|
Bras D'Or
Bras d'Or Lake ( Mi'kmawi'simk: Pitupaq) is an irregular estuary in the centre of Cape Breton Island in Nova Scotia, Canada. It has a connection to the open sea, and is tidal. It also has inflows of fresh water from rivers, making the brackish water a very productive natural habitat. It was designated the Bras d'Or Lake Biosphere Reserve by UNESCO in 2011. Toponym Pronounced ( or ), maps before 1872 name it ''Le Lac de Labrador'' (or more simply ''Labrador''). ''Labrador'' was the name given by the Portuguese to much of eastern Canada. It meant ''farmer'', and is cognate with ''laborer''. An error of folk etymology, the name is spelt to resemble the French language ''Arm of'' ''Gold'', a homonym. It is also called locally ''The Bras d'Or Lakes''. In Mi'kmawi'simk, the lake's name, ''Pitupaq'', refers to the brackish waters, meaning "the long salt water." Geography The lake has a surface area of 1099 square kilometers. Three arms stretch out to the north east. At the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Breton Island
Cape Breton Island (french: link=no, île du Cap-Breton, formerly '; gd, Ceap Breatainn or '; mic, Unamaꞌki) is an island on the Atlantic coast of North America and part of the province of Nova Scotia, Canada. The island accounts for 18.7% of Nova Scotia's total area. Although the island is physically separated from the Nova Scotia peninsula by the Strait of Canso, the long Canso Causeway connects it to mainland Nova Scotia. The island is east-northeast of the mainland with its northern and western coasts fronting on the Gulf of Saint Lawrence with its western coast forming the eastern limits of the Northumberland Strait. The eastern and southern coasts front the Atlantic Ocean with its eastern coast also forming the western limits of the Cabot Strait. Its landmass slopes upward from south to north, culminating in the highlands of its northern cape. One of the world's larger saltwater lakes, ("Arm of Gold" in French), dominates the island's centre. The total population ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drumlin
A drumlin, from the Irish word ''droimnín'' ("littlest ridge"), first recorded in 1833, in the classical sense is an elongated hill in the shape of an inverted spoon or half-buried egg formed by glacial ice acting on underlying unconsolidated till or ground moraine. Assemblages of drumlins are referred to as fields or swarms; they can create a landscape which is often described as having a 'basket of eggs topography'. The low ground between two drumlins is known as a dungeon; dungeons have colder microclimates in winter from settling cold air. Morphology Drumlins occur in various shapes and sizes, including symmetrical (about the long axis), spindle, parabolic forms, and transverse asymmetrical forms. Generally, they are elongated, oval-shaped hills, with a long axis parallel to the orientation of ice flow and with an up-ice (stoss) face that is generally steeper than the down-ice (lee) face. Drumlins are typically 250 to 1,000 meters long and between 120 and 300 meters wide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
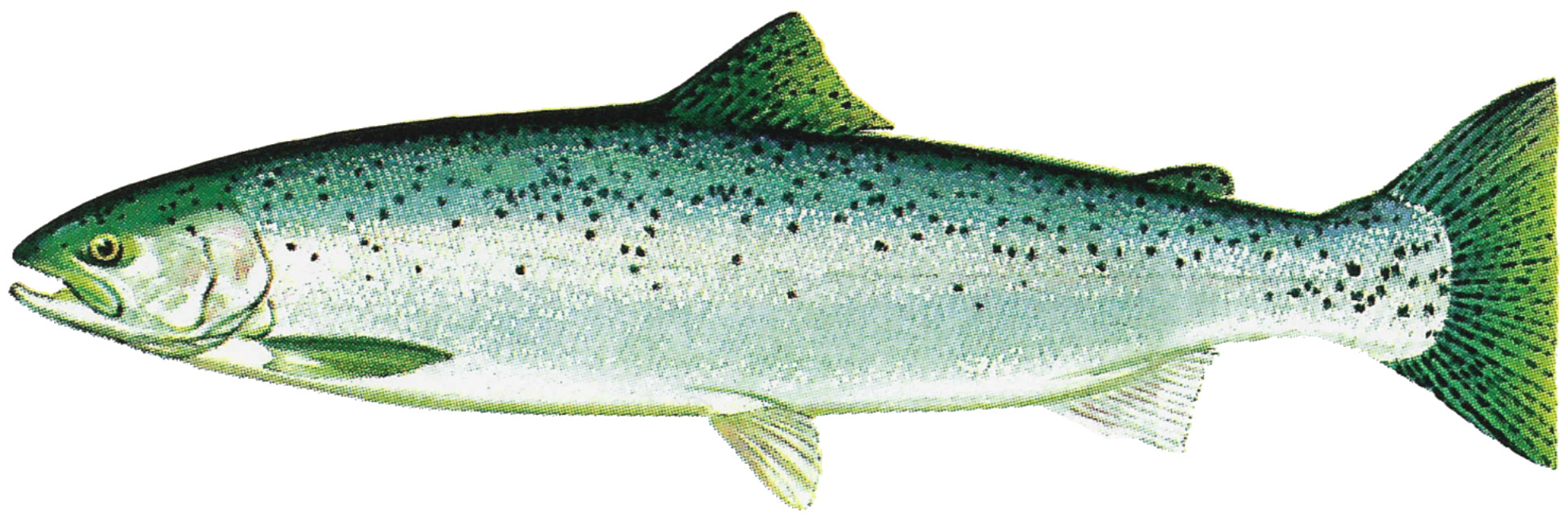
Rainbow Trout
The rainbow trout (''Oncorhynchus mykiss'') is a species of trout native to cold-water tributaries of the Pacific Ocean in Asia and North America. The steelhead (sometimes called "steelhead trout") is an anadromous (sea-run) form of the coastal rainbow trout or Columbia River redband trout that usually returns to freshwater to spawn after living two to three years in the ocean. Freshwater forms that have been introduced into the Great Lakes and migrate into tributaries to spawn are also called steelhead. Adult freshwater stream rainbow trout average between , while lake-dwelling and anadromous forms may reach . Coloration varies widely based on subspecies, forms, and habitat. Adult fish are distinguished by a broad reddish stripe along the lateral line, from gills to the tail, which is most vivid in breeding males. Wild-caught and hatchery-reared forms of the species have been transplanted and introduced for food or sport in at least 45 countries and every continent except ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenland Cod
The Greenland cod (''Gadus ogac''), commonly known also as ogac, is a species of ray-finned fish in the cod family, Gadidae. Genetic analysis has shown that it may be the same species as the Pacific cod (''Gadus macrocephalus''). It is a bottom-dwelling fish and is found on the continental shelf in the Arctic Ocean and northwestern Atlantic Ocean, its range extending from Alaska to West Greenland, then southwards along the Canadian coast to the Gulf of St. Lawrence and Cape Breton Island. It is a commercially harvested food fish, but landings have been greatly reduced in recent years. Taxonomy Molecular genetic analyses strongly suggest that Greenland cod is not different from Pacific cod, ''Gadus macrocephalus'' - ''Gadus ogac'' is then a junior synonym of ''G. macrocephalus''. ITIS and the Catalogue of Life list ''Gadus ogac'' as synonym of ''G. macrocephalus''.Catalogue of Life: Gadus macrocephalus'. Description In colour the Greenland cod is generally sombre, ranging from tan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
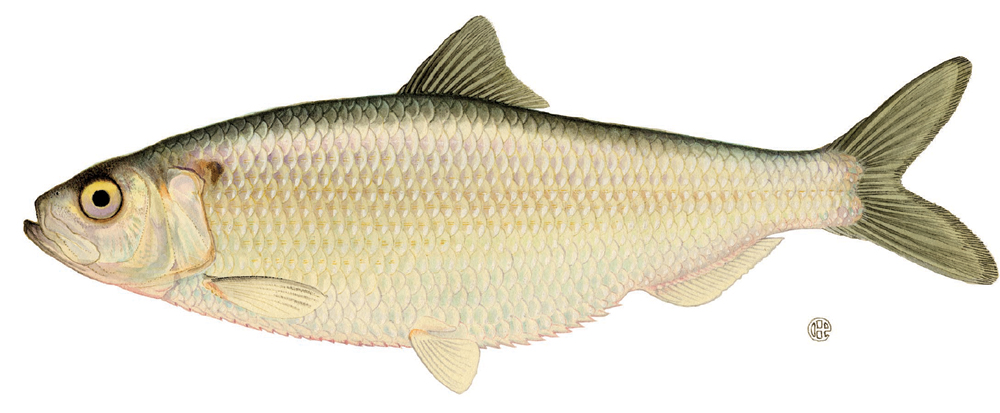
Blueback Herring
The blueback herring, blueback shad, or summer shad (''Alosa aestivalis'') is an anadromous species of herring from the east coast of North America, with a range from Nova Scotia to Florida. Blueback herring form schools and are believed to migrate offshore to overwinter near the bottom. These fish are silvery in color, have a series of scutes (modified, spiny and keeled scales) along their bellies, and are characterized by deep bluish-green backs. They reach a maximum size of approximately and are believed to live up to 8 years. The most distinguishing characteristic of this species is the black to dusky color of its peritoneum (the lining of the abdominal cavity). It is one of the "typical" North American shads. They are often confused with alewifes because blueback shad and alewives are difficult to distinguish from one another, and together these two species are often regarded collectively as "river herring". Alewives have larger eyes, greater body depth, and pearly t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Hake
The white hake or mud hake (''Urophycis tenuis'') is a phycid hake. It is found in the deeper waters in the northwest Atlantic Ocean. Description The species can grow to be up to 30 cm by the end of the first year, and 400 mm if male and 480 mm if female by the first reproduction. It grows to a maximum length of . Distribution and habitat The white hake is found in the northwest Atlantic from North Carolina to Newfoundland Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region ..., at depths of about . Reproduction and development Spawning season for the white hake starts in late winter or early spring. It has been difficult to study the breeding habits of the white hake due to researchers’ issue with finding ripe females. Studies have found that larvae for the sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blackspotted Stickleback
The blackspotted stickleback (''Gasterosteus wheatlandi'') is species of ray-finned fish belonging to the family Gasterosteidae, the sticklebacks. This fish is found in the western Atlantic from the coasts of Newfoundland (Canada) to Massachusetts (United States). This is a benthopelagic species of marine and brackish waters, rarely entering freshwater, which remains near the shore. It is frequently associated with floating vegetation. The male builds a nest, in which the females deposit eggs and the male guards and aerates them. It is a small fish which reaches a maximum published total length of , although is more typical. The specific name honors Richard H. Wheatland who was the Cabinet Keeper (and collector of fishes and reptiles), for the Essex County Natural History Society of Salem, Massachusetts and who collected type of this species in 1859. References blackspotted stickleback Fish of the Western Atlantic Fauna of Atlantic Canada Fauna of the Northeastern Uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Oyster
The eastern oyster (''Crassostrea virginica'')—also called the Atlantic oyster, American oyster, or East Coast oyster—is a species of true oyster native to eastern North and South America. Other names in local or culinary use include the Wellfleet oyster, Virginia oyster, Malpeque oyster, Blue Point oyster, Chesapeake Bay oyster, and Apalachicola oyster. ''C. virginica'' ranges from northern New Brunswick through parts of the West Indies and south to Brazil. It is farmed in all of the Maritime provinces of Canada and all Eastern Seaboard and Gulf states of the United States, as well as Puget Sound, Washington, where it is known as the Totten Inlet Virginica. It was introduced to the Hawaiian Islands in the nineteenth century and is common in Pearl Harbor. The eastern oyster is an important commercial species. Its distribution has been affected by habitat change; less than 1% of the population present when the first European colonists arrived is thought to remain in the Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tidal Range
Tidal range is the difference in height between high tide and low tide. Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by gravitational forces exerted by the Moon and Sun and the rotation of Earth. Tidal range depends on time and location. Larger tidal range occur during spring tides (spring range), when the gravitational forces of both the Moon and Sun are aligned (at syzygy), reinforcing each other in the same direction ( new moon) or in opposite directions (full moon). The largest annual tidal range can be expected around the time of the equinox if it coincides with a spring tide. Spring tides occur at the second and fourth (last) quarters of the lunar phases. By contrast, during neap tides, when the Moon and Sun's gravitational force vectors act in quadrature (making a right angle to the Earth's orbit), the difference between high and low tides (neap range) is smallest. Neap tides occur at the first and third quarters of the lunar phases. Tidal data for coastal ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boularderie Island
Boularderie Island (pronounced "bull-awn-dree") is an island separating the Cabot Strait from Bras d'Or Lake on the eastern coast of Cape Breton Island, Nova Scotia, Canada. It takes its name from Louis-Simon le Poupet de la Boularderie, who was granted the area as a concession from the King of France. Geography At 40 km (25 mi) long and between 3 km (2 mi) to 10 km (6 mi) wide, Boularderie Island is Nova Scotia's second largest island after Cape Breton Island. Two outlets of Bras d'Or Lake run on each side of the island to the Atlantic Ocean: * the Great Bras d'Or channel runs along the island's northwestern shore, and * St. Andrews Channel and the Little Bras d'Or channel run along the island's southeastern shore. The extreme northeastern end of the island at Point Aconi fronts the Cabot Strait, whereas the extreme southwestern end at Kempt Head fronts the northern basin of Bras d'Or Lake. The majority of the island is heavily forested, howeve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salinity
Salinity () is the saltiness or amount of salt dissolved in a body of water, called saline water (see also soil salinity). It is usually measured in g/L or g/kg (grams of salt per liter/kilogram of water; the latter is dimensionless and equal to ‰). Salinity is an important factor in determining many aspects of the chemistry of natural waters and of biological processes within it, and is a thermodynamic state variable that, along with temperature and pressure, governs physical characteristics like the density and heat capacity of the water. A contour line of constant salinity is called an ''isohaline'', or sometimes ''isohale''. Definitions Salinity in rivers, lakes, and the ocean is conceptually simple, but technically challenging to define and measure precisely. Conceptually the salinity is the quantity of dissolved salt content of the water. Salts are compounds like sodium chloride, magnesium sulfate, potassium nitrate, and sodium bicarbonate which dissolve into ions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georges River, Nova Scotia
Georges River is a community in the Canada, Canadian province of Nova Scotia, located in the Cape Breton Regional Municipality on Cape Breton Island. ReferencesGeorges River on Destination Nova Scotia Communities in the Cape Breton Regional Municipality {{CapeBretonNS-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |