|
Britannia Bridge
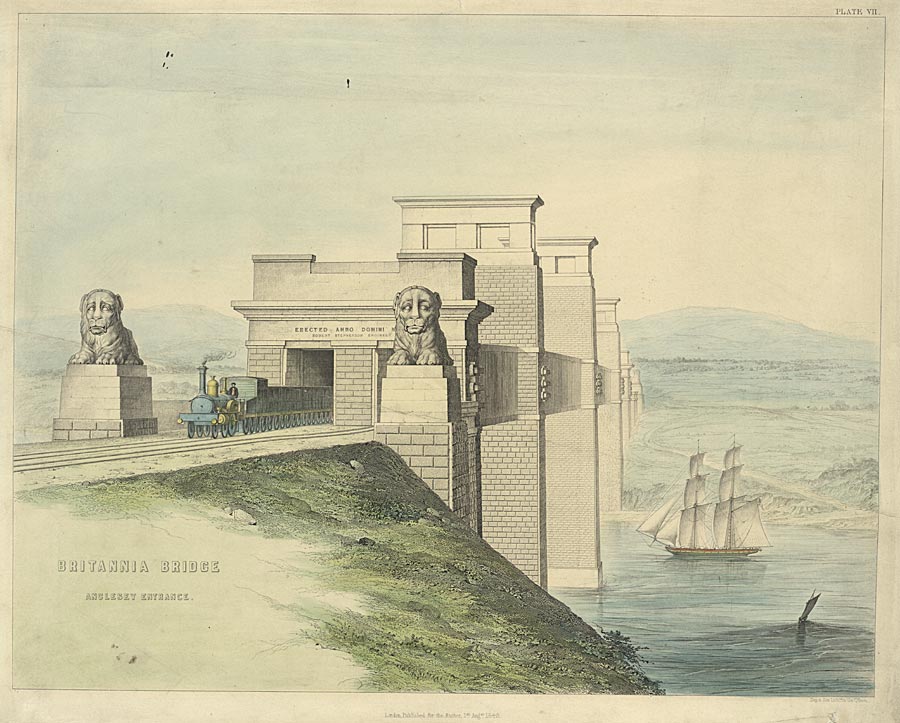
Britannia Bridge ( cy, Pont Britannia) is a bridge across the Menai Strait between the island of Anglesey and the mainland of Wales. It was originally designed and built by the noted railway engineer Robert Stephenson as a tubular bridge of wrought iron rectangular box-section spans for carrying rail traffic. Its importance was to form a critical link of the Chester and Holyhead Railway's route, enabling trains to directly travel between London and the port of Holyhead, thus facilitating a sea link to Dublin, Ireland. Decades before the building of the Britannia Bridge, the Menai Suspension Bridge had been completed, but this structure carried a road rather than track; there was no rail connection to Anglesey before its construction. After many years of deliberation and proposals, on 30 June 1845, a Parliamentary Bill covering the construction of the Britannia Bridge received royal assent. At the Admiralty's insistence, the bridge elements were required to be relatively high ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Wales Coast Line
The North Wales Coast Line ( cy, Llinell Arfordir Gogledd Cymru), also known as the North Wales Main Line ( cy, Prif Linell Gogledd Cymru or cy, label=none, Prif Linell y Gogledd), is a major railway line in the north of Wales and Cheshire, England, running from Crewe on the West Coast Main Line to Holyhead on the Isle of Anglesey. The line has 19 stations, with all except two, Chester and Crewe, being in Wales. The line is not currently electrified, so Avanti West Coast, the current operator of the West Coast Partnership franchise, currently uses Class 221 ''Super Voyagers'', which they have done since December 2007, on routes to Holyhead. The line contains several notable engineering structures, including Conwy railway bridge across the River Conwy, and Britannia Bridge across the Menai Strait. History The first section from Crewe to Chester was built by the Chester and Crewe Railway and absorbed by the Grand Junction Railway shortly before opening in 1840. The remain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menai Suspension Bridge
The Menai Suspension Bridge ( cy, Pont y Borth, Pont Grog y Borth) is a suspension bridge spanning the Menai Strait between the island of Anglesey and the mainland of Wales. Designed by Thomas Telford and completed in 1826, it was the world's first major suspension bridge. The bridge still carries road traffic and is a Grade I listed structure. Background The Menai Strait was created by glacial erosion along a line of weakness associated with the Menai Strait Fault System. During a series of Pleistocene glaciations (that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago), a succession of ice-sheets moved from northeast to southwest across Anglesey and neighbouring Gwynedd, scouring the underlying rock and creating a series of linear bedrock hollows. The deepest of these channels eventually became flooded by the sea as the ice sheets receded, forming the Menai Strait. As Anglesey has been an island throughout recorded human history, the only way to reach it was by crossing the st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Stephenson
George Stephenson (9 June 1781 – 12 August 1848) was a British civil engineer and mechanical engineer. Renowned as the "Father of Railways", Stephenson was considered by the Victorians a great example of diligent application and thirst for improvement. Self-help advocate Samuel Smiles particularly praised his achievements. His chosen rail gauge, sometimes called "Stephenson gauge", was the basis for the standard gauge used by most of the world's railways. Pioneered by Stephenson, rail transport was one of the most important technological inventions of the 19th century and a key component of the Industrial Revolution. Built by George and his son Robert's company Robert Stephenson and Company, the ''Locomotion'' No. 1 was the first steam locomotive to carry passengers on a public rail line, the Stockton and Darlington Railway in 1825. George also built the first public inter-city railway line in the world to use locomotives, the Liverpool and Manchester Railway, which opene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Telford
Thomas Telford FRS, FRSE, (9 August 1757 – 2 September 1834) was a Scottish civil engineer. After establishing himself as an engineer of road and canal projects in Shropshire, he designed numerous infrastructure projects in his native Scotland, as well as harbours and tunnels. Such was his reputation as a prolific designer of highways and related bridges, he was dubbed ''The Colossus of Roads'' (a pun on the Colossus of Rhodes), and, reflecting his command of all types of civil engineering in the early 19th century, he was elected as the first President of the Institution of Civil Engineers, a post he held for 14 years until his death. The town of Telford in Shropshire was named after him. Early career Telford was born on 9 August 1757, at Glendinning, a hill farm east of Eskdalemuir Kirk, in the rural parish of Westerkirk, in Eskdale, Dumfriesshire. His father John Telford, a shepherd, died soon after Thomas was born. Thomas was raised in poverty by his mother Janet Jac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Britannia Bridge - Circa 1852
Britannia () is the national personification of Britain as a helmeted female warrior holding a trident and shield. An image first used in classical antiquity, the Latin ''Britannia'' was the name variously applied to the British Isles, Great Britain, and the Roman province of Britain during the Roman Empire. Typically depicted reclining or seated with spear and shield since appearing thus on Roman coins of the 2nd century AD, the classical national allegory was revived in the early modern period. On coins of the pound sterling issued by Charles II of England, Scotland, and Ireland, Britannia appears with her shield bearing the Union Flag. To symbolise the Royal Navy's victories, Britannia's spear became the characteristic trident in 1797, and a helmet was added to the coinage in 1825. By the 1st century BC, Britannia replaced Albion as the prevalent Latin name for the island of Great Britain. After the Roman conquest in 43 AD, ''Britannia'' also came to refer to the Roman p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Britannia Bridge Anglesey Entrance
Britannia () is the national personification of Britain as a helmeted female warrior holding a trident and shield. An image first used in classical antiquity, the Latin ''Britannia'' was the name variously applied to the British Isles, Great Britain, and the Roman province of Britain during the Roman Empire. Typically depicted reclining or seated with spear and shield since appearing thus on Roman coins of the 2nd century AD, the classical national allegory was revived in the early modern period. On coins of the pound sterling issued by Charles II of England, Scotland, and Ireland, Britannia appears with her shield bearing the Union Flag. To symbolise the Royal Navy's victories, Britannia's spear became the characteristic trident in 1797, and a helmet was added to the coinage in 1825. By the 1st century BC, Britannia replaced Albion as the prevalent Latin name for the island of Great Britain. After the Roman conquest in 43 AD, ''Britannia'' also came to refer to the Roman pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Listed Building
In the United Kingdom, a listed building or listed structure is one that has been placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Historic Environment Scotland in Scotland, in Wales, and the Northern Ireland Environment Agency in Northern Ireland. The term has also been used in the Republic of Ireland, where buildings are protected under the Planning and Development Act 2000. The statutory term in Ireland is " protected structure". A listed building may not be demolished, extended, or altered without special permission from the local planning authority, which typically consults the relevant central government agency, particularly for significant alterations to the more notable listed buildings. In England and Wales, a national amenity society must be notified of any work to a listed building which involves any element of demolition. Exemption from secular listed building control is provided for some buildings in current use for worship, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conwy Railway Bridge
The Conwy Railway Bridge carries the North Wales coast railway line across the River Conwy between Llandudno Junction and the town of Conwy. The wrought iron tubular bridge, which is now Grade I listed, was built in the 19th century. It is the last surviving example of this type of design by Stephenson after the original Britannia Bridge across the Menai Strait was partially destroyed in a fire in 1970 and rebuilt as a two-tier truss arch bridge design. The Conwy Railway Bridge was designed by railway engineer Robert Stephenson in collaboration with William Fairbairn and Eaton Hodgkinson. The original plan had been for suspension bridge complementing Thomas Telford's Conwy Suspension Bridge of 1826. After Stephenson's appointment as chief engineer, the design was changed because a suspension bridge was considered unsuitable for trains. Stephenson and his collaborators invented the wrought-iron box-girder structure to bridge the River Conwy in a single span. During May 1846, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rivet
A rivet is a permanent mechanical fastener. Before being installed, a rivet consists of a smooth cylindrical shaft with a head on one end. The end opposite to the head is called the ''tail''. On installation, the rivet is placed in a punched or drilled hole, and the tail is ''upset'', or ''bucked'' (i.e., deformed), so that it expands to about 1.5 times the original shaft diameter, holding the rivet in place. In other words, the pounding or pulling creates a new "head" on the tail end by smashing the "tail" material flatter, resulting in a rivet that is roughly a dumbbell shape. To distinguish between the two ends of the rivet, the original head is called the ''factory head'' and the deformed end is called the ''shop head'' or buck-tail. Because there is effectively a head on each end of an installed rivet, it can support tension loads. However, it is much more capable of supporting shear loads (loads perpendicular to the axis of the shaft). Fastenings used in traditional w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Fairbairn
Sir William Fairbairn, 1st Baronet of Ardwick (19 February 1789 – 18 August 1874) was a Scottish civil engineer, structural engineer Structural engineers analyze, design, plan, and research structural components and structural systems to achieve design goals and ensure the safety and comfort of users or occupants. Their work takes account mainly of safety, technical, economic ... and shipbuilder. In 1854 he succeeded George Stephenson and Robert Stephenson to become the third president of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers. Early career Born in Kelso, Scotland, Kelso to a local farmer, Fairbairn showed an early mechanical aptitude and served as an apprentice millwright in Newcastle upon Tyne where he befriended the young George Stephenson. He moved to Manchester in 1813 to work for Adam Parkinson and Thomas Hewes. In 1817, he launched his mill-machinery business with James Lillie as William Fairbairn & Sons, Fairbairn and Lillie Engine Makers. Structural studies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Man-of-war
The man-of-war (also man-o'-war, or simply man) was a Royal Navy expression for a powerful warship or frigate from the 16th to the 19th century. Although the term never acquired a specific meaning, it was usually reserved for a ship armed with cannon and propelled primarily by sails, as opposed to a galley which is propelled primarily by oars. Description The man-of-war was developed in Portugal in the early 15th century from earlier roundships with the addition of a second mast to form the carrack. The 16th century saw the carrack evolve into the galleon and then the ship of the line. The evolution of the term has been given thus: The man-of-war design developed by Sir John Hawkins had three masts, each with three to four sails. The ship could be up to 60 metres long and could have up to 124 guns: four at the bow, eight at the stern, and 56 in each broadside. All these cannons required three gun decks to hold them, one more than any earlier ship. It had a maximum sailing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)






.jpg)