawn on wind-swept shorelines of lakes. ''S. trutta'' morpha ''fario'' forms stream-resident populations, typically in alpine stre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salmon
Salmon () is the common name for several list of commercially important fish species, commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the family (biology), family Salmonidae, which are native to tributary, tributaries of the North Atlantic (genus ''Salmo'') and North Pacific (genus ''Oncorhynchus'') basin. Other closely related fish in the same family include trout, Salvelinus, char, Thymallus, grayling, Freshwater whitefish, whitefish, lenok and Hucho, taimen. Salmon are typically fish migration, anadromous: they hatch in the gravel stream bed, beds of shallow fresh water streams, migrate to the ocean as adults and live like sea fish, then return to fresh water to reproduce. However, populations of several species are restricted to fresh water throughout their lives. Folklore has it that the fish return to the exact spot where they hatched to spawn (biology), spawn, and tracking studies have shown this to be mostly true. A portion of a returning salmon run ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |