|
Boyacá Department
Boyacá () is one of the thirty-two departments of Colombia, and the remnant of Boyacá State, one of the original nine states of the "United States of Colombia". Boyacá is centrally located within Colombia, almost entirely within the mountains of the Eastern Cordillera to the border with Venezuela, although the western end of the department extends to the Magdalena River at the town of Puerto Boyacá. Boyacá borders to the north with the Department of Santander, to the northeast with the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela and Norte de Santander, to the east with the departments of Arauca and Casanare. To the south, Boyacá borders the department of Cundinamarca and to the west with the Department of Antioquia covering a total area of . The capital of Boyacá is the city of Tunja. Boyacá is known as "The Land of Freedom" because this region was the scene of a series of battles which led to Colombia's independence from Spain. The first one took place on 25 July 1819 in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Departments Of Colombia
Colombia is a unitary state, unitary republic made up of thirty-two departments (Spanish language, Spanish: ''departamentos'', sing. ''departamento'') and a Capital District (''Capital districts and territories, Distrito Capital''). Each department has a governor (''gobernador'') and an Assembly (''Asamblea Departamental''), elected by popular vote for a four-year period. The governor cannot be re-elected in consecutive periods. Departments are administrative division, country subdivisions and are granted a certain degree of autonomy. Departments are formed by a grouping of municipalities of Colombia, municipalities (''municipios'', sing. ''municipio''). Municipal government is headed by mayor (''alcalde'') and administered by a municipal council (''concejo municipal''), both of which are elected for four-year periods. Some departments have subdivisions above the level of municipalities, commonly known as provinces of Colombia, provinces. Chart of departments Each one of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
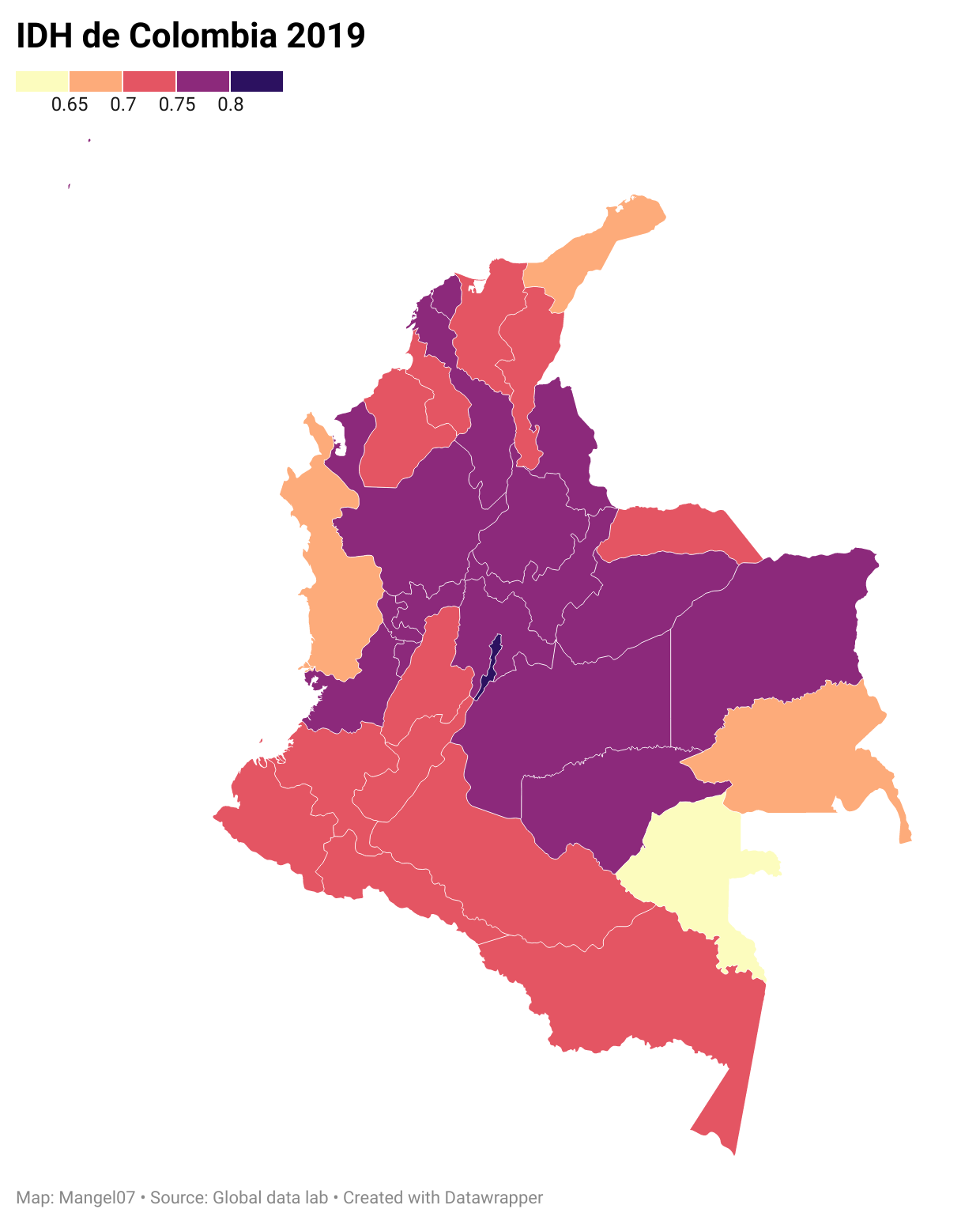
List Of Colombian Departments By Human Development Index ...
This is a list of Colombian departments and the capital district of Bogota by Human Development Index as of 2020 with data for the year 2019. See also *List of countries by Human Development Index References {{reflist Human Development Index Colombia Colombia Colombia (, ; ), officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with insular regions in North America—near Nicaragua's Caribbean coast—as well as in the Pacific Ocean. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casanare Department
Casanare Department (, es, Departamento de Casanare) is a department in the central eastern region of Colombia. Its capital is Yopal, which is also the episcopal seat of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Yopal. It contains oil fields and an 800 km pipeline leading to the coastal port of Coveñas owned by BP. Rivers and dams The Upía River (Río Upía) is in Casanare. History A former subregion of Boyacá, Casanare became separate department in 1973. Municipalities # Aguazul # Chámeza # Hato Corozal # La Salina # Maní # Monterrey # Nunchía # Orocué # Paz de Ariporo # Pore # Recetor # Sabanalarga # Sácama # San Luis de Palenque # Támara # Tauramena # Trinidad # Villanueva # Yopal, capital See also * Apostolic Vicariate of Casanare * Casanare Province (historical) * Casanare River Casanare River () is a river in Colombia. It is part of the Orinoco River basin. See also *List of rivers of Colombia Atlantic Ocean Amazon River Basin * Ama ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arauca Department
Arauca () is a department of Eastern Colombia located in the extreme north of the Orinoco Basin of Colombia (the Llanos Orientales), bordering Venezuela. The southern boundary of Arauca is formed by the Casanare and Meta Rivers, separating Arauca from the departments of Casanare and Vichada. To the west, Arauca borders the department of Boyacá. The Caño Limón oil fields located within Arauca account for almost a third of the Colombian oil output. Its capital is the town of Arauca. Etymology The name Arauca is believed to derive from the name of an Indigenous people, who are thought to be related to the Arawak or Arhuaco people. Some have also speculated that the name Arauca is connected with the Araucanian or Mapuche Indians of Chile and Argentina. History The first conquistador to set foot in the region of present-day Arauca was Nikolaus Federmann in 1539. He was first a soldier in the company of Georg von Speyer, who passed through the south of present Venezu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norte De Santander
North Santander (Spanish: Norte de Santander) () is a department of Northeastern Colombia. It is in the north of the country, bordering Venezuela. Its capital is Cúcuta, one of the country's major cities. North Santander is bordered by Venezuela to the east and north, by Santander Department and Boyacá Department to the south, and by Santander Department and Cesar Department to the west. The official Department name is "''Departamento de Norte de Santander''" (North Santander Department) in honor of Colombian military and political leader Francisco de Paula Santander, who was born and raised near Cúcuta. North Santander Department is located in the northwestern zone of the Colombian Andean Region. The area of present-day Norte de Santander played an important role in the history of Colombia, during the War of Independence from Spain when Congress gave origin to the Greater Colombia in Villa del Rosario. History Pre-Colombian The jungle zone and the valleys of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolivarian Republic Of Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in the Caribbean Sea. It has a territorial extension of , and its population was estimated at 29 million in 2022. The capital and largest urban agglomeration is the city of Caracas. The continental territory is bordered on the north by the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean, on the west by Colombia, Brazil on the south, Trinidad and Tobago to the north-east and on the east by Guyana. The Venezuelan government maintains a claim against Guyana to Guayana Esequiba. Venezuela is a federal presidential republic consisting of 23 states, the Capital District and federal dependencies covering Venezuela's offshore islands. Venezuela is among the most urbanized countries in Latin America; the vast majority of Venezuelans live in the cities of the nort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puerto Boyacá, Boyacá
{{disambiguation, geo ...
Puerto, a Spanish word meaning ''seaport'', may refer to: Places *El Puerto de Santa María, Andalusia, Spain *Puerto, a seaport town in Cagayan de Oro City, Philippines *Puerto Colombia, Colombia *Puerto Cumarebo, Venezuela *Puerto Galera, Oriental Mindoro, Philippines * Puerto La Cruz, Venezuela *Puerto Píritu, Venezuela *Puerto Princesa, Palawan, Philippines *Puerto Rico, an unincorporated territory of the United States *Puerto Vallarta, Mexico Others * ''Puerto Rico'' (board game) *Operación Puerto doping case See also * * Puerta (other) Puerta refers to the old original gates of the Walled City of Intramuros in Manila. Puerta may also refer to: People *Antonio Puerta, Spanish footballer *Alonso José Puerta, Spanish politician *Lina Puerta, American artist *Mariano Puerta, Argent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magdalena River
The Magdalena River ( es, Río Magdalena, ; less commonly ) is the main river of Colombia, flowing northward about through the western half of the country. It takes its name from the biblical figure Mary Magdalene. It is navigable through much of its lower reaches, in spite of the shifting sand bars at the mouth of its delta, as far as Honda, at the downstream base of its rapids. It flows through the Magdalena River Valley. Its drainage basin covers a surface of , which is 24% of the country's area and where 66% of its population lives. Course The Magdalena River is the largest river system of the northern Andes, with a length of 1,612 km. Its headwaters are in the south of Colombia, where the Andean subranges Cordillera Central and Cordillera Oriental separate, in Huila Department. The river runs east then north in a great valley between the two cordilleras. It reaches the coastal plain at about nine degrees north, then runs west for about , then north again, reaching th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in the Caribbean Sea. It has a territorial extension of , and its population was estimated at 29 million in 2022. The capital and largest urban agglomeration is the city of Caracas. The continental territory is bordered on the north by the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean, on the west by Colombia, Brazil on the south, Trinidad and Tobago to the north-east and on the east by Guyana. The Venezuelan government maintains a claim against Guyana to Guayana Esequiba. Venezuela is a federal presidential republic consisting of 23 states, the Capital District and federal dependencies covering Venezuela's offshore islands. Venezuela is among the most urbanized countries in Latin America; the vast majority of Venezuelans live in the cities of the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cordillera Oriental, Colombia
The Cordillera Oriental ( en, Eastern Ranges) is the widest of the three branches of the Colombian Andes. The range extends from south to north dividing from the Colombian Massif in Huila Department to Norte de Santander Department where it splits into the Serranía del Perijá and the Cordillera de Mérida in Venezuelan Andes. The highest peak is Ritacuba Blanco at in the Sierra Nevada del Cocuy. Geography The western part of the Cordillera Oriental belongs to the Magdalena River basin, while the eastern part includes the river basins of the Amazon River, Orinoco River, and Catatumbo River. Within it, the Altiplano Cundiboyacense and the Sierra Nevada del Cocuy (with the only snowy peaks in this mountain range) stand out. The mountain range contains the most páramos in the world. Protected areas * Cueva de los Guácharos * Chingaza National Natural Park * Yariguíes National Park * Sierra Nevada del Cocuy * Sumapaz Páramo * Tamá National Natural Park * Los Estoraques ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited Summit (topography), summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least 300 metres (1,000 feet) above the surrounding land. A few mountains are Monadnock, isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountain formation, Mountains are formed through Tectonic plate, tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through Slump (geology), slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce Alpine climate, colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the Montane ecosystems, ecosys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |