|
Bountyphaps
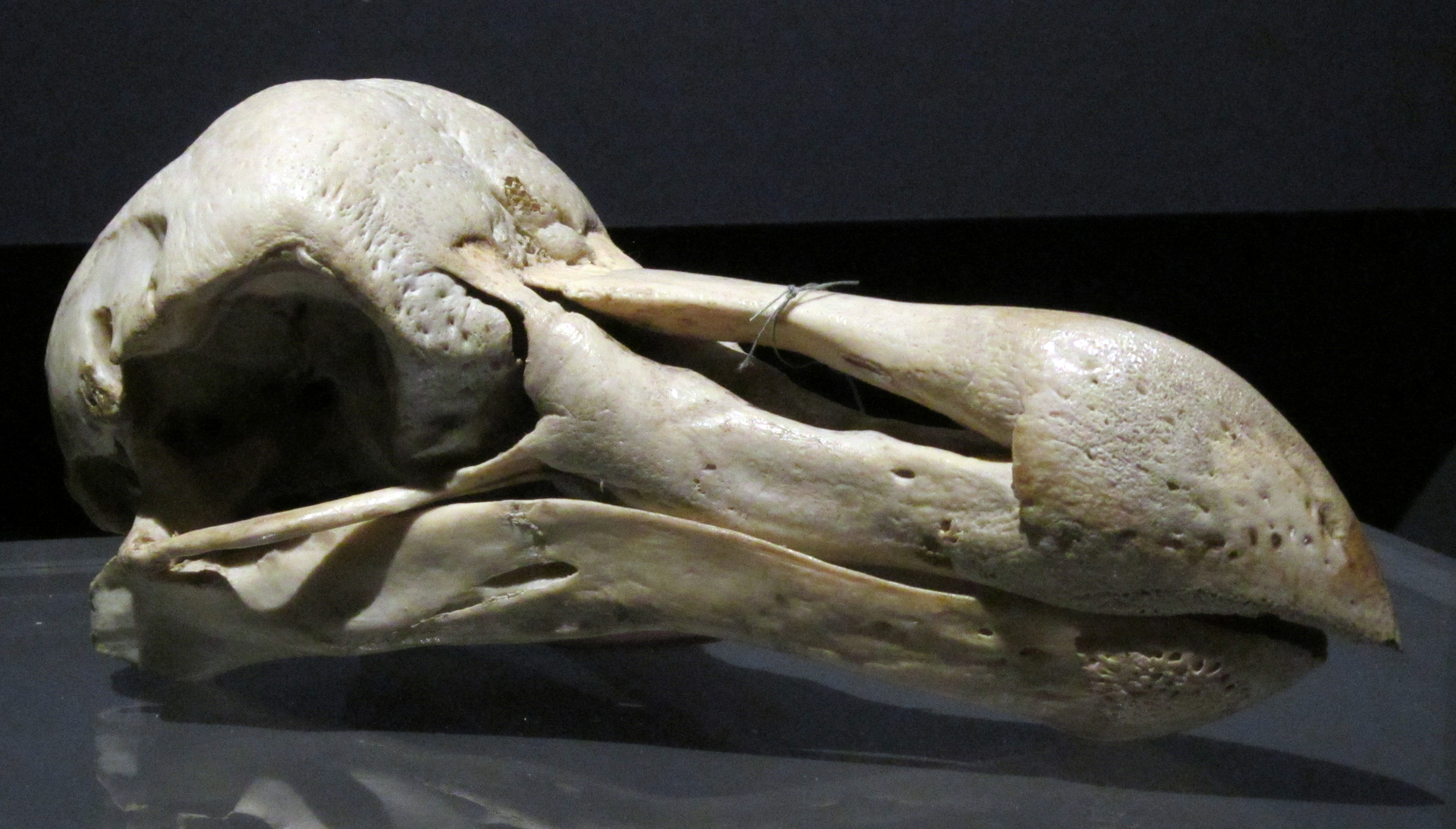
''Bountyphaps obsoleta'' is an extinct species of pigeon. It was described in 2008 as a new genus and species from subfossil remains found on Henderson Island in the Pitcairn Group of southeastern Polynesia. Additionally, an indeterminate species, possibly the same as ''B. obsoleta'', has been found in the Gambier archipelago. Etymology The genus was named for both the ship HMS ''Bounty'' with which, following the famous mutiny, Europeans first discovered the Pitcairn Islands, and for the former bounty the bird provided as food; with the Greek ''phaps'' (wild pigeon). The specific epithet comes from the Latin adjective for "extinct" or "forgotten about".Worthy & Wragg, p.505. Description and taxonomy The species was a large pigeon, comparable in size to large species of ''Columba'' or ''Ducula'', and larger than the other three species of pigeon it coexisted with on the island. It had relatively small wings for its body size, suggesting that it was a weak flier, though not f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Quaternary Prehistoric Birds
Late Quaternary prehistoric birds are avian taxa that became extinct during the Late Quaternary – the Holocene or Late Pleistocene – and before recorded history, or more precisely, before they could be studied alive by ornithological science. They became extinct before the period of global scientific exploration that started in the late 15th century. In other words, this list basically deals with extinctions between 40,000 BC and 1500 AD. For the purposes of this article, a "bird" is any member of the clade Neornithes, that is, any descendant of the most recent common ancestor of all currently living birds. The birds are known from their remains, which are subfossil (not fossilized, or not completely fossilized). Some are also known from folk memory, as in the case of Haast's eagle in New Zealand. As the remains are not completely fossilized, they may yield organic material for molecular analyses to provide additional clues for resolving their taxonomic affil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pigeon
Columbidae () is a bird family consisting of doves and pigeons. It is the only family in the order Columbiformes. These are stout-bodied birds with short necks and short slender bills that in some species feature fleshy ceres. They primarily feed on seeds, fruits, and plants. The family occurs worldwide, but the greatest variety is in the Indomalayan and Australasian realms. The family contains 344 species divided into 50 genera. Thirteen of the species are extinct. In English, the smaller species tend to be called "doves" and the larger ones "pigeons". However, the distinction is not consistent, and does not exist in most other languages. Historically, the common names for these birds involve a great deal of variation between the terms. The bird most commonly referred to as just "pigeon" is the domestic pigeon, which is common in many cities as the feral pigeon. Doves and pigeons build relatively flimsy nests, often using sticks and other debris, which may be placed on bra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Columbidae
Columbidae () is a bird family consisting of doves and pigeons. It is the only family in the order Columbiformes. These are stout-bodied birds with short necks and short slender bills that in some species feature fleshy ceres. They primarily feed on seeds, fruits, and plants. The family occurs worldwide, but the greatest variety is in the Indomalayan and Australasian realms. The family contains 344 species divided into 50 genera. Thirteen of the species are extinct. In English, the smaller species tend to be called "doves" and the larger ones "pigeons". However, the distinction is not consistent, and does not exist in most other languages. Historically, the common names for these birds involve a great deal of variation between the terms. The bird most commonly referred to as just "pigeon" is the domestic pigeon, which is common in many cities as the feral pigeon. Doves and pigeons build relatively flimsy nests, often using sticks and other debris, which may be placed on bra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holocene
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene together form the Quaternary period. The Holocene has been identified with the current warm period, known as MIS 1. It is considered by some to be an interglacial period within the Pleistocene Epoch, called the Flandrian interglacial.Oxford University Press – Why Geography Matters: More Than Ever (book) – "Holocene Humanity" section https://books.google.com/books?id=7P0_sWIcBNsC The Holocene corresponds with the rapid proliferation, growth and impacts of the human species worldwide, including all of its written history, technological revolutions, development of major civilizations, and overall significant transition towards urban living in the present. The human impact on modern-era Earth and its ecosystems may be considered of global si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ducula
''Ducula'' is a genus of the pigeon family Columbidae, collectively known as imperial pigeons. They are large to very large pigeons with a heavy build and medium to long tails. They are arboreal, feed mainly on fruit and are closely related to the other genus of fruit-eating doves, ''Ptilinopus''. Both genera display brightly coloured plumage, predominantly green, often with contrasting under-parts of purple, orange or red. Some ''Ducula'' have prominently swollen ceres. They have large gapes and swallow seeds whole, playing an important role in seed dispersal. Imperial pigeons are found in forests of southern Asia, New Guinea, northern Australia and the Pacific islands. Many species are nomadic, travelling long distances to exploit seasonal fruit sources. Some undertake migrations and all are strong fliers. Because of habitat loss and predation, species of ''Ducula'' are amongst the most threatened of avian species globally. Taxonomy The genus ''Ducula'' was introduced in 183 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holocene Extinctions
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene together form the Quaternary period. The Holocene has been identified with the current warm period, known as MIS 1. It is considered by some to be an interglacial period within the Pleistocene Epoch, called the Flandrian interglacial.Oxford University Press – Why Geography Matters: More Than Ever (book) – "Holocene Humanity" section https://books.google.com/books?id=7P0_sWIcBNsC The Holocene corresponds with the rapid proliferation, growth and impacts of the human species worldwide, including all of its written history, technological revolutions, development of major civilizations, and overall significant transition towards urban living in the present. The human impact on modern-era Earth and its ecosystems may be considered of global sig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extinct Birds Of Oceania
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and recover may have been lost before this point. Because a species' potential range may be very large, determining this moment is difficult, and is usually done retrospectively. This difficulty leads to phenomena such as Lazarus taxa, where a species presumed extinct abruptly "reappears" (typically in the fossil record) after a period of apparent absence. More than 99% of all species that ever lived on Earth, amounting to over five billion species, are estimated to have died out. It is estimated that there are currently around 8.7 million species of eukaryote globally, and possibly many times more if microorganisms, like bacteria, are included. Notable extinct animal species include non-avian dinosaurs, saber-toothed cats, dodos, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birds Of Henderson Island
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight skeleton. Birds live worldwide and range in size from the bee hummingbird to the ostrich. There are about ten thousand living species, more than half of which are passerine, or "perching" birds. Birds have whose development varies according to species; the only known groups without wings are the extinct moa and elephant birds. Wings, which are modified forelimbs, gave birds the ability to fly, although further evolution has led to the loss of flight in some birds, including ratites, penguins, and diverse endemic island species. The digestive and respiratory systems of birds are also uniquely adapted for flight. Some bird species of aquatic environments, particularly seabirds and some waterbirds, have further evolved for swimming. Birds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Era
Common Era (CE) and Before the Common Era (BCE) are year notations for the Gregorian calendar (and its predecessor, the Julian calendar), the world's most widely used calendar era. Common Era and Before the Common Era are alternatives to the original Anno Domini (AD) and Before Christ (BC) notations used for the same calendar era. The two notation systems are numerically equivalent: " CE" and "AD " each describe the current year; "400 BCE" and "400 BC" are the same year. The expression traces back to 1615, when it first appeared in a book by Johannes Kepler as the la, annus aerae nostrae vulgaris (), and to 1635 in English as " Vulgar Era". The term "Common Era" can be found in English as early as 1708, and became more widely used in the mid-19th century by Jewish religious scholars. Since the later 20th century, BCE and CE have become popular in academic and scientific publications because BCE and CE are religiously neutral terms. They are used by others who wish to be sensit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dodo
The dodo (''Raphus cucullatus'') is an extinct flightless bird that was endemic to the island of Mauritius, which is east of Madagascar in the Indian Ocean. The dodo's closest genetic relative was the also-extinct Rodrigues solitaire. The two formed the subfamily Raphinae, a clade of extinct flightless birds that were a part of the family which includes pigeons and doves. The closest living relative of the dodo is the Nicobar pigeon. A white dodo was once thought to have existed on the nearby island of Réunion, but it is now believed that this assumption was merely confusion based on the also-extinct Réunion ibis and paintings of white dodos. Subfossil remains show the dodo was about tall and may have weighed in the wild. The dodo's appearance in life is evidenced only by drawings, paintings, and written accounts from the 17th century. Since these portraits vary considerably, and since only some of the illustrations are known to have been drawn from live specimens, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tooth-billed Pigeon
The tooth-billed pigeon (''Didunculus strigirostris''), also known as the ''manumea'', is a large pigeon found only in Samoa. It is the only living species of genus ''Didunculus''. A related extinct species, the Tongan tooth-billed pigeon (''Didunculus placopedetes''), is only known from subfossil remains in several archeological sites in Tonga. The tooth-billed pigeon is the national bird of Samoa and featured on the 20 '' tālā'' bills and the 50 ''sene'' pieces of the 2008/2011 series. Native only to Samoa's primary rainforest, it is considered to be endangered, with only a few hundred individuals thought to remain in existence. Description The tooth-billed pigeon is a medium-sized, approximately 31 cm long, dark pigeon with reddish feet and red bare skin around the eye. The underparts, head and neck are greyish with a slight blue-green iridescence, and the tail, wings-coverts and tertials are rufous chestnut, while the remaining remiges are blackish. It has a larg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicobar Pigeon
The Nicobar pigeon (''Caloenas nicobarica'', Car: ') is a bird found on small islands and in coastal regions from the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India, east through the Malay Archipelago, to the Solomons and Palau. It is the only living member of the genus ''Caloenas'' alongside the extinct spotted green pigeon, and is the closest living relative of the extinct dodo and Rodrigues solitaire. Taxonomy In 1738, the English naturalist Eleazar Albin included a description and two illustrations of the Nicobar pigeon in his ''A Natural History of Birds''. When in 1758 the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus updated his ''Systema Naturae'' for the tenth edition, he placed the Nicobar pigeon with all the other pigeons in the genus ''Columba''. Linnaeus included a brief description, coined the binomial name ''Columba nicobarica'' and cited Albin's work. The species is now placed in the genus ''Caloenas'' erected by English zoologist George Robert Gray in 1840 with the Nicobar pigeon as th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)
.jpg)



