|
Bristol Industrial Museum
The Bristol Industrial Museum was a museum in Bristol, England, located on Prince's Wharf beside the Floating Harbour and which closed in 2006. On display were items from Bristol's industrial past – including aviation, car and bus manufacture, and printing – and exhibits documenting Bristol's maritime history. The museum was managed by Bristol City Council along with nearby preserved industrial relics along Prince's Wharf, including the Bristol Harbour Railway, cranes and a small fleet of preserved vessels. The railway, cranes and vessels all now form part of the working exhibits at M Shed Museum. The museum closed its doors to the public on 29 October 2006. M Shed, the new Museum of Bristol has been created on the site, keeping the same façade and many of the exhibits. It opened 17 June 2011. A website has been created to try to capture the essence of the museum and some of its memories. It can be found at http://bristolindustrialmuseum.epizy.com/ Overview The museu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bristol
Bristol () is a city, ceremonial county and unitary authority in England. Situated on the River Avon, it is bordered by the ceremonial counties of Gloucestershire to the north and Somerset to the south. Bristol is the most populous city in South West England. The wider Bristol Built-up Area is the eleventh most populous urban area in the United Kingdom. Iron Age hillforts and Roman villas were built near the confluence of the rivers Frome and Avon. Around the beginning of the 11th century, the settlement was known as (Old English: 'the place at the bridge'). Bristol received a royal charter in 1155 and was historically divided between Gloucestershire and Somerset until 1373 when it became a county corporate. From the 13th to the 18th century, Bristol was among the top three English cities, after London, in tax receipts. A major port, Bristol was a starting place for early voyages of exploration to the New World. On a ship out of Bristol in 1497, John Cabot, a Venetia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bristol Aero Engines
The Bristol Aeroplane Company, originally the British and Colonial Aeroplane Company, was both one of the first and one of the most important British aviation companies, designing and manufacturing both airframes and aircraft engines. Notable aircraft produced by the company include the 'Boxkite', the Bristol Fighter, the Bulldog, the Blenheim, the Beaufighter, and the Britannia, and much of the preliminary work which led to Concorde was carried out by the company. In 1956 its major operations were split into Bristol Aircraft and Bristol Aero Engines. In 1959, Bristol Aircraft merged with several major British aircraft companies to form the British Aircraft Corporation (BAC) and Bristol Aero Engines merged with Armstrong Siddeley to form Bristol Siddeley. BAC went on to become a founding component of the nationalised British Aerospace, now BAE Systems. Bristol Siddeley was purchased by Rolls-Royce in 1966, who continued to develop and market Bristol-designed engines. The B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crane (machine)
A crane is a type of machine, generally equipped with a hoist rope, wire ropes or chains, and sheaves, that can be used both to lift and lower materials and to move them horizontally. It is mainly used for lifting heavy objects and transporting them to other places. The device uses one or more simple machines to create mechanical advantage and thus move loads beyond the normal capability of a human. Cranes are commonly employed in transportation for the loading and unloading of freight, in construction for the movement of materials, and in manufacturing for the assembling of heavy equipment. The first known crane machine was the shaduf, a water-lifting device that was invented in ancient Mesopotamia (modern Iraq) and then appeared in ancient Egyptian technology. Construction cranes later appeared in ancient Greece, where they were powered by men or animals (such as donkeys), and used for the construction of buildings. Larger cranes were later developed in the Roman Empire, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mayflower Steam Tug 1861
''Mayflower'' is a steam tug built in Bristol in 1861 and now preserved by Bristol Museums Galleries & Archives. She is based in Bristol Harbour at M Shed (formerly Bristol Industrial Museum). She is the oldest Bristol-built ship afloat, and is believed to be the oldest surviving tug in the world. Building ''Mayflower'' was built by GK Stothert & Co, who were connected with the Bath-based engineering company Stothert & Pitt. A branch of the family came to Bristol to build railway locomotives (later to become the Avonside Engine Company). After 1852, a separate shipbuilding company was established which survived in business until the 1930s. The tug has an iron hull. She is long, her beam is , her depth is and her tonnage is . Her United Kingdom official number is 105412. Service ''Mayflower'' was built to work on the Gloucester and Sharpness Canal and in the River Severn, one of three tugs ordered after trials had shown they were much more efficient than hor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyronaut
''Pyronaut'' (originally ''Bristol Phoenix II'') is a specialised form of fireboat known as a fire-float. It was built in 1934 by Charles Hill & Sons Ltd., Albion Dock Bristol, Yard No. 208. Registered number 333833. She is owned by Bristol Museums and based at M Shed in Bristol's Floating Harbour. Originally powered by two Petter ''Atomic'' diesel engines rates at each. Two Merryweather & Sons three-cylinder reciprocating pumps capable of delivering of water per minute. This equipment was replaced in 1968 by two Ruston & Hornsby 6YDM six-cylinder diesel engines rated at each, driving screw propellers from the front power-take-off, and Coventry Climax centrifugal pumps capable of delivering of water per minute from the main drive. Fire-floats in Bristol When ships loaded with valuable cargoes are berthed together in crowded docks surrounded by warehouses, a fire can be disastrous. Although land-based fire-engines are able to reach much of the fire ground, waterborne fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fireboat
A fireboat or fire-float is a specialized watercraft with pumps and nozzles designed for fighting shoreline and shipboard fires. The first fireboats, dating to the late 18th century, were tugboats, retrofitted with firefighting equipment. Older designs derived from tugboats and modern fireboats more closely resembling seafaring ships can both be found in service today. Some departments would give their multi-purpose craft the title of "fireboat" also. They are frequently used for fighting fires on docks and shore side warehouses as they can directly attack fires in the supporting underpinnings of these structures. They also have an effectively unlimited supply of water available, pumping directly from below the hull. Fireboats can be used to assist shore-based firefighters when other water is in low supply or is unavailable, for example, due to earthquake breakage of water mains, as happened in San Francisco due to the 1989 Loma Prieta earthquake. Some modern firebo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caribbean
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean) and the surrounding coasts. The region is southeast of the Gulf of Mexico and the North American mainland, east of Central America, and north of South America. Situated largely on the Caribbean Plate, the region has more than 700 islands, islets, reefs and cays (see the list of Caribbean islands). Island arcs delineate the eastern and northern edges of the Caribbean Sea: The Greater Antilles and the Lucayan Archipelago on the north and the Lesser Antilles and the on the south and east (which includes the Leeward Antilles). They form the West Indies with the nearby Lucayan Archipelago (the Bahamas and Turks and Caicos Islands), which are considered to be part of the Caribbean despite not bordering the Caribbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area and 20% of its land area.Sayre, April Pulley (1999), ''Africa'', Twenty-First Century Books. . With billion people as of , it accounts for about of the world's human population. Africa's population is the youngest amongst all the continents; the median age in 2012 was 19.7, when the worldwide median age was 30.4. Despite a wide range of natural resources, Africa is the least wealthy continent per capita and second-least wealthy by total wealth, behind Oceania. Scholars have attributed this to different factors including geography, climate, tribalism, colonialism, the Cold War, neocolonialism, lack of democracy, and corruption. Despite this low concentration of wealth, recent economic expansion and the large and young population make Afr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. The United Kingdom includes the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland, and many smaller islands within the British Isles. Northern Ireland shares a land border with the Republic of Ireland; otherwise, the United Kingdom is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea, the English Channel, the Celtic Sea and the Irish Sea. The total area of the United Kingdom is , with an estimated 2020 population of more than 67 million people. The United Kingdom has evolved from a series of annexations, unions and separations of constituent countries over several hundred years. The Treaty of Union between the Kingdom of England (which included Wales, annexed in 1542) and the Kingdom of Scotland in 170 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic Slave Trade
The Atlantic slave trade, transatlantic slave trade, or Euro-American slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of enslaved African people, mainly to the Americas. The slave trade regularly used the triangular trade route and its Middle Passage, and existed from the 16th to the 19th centuries. The vast majority of those who were transported in the transatlantic slave trade were people from Central and West Africa that had been sold by other West Africans to Western European slave traders,Thornton, p. 112. while others had been captured directly by the slave traders in coastal raids; Europeans gathered and imprisoned the enslaved at forts on the African coast and then brought them to the Americas. Except for the Portuguese, European slave traders generally did not participate in the raids because life expectancy for Europeans in sub-Saharan Africa was less than one year during the period of the slave trade (which was prior to the widespread availability of quini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Letterpress Printing
Letterpress printing is a technique of relief printing. Using a printing press, the process allows many copies to be produced by repeated direct impression of an inked, raised surface against sheets or a continuous roll of paper. A worker composes and locks movable type into the "bed" or "chase" of a press, inks it, and presses paper against it to transfer the ink from the type, which creates an impression on the paper. In practice, letterpress also includes other forms of relief printing with printing presses, such as wood engravings, photo-etched zinc "cuts" (plates), and linoleum blocks, which can be used alongside metal type, or wood type in a single operation, as well as stereotypes and electrotypes of type and blocks. With certain letterpress units, it is also possible to join movable type with slugs cast using hot metal typesetting. In theory, anything that is "type high" and so forms a layer exactly 0.918 in. thick between the bed and the paper can be printed using l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
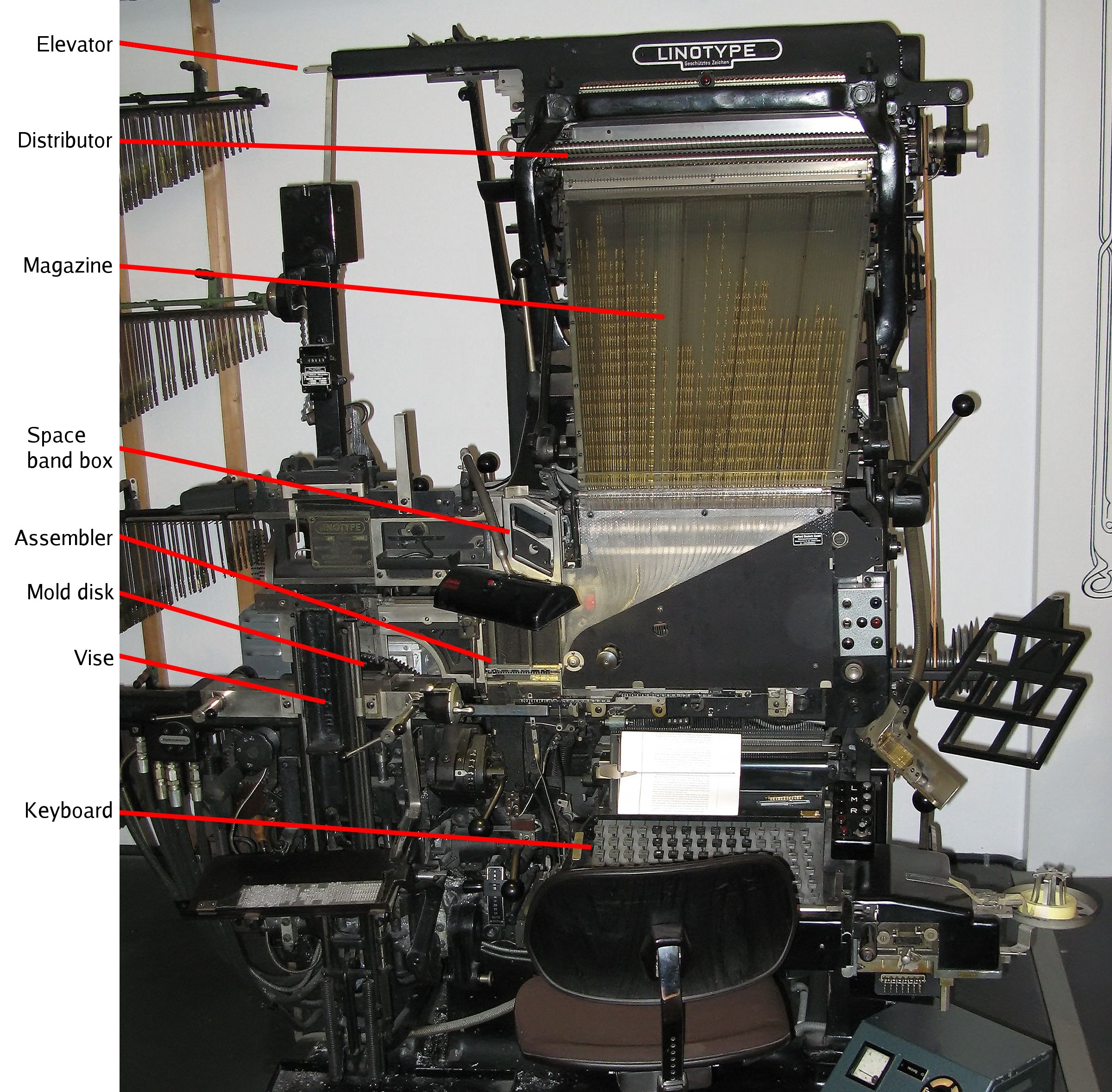
Linotype Machine
The Linotype machine ( ) is a "line casting" machine used in printing; manufactured and sold by the former Mergenthaler Linotype Company and related It was a hot metal typesetting system that cast lines of metal type for individual uses. Linotype became one of the mainstay methods to set type, especially small-size body text, for newspapers, magazines, and posters from the late 19th century to the 1970s and 1980s, when it was largely replaced by phototypesetting and digital typesetting. The name of the machine comes from the fact that it produces an entire line of metal type at once, hence a ''line-o'-type''. It was a significant improvement over the previous industry standard of manual, letter-by-letter typesetting using a composing stick and shallow subdivided trays, called "cases". The Linotype machine operator enters text on a 90-character keyboard. The machine assembles ''matrices'', which are molds for the letter forms, in a line. The assembled line is then cast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)