|
Broadleaf Plantain
''Plantago major'', the broadleaf plantain, white man's footprint, waybread, or greater plantain, is a species of flowering plant in the plantain family Plantaginaceae. The plant is native to Eurasia. The young, tender leaves can be eaten raw, and the older, stringier leaves can be boiled in stews and eaten. Description ''Plantago major'' is a herbaceous, perennial plant with a rosette of leaves in diameter.Blamey, M. & Grey-Wilson, C. (1989). ''Flora of Britain and Northern Europe''. Each leaf is oval-shaped, long and broad, rarely up to long and broad, with an acute apex, a smooth margin, and a distinct petiole almost as long as the leaf itself. There are five to nine conspicuous veins over the length of the leaf. The flowers are small, greenish-brown with purple stamens, produced in a dense spike long on top of a stem tall and rarely to tall. Plantain is wind-pollinated and propagates primarily by seeds, which are held on the long, narrow spikes which rise well a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming organisms. He is known as the "father of modern taxonomy". Many of his writings were in Latin; his name is rendered in Latin as and, after his 1761 ennoblement, as . Linnaeus was born in Råshult, the countryside of Småland, in southern Sweden. He received most of his higher education at Uppsala University and began giving lectures in botany there in 1730. He lived abroad between 1735 and 1738, where he studied and also published the first edition of his ' in the Netherlands. He then returned to Sweden where he became professor of medicine and botany at Uppsala. In the 1740s, he was sent on several journeys through Sweden to find and classify plants and animals. In the 1750s and 1760s, he continued to collect an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naturalisation (biology)
Naturalisation (or naturalization) is the ecological phenomenon through which a species, taxon, or population of exotic (as opposed to native) origin integrates into a given ecosystem, becoming capable of reproducing and growing in it, and proceeds to disseminate spontaneously. In some instances, the presence of a species in a given ecosystem is so ancient that it cannot be presupposed whether it is native or introduced. Generally, any introduced species may (in the wild) either go extinct or naturalise in its new environment. Some populations do not sustain themselves reproductively, but exist because of continued influx from elsewhere. Such a non-sustaining population, or the individuals within it, are said to be adventive. Cultivated plants are a major source of adventive populations. The above refers to ''naturalize'' as an intransitive verb, as in, "The species naturalized". In North America it is common to use ''naturalize'' as a transitive verb, as in, "City staff nat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garden
A garden is a planned space, usually outdoors, set aside for the cultivation, display, and enjoyment of plants and other forms of nature. The single feature identifying even the wildest wild garden is ''control''. The garden can incorporate both natural and artificial materials. Gardens often have design features including statuary, follies, pergolas, trellises, stumperies, dry creek beds, and water features such as fountains, ponds (with or without fish), waterfalls or creeks. Some gardens are for ornamental purposes only, while others also produce food crops, sometimes in separate areas, or sometimes intermixed with the ornamental plants. Food-producing gardens are distinguished from farms by their smaller scale, more labor-intensive methods, and their purpose (enjoyment of a hobby or self-sustenance rather than producing for sale, as in a market garden). Flower gardens combine plants of different heights, colors, textures, and fragrances to create interest and delight the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ornamental Plant
Ornamental plants or garden plants are plants that are primarily grown for their beauty but also for qualities such as scent or how they shape physical space. Many flowering plants and garden varieties tend to be specially bred cultivars that improve on the original species in qualities such as color, shape, scent, and long-lasting blooms. There are many examples of fine ornamental plants that can provide height, privacy, and beauty for any garden. These ornamental perennial plants have seeds that allow them to reproduce. One of the beauties of ornamental grasses is that they are very versatile and low maintenance. Almost any types of plant have ornamental varieties: trees, shrubs, climbers, grasses, succulents. aquatic plants, herbaceous perennials and annual plants. Non-botanical classifications include houseplants, bedding plants, hedges, plants for cut flowers and foliage plants. The cultivation of ornamental plants comes under floriculture and tree nurseries, which is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cultivar
A cultivar is a type of cultivated plant that people have selected for desired traits and when propagated retain those traits. Methods used to propagate cultivars include: division, root and stem cuttings, offsets, grafting, tissue culture, or carefully controlled seed production. Most cultivars arise from purposeful human manipulation, but some originate from wild plants that have distinctive characteristics. Cultivar names are chosen according to rules of the International Code of Nomenclature for Cultivated Plants (ICNCP), and not all cultivated plants qualify as cultivars. Horticulturists generally believe the word ''cultivar''''Cultivar'' () has two meanings, as explained in ''Formal definition'': it is a classification category and a taxonomic unit within the category. When referring to a taxon, the word does not apply to an individual plant but to all plants that share the unique characteristics that define the cultivar. was coined as a term meaning "cultivated variety ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Braid
A braid (also referred to as a plait) is a complex structure or pattern formed by interlacing two or more strands of flexible material such as textile yarns, wire, or hair. The simplest and most common version is a flat, solid, three-stranded structure. More complex patterns can be constructed from an arbitrary number of strands to create a wider range of structures (such as a fishtail braid, a five-stranded braid, rope braid, a French braid and a waterfall braid). The structure is usually long and narrow with each component strand functionally equivalent in zigzagging forward through the overlapping mass of the others. It can be compared with the process of weaving, which usually involves two separate perpendicular groups of strands ( warp and weft). Historically, the materials used have depended on the indigenous plants and animals available in the local area. During the Industrial Revolution, mechanized braiding equipment was invented to increase production. The braiding t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
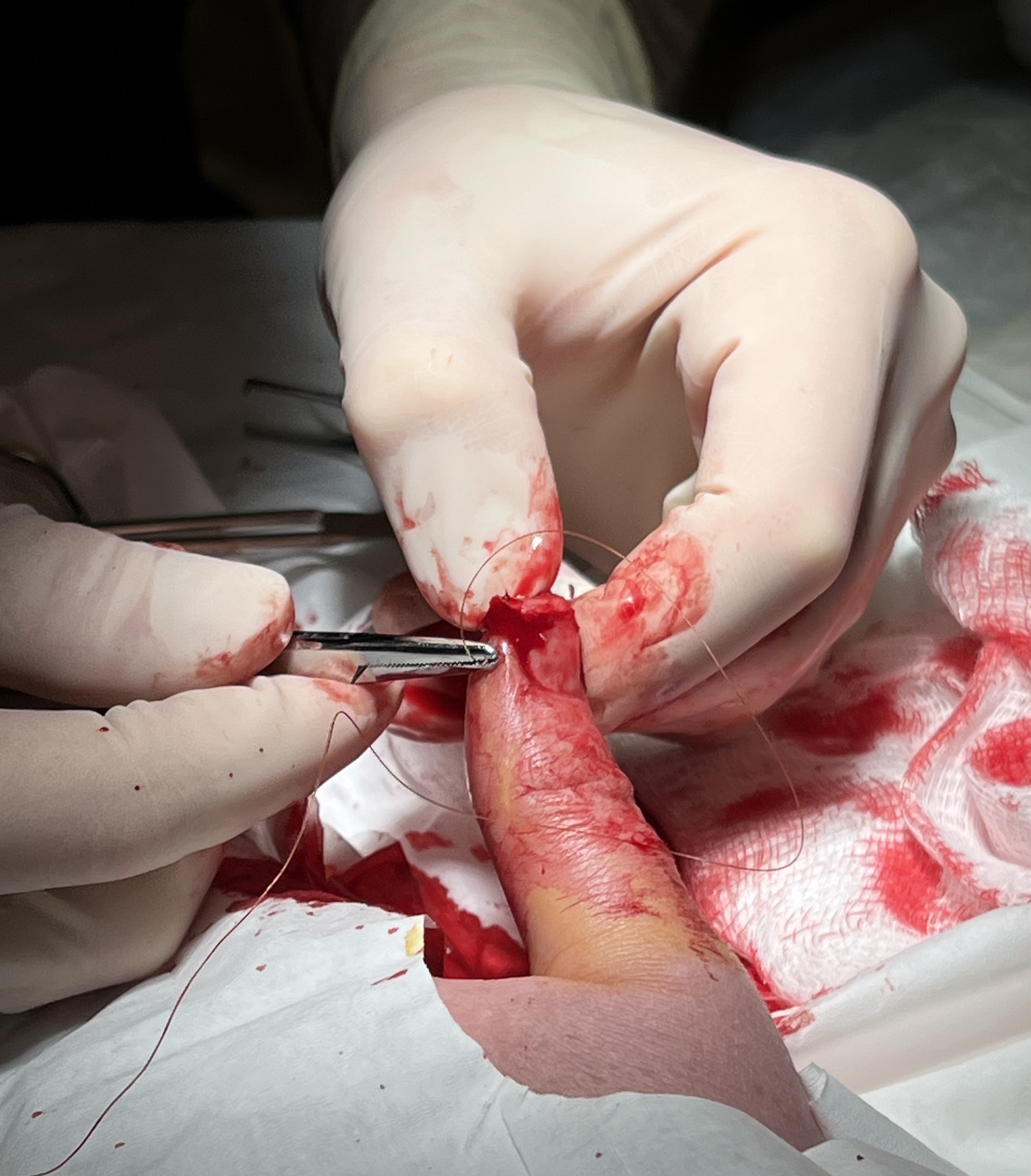
Surgical Suture
A surgical suture, also known as a stitch or stitches, is a medical device used to hold body tissues together and approximate wound edges after an injury or surgery. Application generally involves using a needle with an attached length of thread. There are numerous types of suture which differ by needle shape and size as well as thread material and characteristics. Selection of surgical suture should be determined by the characteristics and location of the wound or the specific body tissues being approximated. In selecting the needle, thread, and suturing technique to use for a specific patient, a medical care provider must consider the tensile strength of the specific suture thread needed to efficiently hold the tissues together depending on the mechanical and shear forces acting on the wound as well as the thickness of the tissue being approximated. One must also consider the elasticity of the thread and ability to adapt to different tissues, as well as the memory of the threa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fishing Line
A fishing line is a flexible, high-tensile cord used in angling to tether and pull in fish, in conjunction with at least one hook. Fishing lines are usually pulled by and stored in a reel, but can also be retrieved by hand, with a fixed attachment to the end of a rod, or via a motor. Fishing lines generally resemble a long, ultra-thin rope, with important attributes including length, material, weight and thickness. Other factors relevant to certain fishing environments include breaking strength, knot strength, UV resistance, castability, limpness, stretch, abrasion resistance, and visibility. Traditional fishing lines are made of silk, while most modern lines are made from synthetic polymers such as nylon, polyethylene or polyvinylidene fluoride ("fluorocarbon") and may come in monofilament or braided ( multifilament) forms. Terminology Fishing with a hook-and-line setup is called angling. Fish are caught when one are drawn by the bait/ lure dressed on the hook into swallow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiber Crop
Fiber crops are field crops grown for their fibers, which are traditionally used to make paper, cloth, or rope. Fiber crops are characterized by having a large concentration of cellulose, which is what gives them their strength. The fibers may be chemically modified, like in viscose (used to make rayon and cellophane). In recent years, materials scientists have begun exploring further use of these fibers in composite materials. Due to cellulose being the main factor of a plant fiber's strength, this is what scientists are looking to manipulate to create different types of fibers. Fiber crops are generally harvestable after a single growing season, as distinct from trees, which are typically grown for many years before being harvested for such materials as wood pulp fiber or lacebark. In specific circumstances, fiber crops can be superior to wood pulp fiber in terms of technical performance, environmental impact or cost. There are a number of issues regarding the use of fiber c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cereal
A cereal is any Poaceae, grass cultivated for the edible components of its grain (botanically, a type of fruit called a caryopsis), composed of the endosperm, Cereal germ, germ, and bran. Cereal Grain, grain crops are grown in greater quantities and provide more food energy worldwide than any other type of crop and are therefore Staple food, staple crops. They include wheat, rye, Oat, oats, and barley. Edible grains from other plant families, such as buckwheat, quinoa and Salvia hispanica, chia, are referred to as pseudocereals. In their unprocessed whole grain form, cereals are a rich source of vitamins, Mineral (nutrient), minerals, carbohydrates, fats, oils, and Protein (nutrient), protein. When processed by the removal of the bran and germ the remaining endosperm is mostly carbohydrate. In some Developing country, developing countries, grain in the form of rice, wheat, millet, or maize constitutes a majority of daily sustenance. In Developed country, developed countries, c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is distinct from weathering which involves no movement. Removal of rock or soil as clastic sediment is referred to as ''physical'' or ''mechanical'' erosion; this contrasts with ''chemical'' erosion, where soil or rock material is removed from an area by dissolution. Eroded sediment or solutes may be transported just a few millimetres, or for thousands of kilometres. Agents of erosion include rainfall; bedrock wear in rivers; coastal erosion by the sea and waves; glacial plucking, abrasion, and scour; areal flooding; wind abrasion; groundwater processes; and mass movement processes in steep landscapes like landslides and debris flows. The rates at which such processes act control how fast a surface is eroded. Typically, physical erosion procee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hardpan
In soil science, agriculture and gardening, hardpan or soil pan is a dense layer of soil, usually found below the uppermost topsoil layer. There are different types of hardpan, all sharing the general characteristic of being a distinct soil layer that is largely impervious to water. Some hardpans are formed by deposits in the soil that fuse and bind the soil particles. These deposits can range from dissolved silica to matrices formed from iron oxides and calcium carbonate. Others are man-made, such as hardpan formed by compaction from repeated plowing, particularly with moldboard plows, or by heavy traffic or pollution. Formations Soil structure strongly affects its tendency to form a hard pan. One such common soil condition related to hardpan is soil pH. Acidic soils are most often affected due to the propensity of certain mineral salts, most notably iron and calcium, to form hard complexes with soil particles under acidic conditions. Another major determinant is the soil pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)