|
Bubble Point
In thermodynamics, the bubble point is the temperature (at a given pressure) where the first bubble of vapor is formed when heating a liquid consisting of two or more components. Given that vapor will probably have a different composition than the liquid, the bubble point (along with the dew point) at different compositions are useful data when designing distillation systems. For a single component the bubble point and the dew point are the same and are referred to as the boiling point. Calculating the bubble point At the bubble point, the following relationship holds: :\sum_^ y_i = \sum_^ K_i x_i = 1 where :K_i \equiv \frac. K is the ''distribution coefficient'' or ''K factor'', defined as the ratio of mole fraction in the vapor phase \big(y_\big) to the mole fraction in the liquid phase \big(x_\big) at equilibrium. When Raoult's law and Dalton's law hold for the mixture, the K factor is defined as the ratio of the vapor pressure to the total pressure of the system: :K_i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary Boiling Point Diagram New
Binary may refer to: Science and technology Mathematics * Binary number, a representation of numbers using only two digits (0 and 1) * Binary function, a function that takes two arguments * Binary operation, a mathematical operation that takes two arguments * Binary relation, a relation involving two elements * Binary-coded decimal, a method for encoding for decimal digits in binary sequences * Finger binary, a system for counting in binary numbers on the fingers of human hands Computing * Binary code, the digital representation of text and data * Bit, or binary digit, the basic unit of information in computers * Binary file, composed of something other than human-readable text ** Executable, a type of binary file that contains machine code for the computer to execute * Binary tree, a computer tree data structure in which each node has at most two children Astronomy * Binary star, a star system with two stars in it * Binary planet, two planetary bodies of comparable ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boiling Point
The boiling point of a substance is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid equals the pressure surrounding the liquid and the liquid changes into a vapor. The boiling point of a liquid varies depending upon the surrounding environmental pressure. A liquid in a partial vacuum has a lower boiling point than when that liquid is at atmospheric pressure. A liquid at low pressure has a lower boiling point than when that liquid is at atmospheric pressure. Because of this, water boils at under standard pressure at sea level, but at at altitude. For a given pressure, different liquids will boiling, boil at different temperatures. The normal boiling point (also called the atmospheric boiling point or the atmospheric pressure boiling point) of a liquid is the special case in which the vapor pressure of the liquid equals the defined atmospheric pressure at sea level, one Atmosphere (unit), atmosphere. At that temperature, the vapor pressure of the liquid becomes suffici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measured with a thermometer. Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied on various reference points and thermometric substances for definition. The most common scales are the Celsius scale with the unit symbol °C (formerly called ''centigrade''), the Fahrenheit scale (°F), and the Kelvin scale (K), the latter being used predominantly for scientific purposes. The kelvin is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units (SI). Absolute zero, i.e., zero kelvin or −273.15 °C, is the lowest point in the thermodynamic temperature scale. Experimentally, it can be approached very closely but not actually reached, as recognized in the third law of thermodynamics. It would be impossible to extract energy as heat from a body at that temperature. Temperature is important in all fields of natur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dew Point
The dew point is the temperature to which air must be cooled to become saturated with water vapor, assuming constant air pressure and water content. When cooled below the dew point, moisture capacity is reduced and airborne water vapor will condense to form liquid water known as dew. When this occurs via contact with a colder surface, dew will form on that surface. The dew point is affected by humidity. When there is more moisture in the air, the dew point is higher. When the temperature is below the freezing point of water, the dew point is called the frost point, as frost is formed via deposition rather than condensation. In liquids, the analog to the dew point is the cloud point. Humidity If all the other factors influencing humidity remain constant, at ground level the relative humidity rises as the temperature falls; this is because less vapor is needed to saturate the air. In normal conditions, the dew point temperature will not be greater than the air temperature, sinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
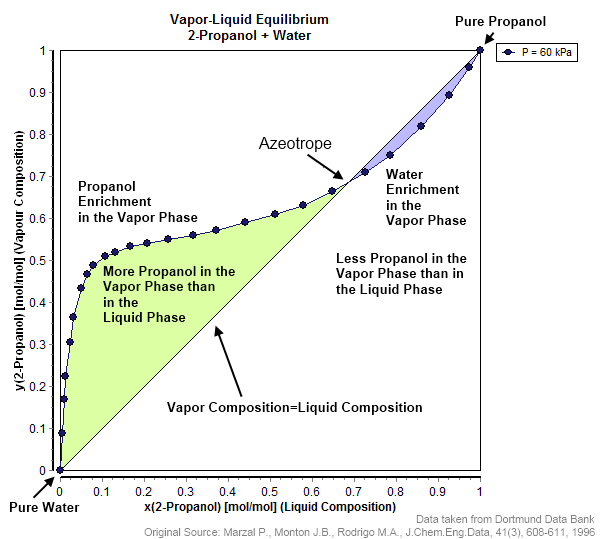
Azeotrope
An azeotrope () or a constant heating point mixture is a mixture of two or more liquids whose proportions cannot be altered or changed by simple distillation.Moore, Walter J. ''Physical Chemistry'', 3rd e Prentice-Hall 1962, pp. 140–142 This happens when an azeotrope is boiled, the vapour has the same proportions of constituents as the unboiled mixture. Because their composition is unchanged by distillation, azeotropes are also called (especially in older texts) ''constant boiling point mixtures''. Some azeotropic mixtures of pairs of compounds are known, and many azeotropes of three or more compounds are also known. In such a case it is not possible to separate the components by fractional distillation and azeotropic distillation is usually used instead. There are two types of azeotropes: minimum boiling azeotrope and maximum boiling azeotrope. A Solution (chemistry), solution that shows greater positive deviation from Raoult's law forms a minimum boiling azeotrope at a speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase Diagram
A phase diagram in physical chemistry, engineering, mineralogy, and materials science is a type of chart used to show conditions (pressure, temperature, volume, etc.) at which thermodynamically distinct phases (such as solid, liquid or gaseous states) occur and coexist at equilibrium. Overview Common components of a phase diagram are ''lines of equilibrium'' or ''phase boundaries'', which refer to lines that mark conditions under which multiple phases can coexist at equilibrium. Phase transitions occur along lines of equilibrium. Metastable phases are not shown in phase diagrams as, despite their common occurrence, they are not equilibrium phases. Triple points are points on phase diagrams where lines of equilibrium intersect. Triple points mark conditions at which three different phases can coexist. For example, the water phase diagram has a triple point corresponding to the single temperature and pressure at which solid, liquid, and gaseous water can coexist in a stabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dalton's Law
Dalton's law (also called Dalton's law of partial pressures) states that in a mixture of non-reacting gases, the total pressure exerted is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of the individual gases. This empirical law was observed by John Dalton in 1801 and published in 1802.J. Dalton (1802)"Essay IV. On the expansion of elastic fluids by heat,"''Memoirs of the Literary and Philosophical Society of Manchester'', vol. 5, pt. 2, pages 595–602; see page 600. Dalton's law is related to the ideal gas laws. Formula Mathematically, the pressure of a mixture of non-reactive gases can be defined as the summation: p_\text = \sum_^n p_i = p_1+p_2+p_3+\cdots+p_n where ''p''1, ''p''2, ..., ''pn'' represent the partial pressures of each component. p_ = p_\text x_i where ''xi'' is the mole fraction of the ''i''th component in the total mixture of ''n'' components . Volume-based concentration The relationship below provides a way to determine the volume-based concentration of any ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perry's Chemical Engineers' Handbook
''Perry's Chemical Engineers' Handbook'' (also known as ''Perry's Handbook'', ''Perry's'', or ''The Chemical Engineer's Bible'') was first published in 1934 and the most current ninth edition was published in July 2018. It has been a source of chemical engineering knowledge for chemical engineers, and a wide variety of other engineers and scientists, through eight previous editions spanning more than 80 years. Subjects The subjects covered in the book include: physical properties of chemicals and other materials; mathematics; thermodynamics; heat transfer; mass transfer; fluid dynamics; chemical reactors and chemical reaction kinetics; transport and storage of fluid; heat transfer equipment; psychrometry and evaporative cooling; distillation; gas absorption; liquid-liquid extraction; adsorption and ion exchange; gas–solid, liquid–solid and solid–solid operations; biochemical engineering; waste management, materials of construction, process economics and cost estimation; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics is a branch of physics that deals with heat, work, and temperature, and their relation to energy, entropy, and the physical properties of matter and radiation. The behavior of these quantities is governed by the four laws of thermodynamics which convey a quantitative description using measurable macroscopic physical quantities, but may be explained in terms of microscopic constituents by statistical mechanics. Thermodynamics applies to a wide variety of topics in science and engineering, especially physical chemistry, biochemistry, chemical engineering and mechanical engineering, but also in other complex fields such as meteorology. Historically, thermodynamics developed out of a desire to increase the efficiency of early steam engines, particularly through the work of French physicist Sadi Carnot (1824) who believed that engine efficiency was the key that could help France win the Napoleonic Wars. Scots-Irish physicist Lord Kelvin was the first to formulate a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dew Point
The dew point is the temperature to which air must be cooled to become saturated with water vapor, assuming constant air pressure and water content. When cooled below the dew point, moisture capacity is reduced and airborne water vapor will condense to form liquid water known as dew. When this occurs via contact with a colder surface, dew will form on that surface. The dew point is affected by humidity. When there is more moisture in the air, the dew point is higher. When the temperature is below the freezing point of water, the dew point is called the frost point, as frost is formed via deposition rather than condensation. In liquids, the analog to the dew point is the cloud point. Humidity If all the other factors influencing humidity remain constant, at ground level the relative humidity rises as the temperature falls; this is because less vapor is needed to saturate the air. In normal conditions, the dew point temperature will not be greater than the air temperature, sinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unit Operations Of Chemical Engineering
''Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering'', first published in 1956, is one of the oldest chemical engineering textbooks still in widespread use. The current Seventh Edition, published in 2004, continues its successful tradition of being used as a textbook in university undergraduate chemical engineering courses. It is widely used in colleges and universities throughout the world, and often referred just "McCabe-Smith-Harriott" or "MSH". Subjects covered in the book The book starts with an introductory chapter devoted to definitions and principles. It then follows with 28 additional chapters, each covering a principal chemical engineering unit operation. The 28 chapters are grouped into four major sections: * Fluid mechanics * Heat transfer * Mass transfer and equilibrium stages * Operations involving particulate solids. A more detailed table of contents is available on the Internet. See also *Chemical engineer * :Unit operations *''Distillation Design'' *Perry's Chemical E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |