|
Bourn Hall Clinic
Bourn Hall Clinic in Bourn, Cambridgeshire, England, is a centre for the treatment of infertility. The original building, Bourn Hall, is about 400 years old. Since becoming a medical centre, it has been greatly extended. History Bourn Hall Clinic was founded in 1980 by IVF pioneers Mr Patrick Steptoe, embryologist Jean Purdy and Professor Robert Edwards, who were responsible for the conception of Louise Brown, the world's first IVF or test-tube baby in 1977. Since its foundation the clinic has assisted in the conception of over 10,000 babies. Following the death of Patrick Steptoe in 1988, Peter Brinsden was appointed Medical Director in March 1989. Bourn Hall Clinic is one of five fertility centres selected by the NHS East of England Specialised Commissioning Group to provide treatment to patients in the region. As of 1 May 2009, childless couples in Cambridgeshire, Norfolk, Suffolk, Essex, Bedfordshire and Hertfordshire will be able to access up to three cycles of IVF, pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bourn
Bourn is a small village and civil parish in South Cambridgeshire, England. Surrounding villages include Caxton, Eltisley and Cambourne. It is 8 miles (12 km) from the county town of Cambridge. The population of the parish was 1,015 people at the time of the 2011 census. Bourn has a Church of England primary school, a doctors' surgery, the Church of St. Mary & St. Helena, a golf club, a former Royal Air Force bomber airfield (RAF Station Bourn 1940–1945), which today is used for light aircraft, and an old windmill. Bourn Hall Clinic, the centre for infertility treatment founded in 1980 by IVF pioneers Mr Patrick Steptoe and Professor Robert Edwards, who were responsible for the conception of Louise Brown, the world's first IVF or test-tube baby in 1978, is also located here. Since its foundation the clinic has assisted in the conception of over 10,000 babies. A small stream called Bourn Brook runs through the village, eventually joining the River Cam. History The name B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hertfordshire
Hertfordshire ( or ; often abbreviated Herts) is one of the home counties in southern England. It borders Bedfordshire and Cambridgeshire to the north, Essex to the east, Greater London to the south, and Buckinghamshire to the west. For government statistical purposes, it forms part of the East of England region. Hertfordshire covers . It derives its name – via the name of the county town of Hertford – from a hart (stag) and a ford, as represented on the county's coat of arms and on the flag. Hertfordshire County Council is based in Hertford, once the main market town and the current county town. The largest settlement is Watford. Since 1903 Letchworth has served as the prototype garden city; Stevenage became the first town to expand under post-war Britain's New Towns Act of 1946. In 2013 Hertfordshire had a population of about 1,140,700, with Hemel Hempstead, Stevenage, Watford and St Albans (the county's only ''city'') each having between 50,000 and 100,000 r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
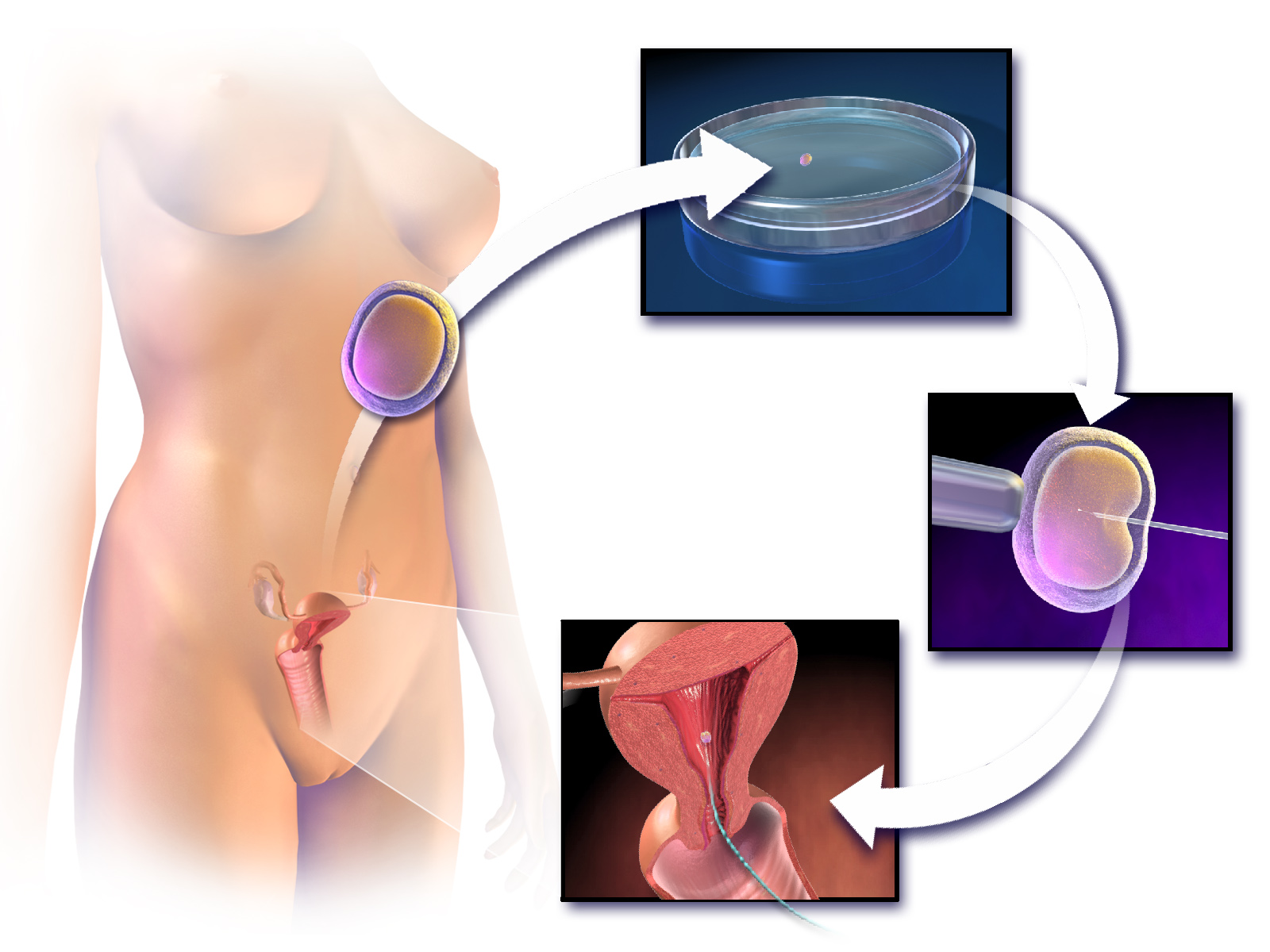
In Vitro Fertilisation
In vitro fertilisation (IVF) is a process of fertilisation where an egg is combined with sperm in vitro ("in glass"). The process involves monitoring and stimulating an individual's ovulatory process, removing an ovum or ova (egg or eggs) from their ovaries and letting sperm fertilise them in a culture medium in a laboratory. After the fertilised egg (zygote) undergoes embryo culture for 2–6 days, it is transferred by catheter into the uterus, with the intention of establishing a successful pregnancy. IVF is a type of assisted reproductive technology used for infertility treatment, gestational surrogacy, and, in combination with pre-implantation genetic testing, avoiding transmission of genetic conditions. A fertilised egg from a donor may implant into a surrogate's uterus, and the resulting child is genetically unrelated to the surrogate. Some countries have banned or otherwise regulate the availability of IVF treatment, giving rise to fertility tourism. Restrictions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obstetrics And Gynaecology Organizations
Obstetrics is the field of study concentrated on pregnancy, childbirth and the postpartum period. As a medical specialty, obstetrics is combined with gynecology under the discipline known as obstetrics and gynecology (OB/GYN), which is a surgical field. Main areas Prenatal care Prenatal care is important in screening for various complications of pregnancy. This includes routine office visits with physical exams and routine lab tests along with telehealth care for women with low-risk pregnancies: Image:Ultrasound_image_of_a_fetus.jpg, 3D ultrasound of fetus (about 14 weeks gestational age) Image:Sucking his thumb and waving.jpg, Fetus at 17 weeks Image:3dultrasound 20 weeks.jpg, Fetus at 20 weeks First trimester Routine tests in the first trimester of pregnancy generally include: * Complete blood count * Blood type ** Rh-negative antenatal patients should receive RhoGAM at 28 weeks to prevent Rh disease. * Indirect Coombs test (AGT) to assess risk of hemolytic disea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Research Institutes In The United Kingdom
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness. Contemporary medicine applies biomedical sciences, biomedical research, genetics, and medical technology to diagnose, treat, and prevent injury and disease, typically through pharmaceuticals or surgery, but also through therapies as diverse as psychotherapy, external splints and traction, medical devices, biologics, and ionizing radiation, amongst others. Medicine has been practiced since prehistoric times, and for most of this time it was an art (an area of skill and knowledge), frequently having connections to the religious and philosophical beliefs of local culture. For example, a medicine man would apply herbs and say prayers for healing, or an ancie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal College Of Pathologists
The Royal College of Pathologists (RCPath) is a professional membership organisation. Its main function is the overseeing of postgraduate training, and its Fellowship Examination (FRCPath) is recognised as the standard assessment of fitness to practise in this branch of medicine. Constitution The Royal College of Pathologists is a professional membership organisation, to maintain the standards and reputation of British pathology, through training, assessments, examinations and professional development. It is a registered charity and is not a trades union. Its 11,000 members work in hospital laboratories, universities and industry worldwide. History The College of Pathologists was founded in 1962, to optimise postgraduate training in the relatively young science of pathology, with its high importance in the diagnostic process, and the increasing range of specialist studies within it. The College received its Royal Charter in 1970 and its Patron is Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oldham Chronicle
The ''Oldham Evening Chronicle'' was a daily newspaper published each weekday evening. It served the Metropolitan Borough of Oldham, in Greater Manchester, England. There were also four sister editions, called the ''Oldham Extra'', ''Saddleworth Extra'', ''Tameside Extra'' and ''Dale Times'', which were published on the first Thursday of each month. The paper was owned by Hirst, Kidd and Rennie Ltd. In February 2018, the main Evening Chronicle title relaunched online after it was bought by a local radio station. History On 6 May 1854, the first edition of the ''Oldham Chronicle'' (as it was originally known) was published by a bookseller and printer Daniel Evans in an effort to provide the then thriving cotton manufacturing town of Oldham with its own locally produced newspaper. Oldham was enjoying rapid economic expansion thanks to the Industrial Revolution, but local communities had to rely on Manchester papers for news about the town and surrounding districts. The ''Oldham Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nobel Prize In Physiology Or Medicine
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine is awarded yearly by the Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institute for outstanding discoveries in physiology or medicine. The Nobel Prize is not a single prize, but five separate prizes that, according to Alfred Nobel's 1895 will, are awarded "to those who, during the preceding year, have conferred the greatest benefit to humankind". Nobel Prizes are awarded in the fields of Physics, Chemistry, Physiology or Medicine, Literature, and Peace. The Nobel Prize is presented annually on the anniversary of Alfred Nobel's death, 10 December. As of 2022, 114 Nobel Prizes in Physiology or Medicine have been awarded to 226 laureates, 214 men and 12 women. The first one was awarded in 1901 to the German physiologist, Emil von Behring, for his work on serum therapy and the development of a vaccine against diphtheria. The first woman to receive the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, Gerty Cori, received it in 1947 for her role in elucidati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blastocyst
The blastocyst is a structure formed in the early embryonic development of mammals. It possesses an inner cell mass (ICM) also known as the ''embryoblast'' which subsequently forms the embryo, and an outer layer of trophoblast cells called the trophectoderm. This layer surrounds the inner cell mass and a fluid-filled cavity known as the blastocoel. In the late blastocyst the trophectoderm is known as the trophoblast. The trophoblast gives rise to the chorion and amnion, the two fetal membranes that surround the embryo. The placenta derives from the embryonic chorion (the portion of the chorion that develops villi) and the underlying uterine tissue of the mother. The name "blastocyst" arises from the Greek ' ("a sprout") and ' ("bladder, capsule"). In other animals this is a structure consisting of an undifferentiated ball of cells and is called a blastula. In humans, blastocyst formation begins about five days after fertilization when a fluid-filled cavity opens up in the mor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection
Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI ) is an in vitro fertilization (IVF) procedure in which a single sperm cell is injected directly into the cytoplasm of an egg. This technique is used in order to prepare the gametes for the obtention of embryos that may be transferred to a maternal uterus. With this method, the acrosome reaction is skipped. There are several differences between classic IVF and ICSI. However, the steps to be followed before and after insemination are the same. In terms of insemination, ICSI needs only one sperm cell per oocyte, while IVF needs 50,000–100,000. This is because the acrosome reaction has to take place and thousands of sperm cells have to be involved in IVF. Once fertilized, the egg is transformed into a pre-embryo and it has to be transferred to the uterus to continue its development. The first human pregnancy generated by ICSI was carried out in 1991 by Gianpiero Palermo and his team. Round spermatid injection (ROSI) Round spermatid inject ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surrogacy
Surrogacy is an arrangement, often supported by a legal agreement, whereby a woman agrees to delivery/labour for another person or people, who will become the child's parent(s) after birth. People may seek a surrogacy arrangement when pregnancy is medically impossible, when pregnancy risks are dangerous for the intended mother, or when a single man or a male couple wish to have a child. In surrogacy arrangements, monetary compensation may or may not be involved. Receiving money for the arrangement is known as commercial surrogacy. The legality and cost of surrogacy varies widely between jurisdictions, sometimes resulting in problematic international or interstate surrogacy arrangements. Couples seeking a surrogacy arrangement in a country where it is banned sometimes travel to a jurisdiction that permits it. In some countries, surrogacy is legal only if money does not exchange hands. Where commercial surrogacy is legal, couples may use the help of third-party agencies to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryobiology
Cryobiology is the branch of biology that studies the effects of low temperatures on living things within Earth's cryosphere or in science. The word cryobiology is derived from the Greek words κρῧος ryos "cold", βίος ios "life", and λόγος ogos "word". In practice, cryobiology is the study of biological material or systems at temperatures below normal. Materials or systems studied may include proteins, cells, tissues, organs, or whole organisms. Temperatures may range from moderately hypothermic conditions to cryogenic temperatures. Areas of study At least six major areas of cryobiology can be identified: 1) study of cold-adaptation of microorganisms, plants ( cold hardiness), and animals, both invertebrates and vertebrates (including hibernation), 2) cryopreservation of cells, tissues, gametes, and embryos of animal and human origin for (medical) purposes of long-term storage by cooling to temperatures below the freezing point of water. This usually requires the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |