|
Bulbospongiosus
The bulbospongiosus muscle (bulbocavernosus in older texts) is one of the superficial muscles of the perineum. It has a slightly different origin, insertion and function in males and females. In males, it covers the bulb of the penis. In females, it covers the Bulb of vestibule, vestibular bulb. In both sexes, it is innervated by the deep or muscular branch of the perineal nerve, which is a branch of the pudendal nerve. Structure In males, the bulbospongiosus is located in the middle line of the perineum, in front of the anus. It consists of two symmetrical parts, united along the median line by a tendinous perineal raphe. It arises from the central tendinous point of the perineum and from the median perineal raphe in front. In females, there is no union, nor a tendinous perineal raphe; the parts are disjoint primarily and arise from the same central tendinous point of the perineum, which is the tendon that is formed at the point where the bulbospongiosus muscle, superficial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erection
An erection (clinically: penile erection or penile tumescence) is a physiological phenomenon in which the penis becomes firm, engorged, and enlarged. Penile erection is the result of a complex interaction of psychological, neural, vascular, and endocrine factors, and is often associated with sexual arousal or sexual attraction, although erections can also be spontaneous. The shape, angle, and direction of an erection varies considerably between humans. Physiologically, an erection is required for a male to effect vaginal penetration or sexual intercourse and is triggered by the parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system, causing the levels of nitric oxide (a vasodilator) to rise in the trabecular arteries and smooth muscle of the penis. The arteries dilate causing the corpora cavernosa of the penis (and to a lesser extent the corpus spongiosum) to fill with blood; simultaneously the ischiocavernosus and bulbospongiosus muscles compress the veins of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perineal Nerve
The perineal nerve is a nerve of the pelvis. It arises from the pudendal nerve in the pudendal canal. It gives superficial branches to the skin, and a deep branch to muscles. It supplies the skin and muscles of the perineum. Its latency is tested with electrodes. Structure The perineal nerve is a branch of the pudendal nerve. It lies below the internal pudendal artery. It accompanies the perineal artery. It passes through the pudendal canal for around 2 or 3 cm. Whilst still in the canal, it divides into superficial branches and a deep branch. The superficial branches of the perineal nerve become the posterior scrotal nerves in men,Essential Clinical Anatomy. K.L. Moore & A.M. Agur. Lippincott, 2 ed. 2002. Page 263 and the posterior labial nerves in women. The deep branch of the perineal nerve (also known as the "muscular" branch) travels to the muscles of the perineum. Both of these are superficial to the dorsal nerve of the penis or the dorsal nerve of the clitoris. Functi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perineal Artery
The perineal artery (superficial perineal artery) arises from the internal pudendal artery, and turns upward, crossing either over or under the superficial transverse perineal muscle, and runs forward, parallel to the pubic arch, in the interspace between the bulbospongiosus and ischiocavernosus muscles, both of which it supplies, and finally divides into several posterior scrotal branches which are distributed to the skin and dartos tunic of the scrotum. As it crosses the superficial transverse perineal muscle it gives off the ''transverse perineal artery'' which runs transversely on the cutaneous surface of the muscle, and anastomoses with the corresponding vessel of the opposite side and with the perineal and inferior hemorrhoidal arteries. It supplies the Transversus perinæi superficialis and the structures between the anus and the urethral bulb Just before each crus of the penis meets its fellow, it presents a slight enlargement, which Georg Ludwig Kobelt named the bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
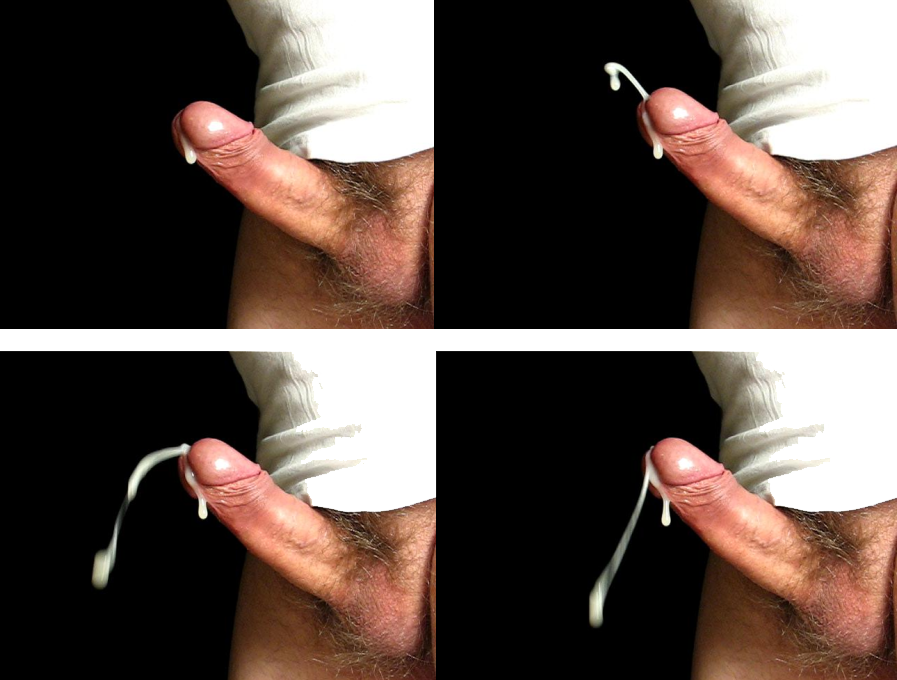
Ejaculation
Ejaculation is the discharge of semen (the ''ejaculate''; normally containing sperm) from the male reproductory tract as a result of an orgasm. It is the final stage and natural objective of male sexual stimulation, and an essential component of natural conception. In rare cases, ejaculation occurs because of prostatic disease. Ejaculation may also occur spontaneously during sleep (a nocturnal emission or "wet dream"). ''Anejaculation'' is the condition of being unable to ejaculate. Ejaculation is usually very pleasurable for men; '' dysejaculation'' is an ejaculation that is painful or uncomfortable. Retrograde ejaculation is the condition where semen travels backwards into the bladder rather than out the urethra. Phases Stimulation A usual precursor to ejaculation is the sexual arousal of the male, leading to the erection of the penis, though not every arousal nor erection leads to ejaculation. Penile sexual stimulation during masturbation or vaginal, anal, oral, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaginal Support Structures
The vaginal support structures are those muscles, bones, ligaments, tendons, membranes and fascia, of the pelvic floor that maintain the position of the vagina within the pelvic cavity and allow the normal functioning of the vagina and other reproductive structures in the female. Defects or injuries to these support structures in the pelvic floor leads to pelvic organ prolapse. Anatomical and congenital variations of vaginal support structures can predispose a woman to further dysfunction and prolapse later in life. The urethra is part of the anterior wall of the vagina and damage to the support structures there can lead to incontinence and urinary retention. Pelvic bones The support for the vagina is provided by muscles, membranes, tendons and ligaments. These structures are attached to the hip bones. These bones are the pubis, ilium and ischium. The interior surface of these pelvic bones and their projections and contours are used as attachment sites for the fascia, muscles, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perineum
The perineum in humans is the space between the anus and scrotum in the male, or between the anus and the vulva in the female. The perineum is the region of the body between the pubic symphysis (pubic arch) and the coccyx (tail bone), including the perineal body and surrounding structures. There is some variability in how the boundaries are defined. The perineal raphe is visible and pronounced to varying degrees. The perineum is an erogenous zone. The word perineum entered English from late Latin via Greek περίναιος ~ περίνεος ''perinaios, perineos'', itself from περίνεος, περίνεοι 'male genitals' and earlier περίς ''perís'' 'penis' through influence from πηρίς ''pērís'' 'scrotum'. The term was originally understood as a purely male body-part with the perineal raphe seen as a continuation of the scrotal septum since masculinization causes the development of a large anogenital distance in men, in comparison to the corresponding lack ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urination
Urination, also known as micturition, is the release of urine from the urinary bladder through the urethra to the outside of the body. It is the urinary system's form of excretion. It is also known medically as micturition, voiding, uresis, or, rarely, emiction, and known colloquially by various names including peeing, weeing, and pissing. In healthy humans (and many other animals), the process of urination is under voluntary control. In infants, some elderly individuals, and those with neurological injury, urination may occur as a reflex. It is normal for adult humans to urinate up to seven times during the day. In some animals, in addition to expelling waste material, urination can mark territory or express submissiveness. Physiologically, urination involves coordination between the central, autonomic, and somatic nervous systems. Brain centres that regulate urination include the pontine micturition center, periaqueductal gray, and the cerebral cortex. In placental ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pudendal Nerve
The pudendal nerve is the main nerve of the perineum. It carries sensation from the external genitalia of both sexes and the skin around the anus and perineum, as well as the motor supply to various pelvic muscles, including the male or female external urethral sphincter and the external anal sphincter. If damaged, most commonly by childbirth, lesions may cause sensory loss or fecal incontinence. The nerve may be temporarily blocked as part of an anaesthetic procedure. The pudendal canal that carries the pudendal nerve is also known by the eponymous term "Alcock's canal", after Benjamin Alcock, an Irish anatomist who documented the canal in 1836. Structure The pudendal nerve is paired, meaning there are two nerves, one on the left and one on the right side of the body. Each is formed as three roots immediately converge above the upper border of the sacrotuberous ligament and the coccygeus muscle. The three roots become two cords when the middle and lower root join to fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
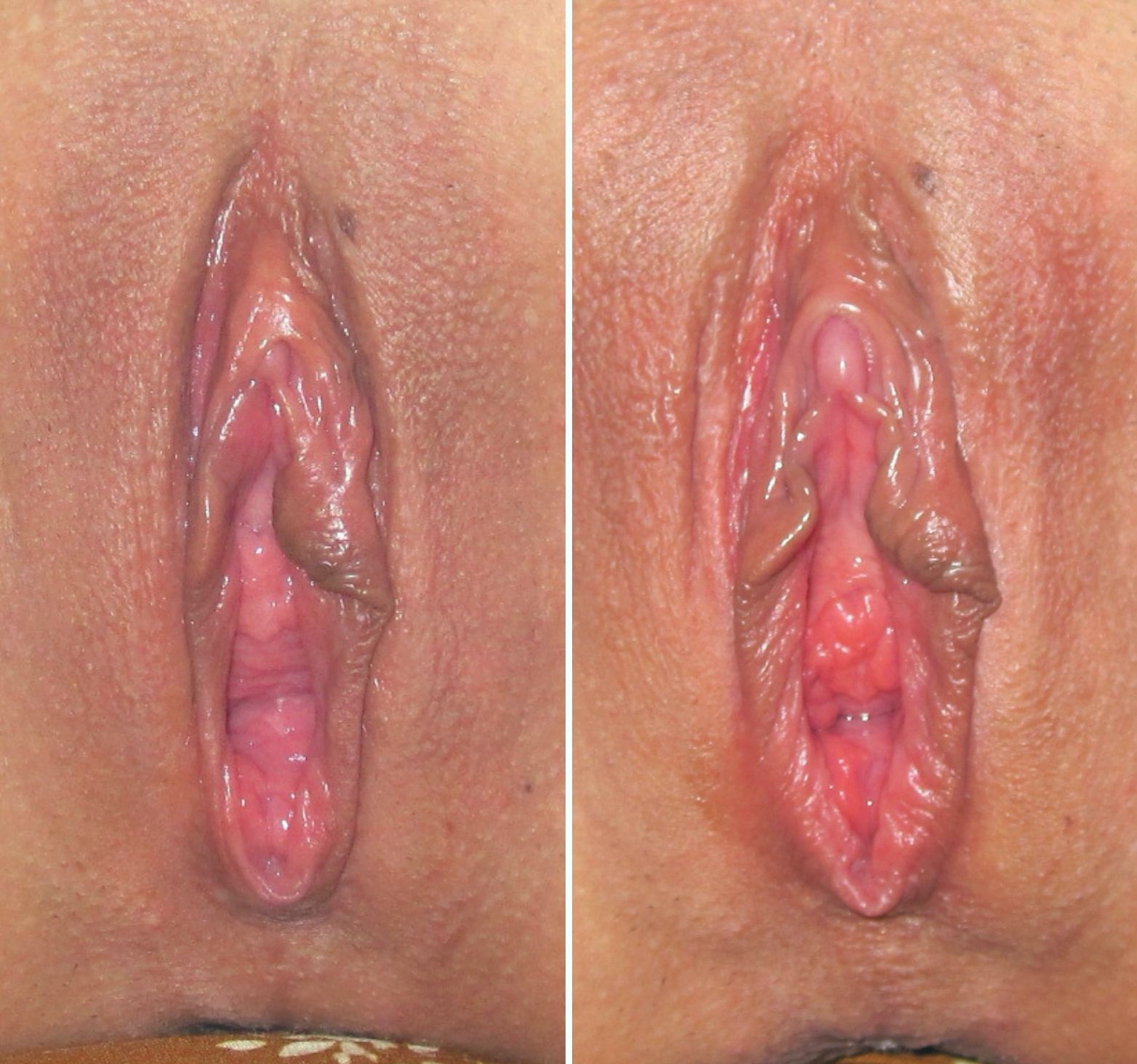
Clitoral Erection
Clitoral erection is a physiological phenomenon where the clitoris becomes enlarged and firm. Clitoral erection is the result of a complex interaction of psychological, neural, vascular, and endocrine factors, and is usually, though not exclusively, associated with sexual arousal. Erections should eventually subside, and the prolonged state of clitoral erection even while not aroused is a condition that could become painful. This swelling and shrinking to a relaxed state seems linked to nitric oxide's effects on tissues in the clitoris, similar to its role in penile erection. Physiology The clitoris is the homologue of the penis in the female. Similarly, the clitoris and the erection of it can subtly differ in size. The visible part of the clitoris, the glans clitoridis, varies in size from a few millimeters to one centimeter and is located at the front junction of the labia minora (inner lips), above the opening of the urethra. It is covered by the clitoral hood. Any t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transverse Perineal Muscles
The transverse perineal muscles (transversus perinei) are the superficial and the deep transverse perineal muscles. Superficial transverse perineal The superficial transverse perineal muscle (transversus superficialis perinei or Lloyd-Beanie muscle) is a narrow muscular slip, which passes more or less transversely across the perineal space in front of the anus. It arises by tendinous fibers from the inner and forepart of the ischial tuberosity and, running medially, is inserted into the central tendinous point of the perineum (perineal body), joining in this situation with the muscle of the opposite side, with the external anal sphincter muscle behind, and with the bulbospongiosus muscle in front. In some cases, the fibers of the deeper layer of the external anal sphincter cross over in front of the anus and are continued into this mus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pudendal Nerve
The pudendal nerve is the main nerve of the perineum. It carries sensation from the external genitalia of both sexes and the skin around the anus and perineum, as well as the motor supply to various pelvic muscles, including the male or female external urethral sphincter and the external anal sphincter. If damaged, most commonly by childbirth, lesions may cause sensory loss or fecal incontinence. The nerve may be temporarily blocked as part of an anaesthetic procedure. The pudendal canal that carries the pudendal nerve is also known by the eponymous term "Alcock's canal", after Benjamin Alcock, an Irish anatomist who documented the canal in 1836. Structure The pudendal nerve is paired, meaning there are two nerves, one on the left and one on the right side of the body. Each is formed as three roots immediately converge above the upper border of the sacrotuberous ligament and the coccygeus muscle. The three roots become two cords when the middle and lower root join to fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orgasm
Orgasm (from Greek , ; "excitement, swelling") or sexual climax is the sudden discharge of accumulated sexual excitement during the sexual response cycle, resulting in rhythmic, involuntary muscular contractions in the pelvic region characterized by sexual pleasure.Se133–135 for orgasm information, anpage 76for G-spot and vaginal nerve ending information. Experienced by males and females, orgasms are controlled by the involuntary or autonomic nervous system. They are usually associated with involuntary actions, including muscular spasms in multiple areas of the body, a general euphoric sensation and, frequently, body movements and vocalizations. The period after orgasm (known as the refractory period) is typically a relaxing experience, attributed to the release of the neurohormones oxytocin and prolactin as well as endorphins (or "endogenous morphine"). Human orgasms usually result from physical sexual stimulation of the penis in males (typically accompanying ejaculat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |