|
Buccal Artery
The buccal artery (buccinator artery) is a small artery in the head. It branches off the second part of the maxillary artery and supplies the cheek and buccinator muscle. Course It runs obliquely forward, between the pterygoideus internus and the insertion of the temporalis, to the outer surface of the buccinator, to which it is distributed, anastomosing with branches of the facial artery and with the infraorbital. From the infraorbital area, it descends bilaterally in the superficial face along the lateral margin of the nose, then running anti-parallel to the facial artery The facial artery (external maxillary artery in older texts) is a branch of the external carotid artery that supplies structures of the superficial face. Structure The facial artery arises in the carotid triangle from the external carotid arte ... across the lateral oral region. Additional images file:Gray508.png, The arteries of the face and scalp. References External links * () {{Authority ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
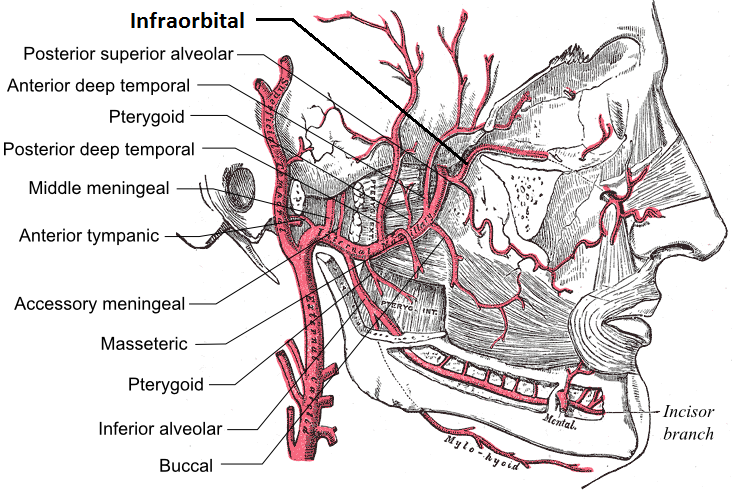
Maxillary Artery
The maxillary artery supplies deep structures of the face. It branches from the external carotid artery just deep to the neck of the mandible. Structure The maxillary artery, the larger of the two terminal branches of the external carotid artery, arises behind the neck of the mandible, and is at first imbedded in the substance of the parotid gland; it passes forward between the ramus of the mandible and the sphenomandibular ligament, and then runs, either superficial or deep to the lateral pterygoid muscle, to the pterygopalatine fossa. It supplies the deep structures of the face, and may be divided into mandibular, pterygoid, and pterygopalatine portions. First portion The ''first'' or ''mandibular '' or ''bony'' portion passes horizontally forward, between the neck of the mandible and the sphenomandibular ligament, where it lies parallel to and a little below the auriculotemporal nerve; it crosses the inferior alveolar nerve, and runs along the lower border of the lateral pte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxillary Artery
The maxillary artery supplies deep structures of the face. It branches from the external carotid artery just deep to the neck of the mandible. Structure The maxillary artery, the larger of the two terminal branches of the external carotid artery, arises behind the neck of the mandible, and is at first imbedded in the substance of the parotid gland; it passes forward between the ramus of the mandible and the sphenomandibular ligament, and then runs, either superficial or deep to the lateral pterygoid muscle, to the pterygopalatine fossa. It supplies the deep structures of the face, and may be divided into mandibular, pterygoid, and pterygopalatine portions. First portion The ''first'' or ''mandibular '' or ''bony'' portion passes horizontally forward, between the neck of the mandible and the sphenomandibular ligament, where it lies parallel to and a little below the auriculotemporal nerve; it crosses the inferior alveolar nerve, and runs along the lower border of the lateral pte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheek
The cheeks ( la, buccae) constitute the area of the face below the eyes and between the nose and the left or right ear. "Buccal" means relating to the cheek. In humans, the region is innervated by the buccal nerve. The area between the inside of the cheek and the teeth and gums is called the vestibule or buccal pouch or buccal cavity and forms part of the mouth. In other animals the cheeks may also be referred to as jowls. Structure Humans Cheeks are fleshy in humans, the skin being suspended by the chin and the jaws, and forming the lateral wall of the human mouth, visibly touching the cheekbone below the eye. The inside of the cheek is lined with a mucous membrane (buccal mucosa, part of the oral mucosa). During mastication (chewing), the cheeks and tongue between them serve to keep the food between the teeth. Other animals The cheeks are covered externally by hairy skin, and internally by stratified squamous epithelium. This is mostly smooth, but may have caudally di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buccinator Muscle
The buccinator () is a thin quadrilateral muscle occupying the interval between the maxilla and the mandible at the side of the face. It forms the anterior part of the cheek or the lateral wall of the oral cavity.Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck, Fehrenbach and Herring, Elsevier, 2012, page 91 Structure It arises from the outer surfaces of the alveolar processes of the maxilla and mandible, corresponding to the three pairs of molar teeth and in the mandible, it is attached upon the buccinator crest posterior to the third molar; and behind, from the anterior border of the pterygomandibular raphe which separates it from the constrictor pharyngis superior. The fibers converge toward the angle of the mouth, where the central fibers intersect each other, those from below being continuous with the upper segment of the orbicularis oris, and those from above with the lower segment; the upper and lower fibers are continued forward into the corresponding lip without decussation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artery
An artery (plural arteries) () is a blood vessel in humans and most animals that takes blood away from the heart to one or more parts of the body (tissues, lungs, brain etc.). Most arteries carry oxygenated blood; the two exceptions are the pulmonary and the umbilical arteries, which carry deoxygenated blood to the organs that oxygenate it (lungs and placenta, respectively). The effective arterial blood volume is that extracellular fluid which fills the arterial system. The arteries are part of the circulatory system, that is responsible for the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all cells, as well as the removal of carbon dioxide and waste products, the maintenance of optimum blood pH, and the circulation of proteins and cells of the immune system. Arteries contrast with veins, which carry blood back towards the heart. Structure The anatomy of arteries can be separated into gross anatomy, at the macroscopic level, and microanatomy, which must be studied with a microscop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Head
In human anatomy, the head is at the top of the human body. It supports the face and is maintained by the skull, which itself encloses the brain. Structure The human head consists of a fleshy outer portion, which surrounds the bony skull. The brain is enclosed within the skull. There are 22 bones in the human head. The head rests on the neck, and the seven cervical vertebrae support it. The human head typically weighs between Over 98% of humans fit into this range. There have been odd incidences where human beings have abnormally small or large heads. The Zika virus was responsible for underdeveloped heads in the early 2000s. The face is the anterior part of the head, containing the eyes, nose, and mouth. On either side of the mouth, the cheeks provide a fleshy border to the oral cavity. The ears sit to either side of the head. Blood supply The head receives blood supply through the internal and external carotid arteries. These supply the area outside of the skull ( e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheek
The cheeks ( la, buccae) constitute the area of the face below the eyes and between the nose and the left or right ear. "Buccal" means relating to the cheek. In humans, the region is innervated by the buccal nerve. The area between the inside of the cheek and the teeth and gums is called the vestibule or buccal pouch or buccal cavity and forms part of the mouth. In other animals the cheeks may also be referred to as jowls. Structure Humans Cheeks are fleshy in humans, the skin being suspended by the chin and the jaws, and forming the lateral wall of the human mouth, visibly touching the cheekbone below the eye. The inside of the cheek is lined with a mucous membrane (buccal mucosa, part of the oral mucosa). During mastication (chewing), the cheeks and tongue between them serve to keep the food between the teeth. Other animals The cheeks are covered externally by hairy skin, and internally by stratified squamous epithelium. This is mostly smooth, but may have caudally di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pterygoideus Internus
The medial pterygoid muscle (or internal pterygoid muscle), is a thick, quadrilateral muscle of the face. It is supplied by the mandibular branch of the trigeminal nerve (V). It is important in mastication (chewing). Structure The medial pterygoid muscle consists of two heads. The bulk of the muscle arises as a deep head from just above the medial surface of the lateral pterygoid plate. The smaller, superficial head originates from the maxillary tuberosity and the pyramidal process of the palatine bone. Its fibers pass downward, lateral, and posterior, and are inserted, by a strong tendinous lamina, into the lower and back part of the medial surface of the ramus and angle of the mandible, as high as the mandibular foramen. The insertion joins the masseter muscle to form a common tendinous sling which allows the medial pterygoid and masseter to be powerful elevators of the jaw. Nerve supply The medial pterygoid muscle is supplied by the medial pterygoid nerve, a branch of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temporalis
In anatomy, the temporalis muscle, also known as the temporal muscle, is one of the muscles of mastication (chewing). It is a broad, fan-shaped convergent muscle on each side of the head that fills the temporal fossa, superior to the zygomatic arch so it covers much of the temporal bone.Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck, Fehrenbach and Herring, Elsevier, 2012, page 98''Temporal'' refers to the head's temples. Structure In humans, the temporalis muscle arises from the temporal fossa and the deep part of temporal fascia. This is a very broad area of attachment. It passes medial to the zygomatic arch. It forms a tendon which inserts onto the coronoid process of the mandible, with its insertion extending into the retromolar fossa posterior to the most distal mandibular molar.Human Anatomy, Jacobs, Elsevier, 2008, page 194 In other mammals, the muscle usually spans the dorsal part of the skull all the way up to the medial line. There, it may be attached to a sagittal crest, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buccinator
The buccinator () is a thin quadrilateral muscle occupying the interval between the maxilla and the mandible at the side of the face. It forms the anterior part of the cheek or the lateral wall of the oral cavity.Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck, Fehrenbach and Herring, Elsevier, 2012, page 91 Structure It arises from the outer surfaces of the alveolar processes of the maxilla and mandible, corresponding to the three pairs of molar teeth and in the mandible, it is attached upon the buccinator crest posterior to the third molar; and behind, from the anterior border of the pterygomandibular raphe which separates it from the constrictor pharyngis superior. The fibers converge toward the angle of the mouth, where the central fibers intersect each other, those from below being continuous with the upper segment of the orbicularis oris, and those from above with the lower segment; the upper and lower fibers are continued forward into the corresponding lip without decussation. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Facial Artery
The facial artery (external maxillary artery in older texts) is a branch of the external carotid artery that supplies structures of the superficial face. Structure The facial artery arises in the carotid triangle from the external carotid artery, a little above the lingual artery and, sheltered by the ramus of the mandible. It passes obliquely up beneath the digastric and stylohyoid muscles, over which it arches to enter a groove on the posterior surface of the submandibular gland. It then curves upward over the body of the mandible at the antero-inferior angle of the masseter; passes forward and upward across the cheek to the angle of the mouth, then ascends along the side of the nose, and ends at the medial commissure of the eye, under the name of the angular artery. The facial artery is remarkably tortuous. This is to accommodate itself to neck movements such as those of the pharynx in deglutition; and facial movements such as those of the mandible, lips, and cheeks. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infraorbital Artery
The infraorbital artery is an artery in the head that branches off the maxillary artery, emerging through the infraorbital foramen, just under the orbit of the eye. Course The infraorbital artery appears, from its direction, to be the continuation of the trunk of the maxillary artery, but often arises in conjunction with the posterior superior alveolar artery. It runs along the infraorbital groove and canal with the infraorbital nerve, and emerges on the face through the infraorbital foramen, beneath the infraorbital head of the levator labii superioris muscle. Branches While in the canal, it gives off * (a) orbital branches which assist in supplying the inferior rectus and inferior oblique and the lacrimal sac, and * (b) anterior superior alveolar arteries - branches which descend through the anterior alveolar canals to supply the upper incisor and canine teeth and the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinus. On the face, some branches pass upward to the medial angle of the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |