|
Brachyceratops
''Brachyceratops'' ('short horned face') is a dubious genus of ceratopsian dinosaur known only from partial juvenile specimens dating to the late Cretaceous Period of Montana, United States. ''Brachyceratops'' has historically been known from juvenile remains, with one specimen having since been re-classified as ''Rubeosaurus ovatus''.Andrew T. McDonald & John R. Horner, (2010). "New Material of "Styracosaurus" ovatus from the Two Medicine Formation of Montana", In: Michael J. Ryan, Brenda J. Chinnery-Allgeier, and David A. Eberth (eds), ''New Perspectives on Horned Dinosaurs: The Royal Tyrrell Museum Ceratopsian Symposium'', Indiana University Press, 656 pp. History of discovery ''Brachyceratops montanensis'', the type species, was first discovered in the Two Medicine Formation (Campanian, about 74 million years old) on a Blackfoot Indian Reservation in Teton County in north-central Montana."Brachyceratops." In: Dodson, Peter & Britt, Brooks & Carpenter, Kenneth & Forster ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
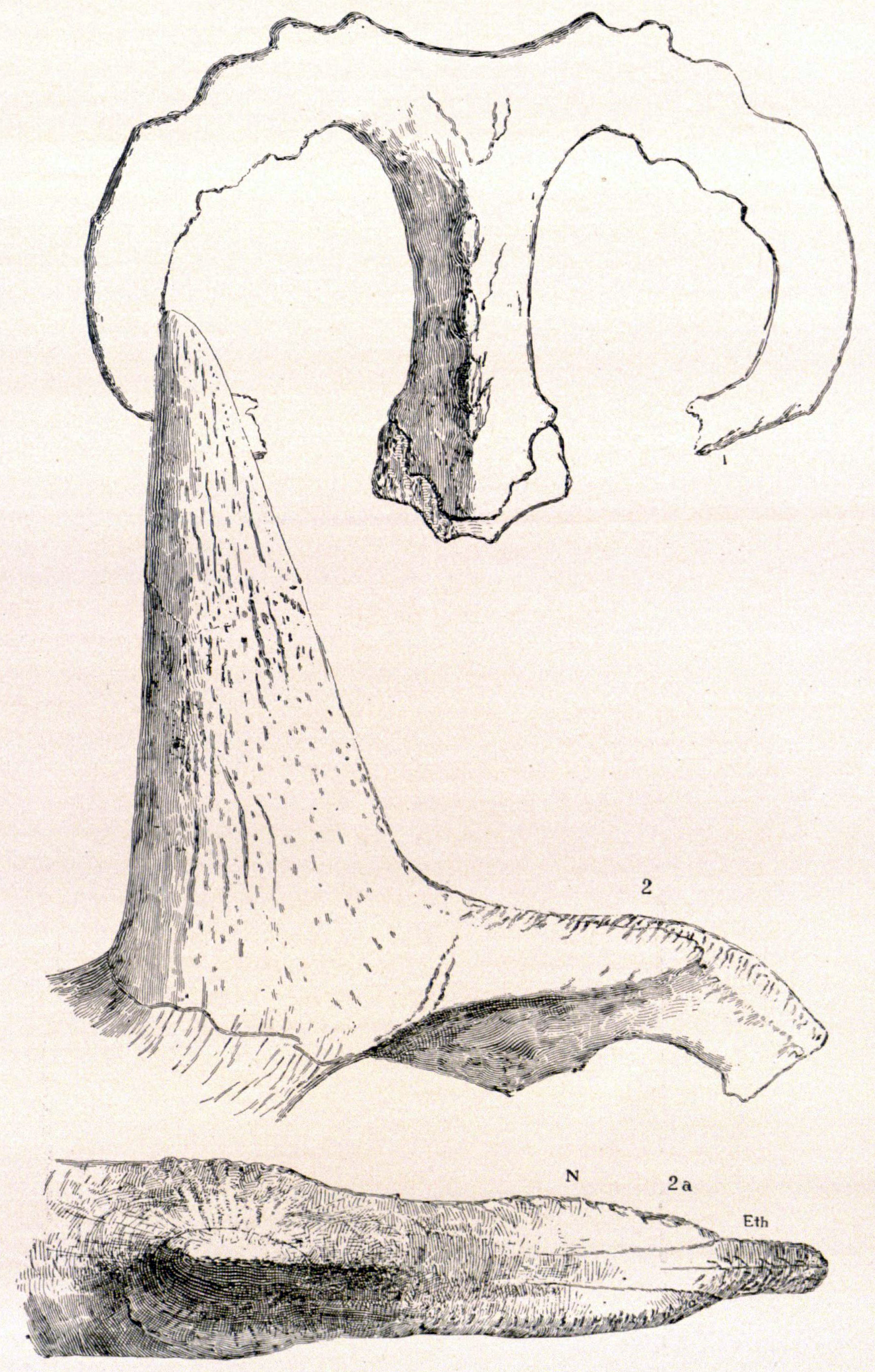
Brachyceratops Skull
''Brachyceratops'' ('short horned face') is a dubious genus of ceratopsian dinosaur known only from partial juvenile specimens dating to the late Cretaceous Period of Montana, United States. ''Brachyceratops'' has historically been known from juvenile remains, with one specimen having since been re-classified as ''Rubeosaurus ovatus''.Andrew T. McDonald & John R. Horner, (2010). "New Material of "Styracosaurus" ovatus from the Two Medicine Formation of Montana", In: Michael J. Ryan, Brenda J. Chinnery-Allgeier, and David A. Eberth (eds), ''New Perspectives on Horned Dinosaurs: The Royal Tyrrell Museum Ceratopsian Symposium'', Indiana University Press, 656 pp. History of discovery ''Brachyceratops montanensis'', the type species, was first discovered in the Two Medicine Formation (Campanian, about 74 million years old) on a Blackfoot Indian Reservation in Teton County in north-central Montana."Brachyceratops." In: Dodson, Peter & Britt, Brooks & Carpenter, Kenneth & Forster ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
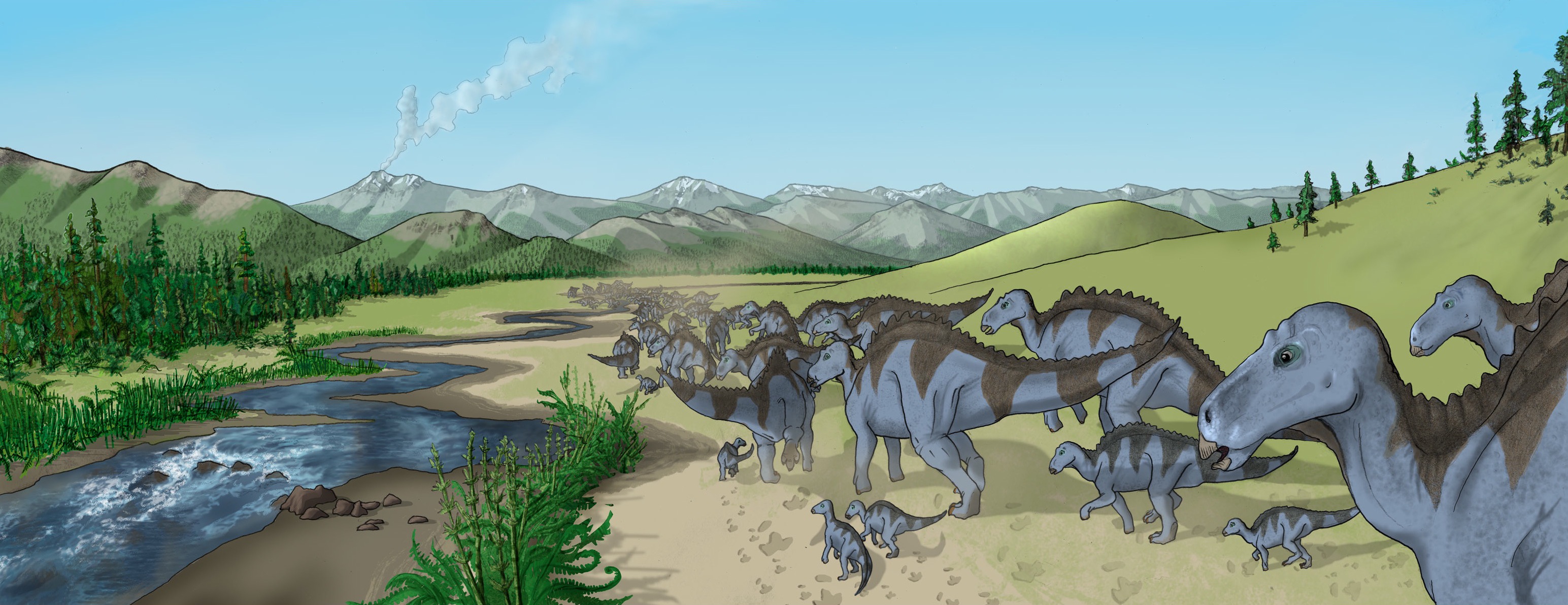
Brachyceratops BW
''Brachyceratops'' ('short horned face') is a dubious genus of ceratopsian dinosaur known only from partial juvenile specimens dating to the late Cretaceous Period of Montana, United States. ''Brachyceratops'' has historically been known from juvenile remains, with one specimen having since been re-classified as ''Rubeosaurus ovatus''.Andrew T. McDonald & John R. Horner, (2010). "New Material of "Styracosaurus" ovatus from the Two Medicine Formation of Montana", In: Michael J. Ryan, Brenda J. Chinnery-Allgeier, and David A. Eberth (eds), ''New Perspectives on Horned Dinosaurs: The Royal Tyrrell Museum Ceratopsian Symposium'', Indiana University Press, 656 pp. History of discovery ''Brachyceratops montanensis'', the type species, was first discovered in the Two Medicine Formation (Campanian, about 74 million years old) on a Blackfoot Indian Reservation in Teton County in north-central Montana."Brachyceratops." In: Dodson, Peter & Britt, Brooks & Carpenter, Kenneth & Forster ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoclonius
''Monoclonius'' (meaning "single sprout") is a dubious genus of herbivorous ceratopsian dinosaur found in the Late Cretaceous layers of the Judith River Formation in Montana, United States, and the uppermost rock layers of the Dinosaur Park Formation in Alberta, Canada dated to between 75 and 74.6 million years ago. ''Monoclonius'' was named by Edward Drinker Cope in 1876. Later, much taxonomic confusion was caused by the discovery of ''Centrosaurus'', a very similar genus of ceratopsian that is known from much better remains. Today, typical ''Monoclonius'' specimens are usually believed to be juveniles or subadults, in many cases of other genera such as ''Centrosaurus''. Those specimens that remain under the name ''Monoclonius'' are mostly too incomplete or immature to be confidently matched with adult specimens from the same time and place. This is especially true of the type species, ''Monoclonius crassus''. Therefore, ''Monoclonius'' is now usually considered a '' nomen dubiu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Whitney Gilmore
Charles Whitney Gilmore (March 11, 1874 – September 27, 1945) was an American paleontologist who gained renown in the early 20th century for his work on vertebrate fossils during his career at the United States National Museum (now the National Museum of Natural History). Gilmore named many dinosaurs in North America and Mongolia, including the Cretaceous sauropod '' Alamosaurus'', ''Alectrosaurus'', ''Archaeornithomimus'', ''Bactrosaurus'', ''Brachyceratops'', ''Chirostenotes'', '' Mongolosaurus'', ''Parrosaurus'', ''Pinacosaurus'', '' Styracosaurus ovatus'' (now ''Rubeosaurus'') and ''Thescelosaurus''. Career Gilmore was working as a paleontologist for the Carnegie Museum of Natural History in 1901 when he found the skeleton of a young sauropod, which was classified the following year as an ''Apatosaurus''. In 1903 Gilmore was hired by the United States National Museum (now the National Museum of Natural History), part of the Smithsonian Institution. His first assignme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rubeosaurus
''Styracosaurus'' ( ; meaning "spiked lizard" from the Ancient Greek / "spike at the butt-end of a spear-shaft" and / "lizard") is a genus of herbivorous ceratopsian dinosaur from the Cretaceous Period (Campanian stage), about 75.5 to 74.5 million years ago. It had four to six long parietal spikes extending from its neck frill, a smaller jugal horn on each of its cheeks, and a single horn protruding from its nose, which may have been up to long and wide. The function or functions of the horns and frills have been debated for many years. ''Styracosaurus'' was a relatively large dinosaur, reaching lengths of and weighing about . It stood about tall. ''Styracosaurus'' possessed four short legs and a bulky body. Its tail was rather short. The skull had a beak and shearing cheek teeth arranged in continuous dental batteries, suggesting that the animal sliced up plants. Like other ceratopsians, this dinosaur may have been a herd animal, travelling in large groups, as sugges ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two Medicine Formation
The Two Medicine Formation is a geological formation, or rock body, in northwestern Montana and southern Alberta that was deposited between and (million years ago), during Campanian (Late Cretaceous) time. It crops out to the east of the Rocky Mountain Overthrust Belt, and the western portion (about thick) of this formation is folded and faulted while the eastern part, which thins out into the Sweetgrass Arch, is mostly undeformed plains. Below the formation are the nearshore (beach and tidal zone) deposits of the Virgelle Sandstone, and above it is the marine Bearpaw Shale. Throughout the Campanian, the Two Medicine Formation was deposited between the western shoreline of the Late Cretaceous Interior Seaway and the eastward advancing margin of the Cordilleran Overthrust Belt. The Two Medicine Formation is mostly sandstone, deposited by rivers and deltas. History of research In 1913 in paleontology, 1913, a US Geological Survey crew headed by Eugene Stebinger and a US Nationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centrosaurinae
Centrosaurinae (from the Greek, meaning "pointed lizards") is a subfamily of ceratopsid dinosaurs, a group of large quadrupedal ornithischians. Centrosaurine fossil remains are known primarily from the northern region of Laramidia (modern day Alberta, Montana, and Alaska) but isolated taxa have been found in China and Utah as well. Defining features of centrosaurines include a large nasal horn, short supratemporal horns, and an ornamented frill projecting from the back of the skull. With the exception of ''Centrosaurus apertus'', all adult centrosaurines have spike-like ornaments midway up the skull. Morphometric analysis shows that centrosaurines differ from other ceratopsian groups in skull, snout, and frill shapes. There is evidence to suggest that male centrosaurines had an extended period of adolescence, and sexual ornamentation did not appear until adulthood. Centrosaurinae was named by paleontologist Lawrence Lambe in 1915, with ''Centrosaurus'' as the type genus. The cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triceratops
''Triceratops'' ( ; ) is a genus of herbivore, herbivorous Chasmosaurinae, chasmosaurine Ceratopsidae, ceratopsid dinosaur that first appeared during the late Maastrichtian stage of the Late Cretaceous Period (geology), period, about 68 million years ago in what is now North America. It is one of the last-known non-avian dinosaur genera, and became extinct in the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event, Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event 66 million years ago. The name ''Triceratops'', which literally means 'three-horned face', is derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek words () meaning 'three', () meaning 'horn', and () meaning 'face'. Bearing a large bony neck frill, frill, three horn (anatomy), horns on the skull, and a large four-legged body, exhibiting convergent evolution with rhinoceroses and bovines, ''Triceratops'' is one of the most recognizable of all dinosaurs and the most well-known ceratopsid. It was also one of the largest, up to long and in body m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceratopsians
Ceratopsia or Ceratopia ( or ; Greek: "horned faces") is a group of herbivorous, beaked dinosaurs that thrived in what are now North America, Europe, and Asia, during the Cretaceous Period, although ancestral forms lived earlier, in the Jurassic. The earliest known ceratopsian, ''Yinlong downsi'', lived between 161.2 and 155.7 million years ago.Holtz, Thomas R. Jr. (2011) ''Dinosaurs: The Most Complete, Up-to-Date Encyclopedia for Dinosaur Lovers of All Ages,'Winter 2010 Appendix./ref> The last ceratopsian species, ''Triceratops prorsus'', became extinct during the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, . ''Triceratops'' is by far the best-known ceratopsian to the general public. It is traditional for ceratopsian genus names to end in "''-ceratops''", although this is not always the case. One of the first named genera was ''Ceratops'' itself, which lent its name to the group, although it is considered a ''nomen dubium'' today as its fossil remains have no distinguishing characte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Washington D
Washington commonly refers to: * Washington (state), United States * Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States ** A metonym for the federal government of the United States ** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered on Washington, D.C. * George Washington (1732–1799), the first president of the United States Washington may also refer to: Places England * Washington, Tyne and Wear, a town in the City of Sunderland metropolitan borough ** Washington Old Hall, ancestral home of the family of George Washington * Washington, West Sussex, a village and civil parish Greenland * Cape Washington, Greenland * Washington Land Philippines *New Washington, Aklan, a municipality *Washington, a barangay in Catarman, Northern Samar *Washington, a barangay in Escalante, Negros Occidental *Washington, a barangay in San Jacinto, Masbate *Washington, a barangay in Surigao City United States * Washington, Wisconsin (other) * Fort Washington (disambiguatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smithsonian Institution
The Smithsonian Institution ( ), or simply the Smithsonian, is a group of museums and education and research centers, the largest such complex in the world, created by the U.S. government "for the increase and diffusion of knowledge". Founded on August 10, 1846, it operates as a trust instrumentality and is not formally a part of any of the three branches of the federal government. The institution is named after its founding donor, British scientist James Smithson. It was originally organized as the United States National Museum, but that name ceased to exist administratively in 1967. Called "the nation's attic" for its eclectic holdings of 154 million items, the institution's 19 museums, 21 libraries, nine research centers, and zoo include historical and architectural landmarks, mostly located in the District of Columbia. Additional facilities are located in Maryland, New York, and Virginia. More than 200 institutions and museums in 45 states,States without Smithsonian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |