|
Botanical Provinces Of Western Australia
The ''botanical provinces of Western Australia (or Beard's Provinces)'' delineate "natural" phytogeographic regions of WA, based on climate and types of vegetation. John Stanley Beard, in "Plant Life of Western Australia" (p. 29-37) gives a short history of the various mappings. In 1906, Ludwig Diels divided the state into an Eremaean Province and a South-West Province (together with further subdivisions), based on rainfall ranges, types of vegetation, and species' distributions (Beard, 2015:p. 30). In 1944, C.A. Gardner modified Diels' description, adding the Northern Province, which comprised the Kimberley and Pilbara districts. With Bennetts in 1956, he further refined this to give state-wide divisions. Subsequent work by Beard and others gave the current set of provinces used by Florabase in its descriptions of plants. (See, for example, the entry where ''Parsonsia diaphanophleba'' is described as being found in Beard's South-West Province.) ''Beard's provi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
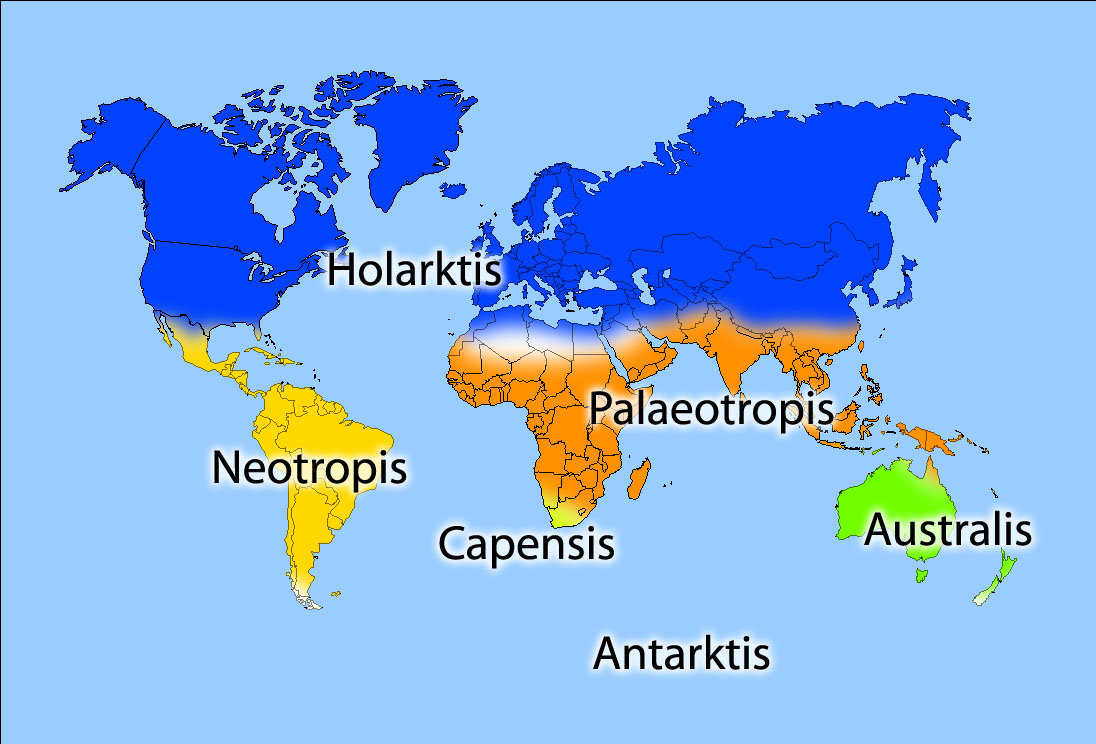
Phytogeographic
Phytogeography (from Greek φυτόν, ''phytón'' = "plant" and γεωγραφία, ''geographía'' = "geography" meaning also distribution) or botanical geography is the branch of biogeography that is concerned with the geographic distribution of plant species and their influence on the earth's surface. Phytogeography is concerned with all aspects of plant distribution, from the controls on the distribution of individual species ranges (at both large and small scales, see species distribution) to the factors that govern the composition of entire communities and floras. Geobotany, by contrast, focuses on the geographic space's influence on plants. Fields Phytogeography is part of a more general science known as biogeography. Phytogeographers are concerned with patterns and process in plant distribution. Most of the major questions and kinds of approaches taken to answer such questions are held in common between phyto- and zoogeographers. Phytogeography in wider sense (or geobot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
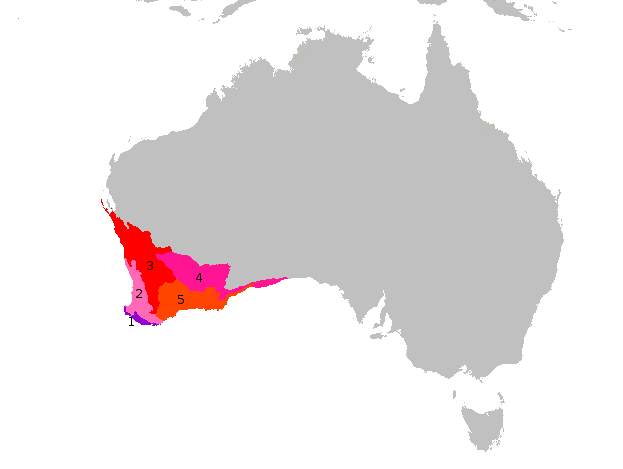
Mallee (biogeographic Region)
Mallee, also known as Roe Botanical District, is a biogeographic region in southern Western Australia. Located between the Esperance Plains, Avon Wheatbelt and Coolgardie bioregions, it has a low, gently undulating topography, a semi-arid mediterranean climate, and extensive ''Eucalyptus'' mallee vegetation. It has an area of . About half of the region has been cleared for intensive agriculture. Recognised as a region under the Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia (IBRA), it was first defined by John Stanley Beard in 1980. Geography and geology The Mallee region has a complex shape with tortuous boundaries, but may be roughly approximated as the triangular area south of a line from Bruce Rock to Eyre, but not within 40 kilometres (25 mi) of the south coast, except at its eastern limits. It has an area of about 79000 square kilometres (31000 mi²), making it about a quarter of the South West Botanic Province, 3% of the state, and 1% of Australia. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floristic Provinces
A phytochorion, in phytogeography, is a geographic area with a relatively uniform composition of plant species. Adjacent phytochoria do not usually have a sharp boundary, but rather a soft one, a transitional area in which many species from both regions overlap. The region of overlap is called a vegetation tension zone. In traditional schemes, areas in phytogeography are classified hierarchically, according to the presence of endemic families, genera or species, e.g., in floral (or floristic, phytogeographic) zones and regions, or also in kingdoms, regions and provinces, sometimes including the categories empire and domain. However, some authors prefer not to rank areas, referring to them simply as "areas", "regions" (in a non hierarchical sense) or "phytochoria". Systems used to classify vegetation can be divided in two major groups: those that use physiognomic-environmental parameters and characteristics and those that are based on floristic (i.e. shared genera and species) rela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytogeography
Phytogeography (from Greek φυτόν, ''phytón'' = "plant" and γεωγραφία, ''geographía'' = "geography" meaning also distribution) or botanical geography is the branch of biogeography that is concerned with the geographic distribution of plant species and their influence on the earth's surface. Phytogeography is concerned with all aspects of plant distribution, from the controls on the distribution of individual species ranges (at both large and small scales, see species distribution) to the factors that govern the composition of entire communities and floras. Geobotany, by contrast, focuses on the geographic space's influence on plants. Fields Phytogeography is part of a more general science known as biogeography. Phytogeographers are concerned with patterns and process in plant distribution. Most of the major questions and kinds of approaches taken to answer such questions are held in common between phyto- and zoogeographers. Phytogeography in wider sense (or geobot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flora Of Western Australia
The flora of Western Australia comprises 10,551 published native vascular plant species and a further 1,131 unpublished species. They occur within 1,543 genera from 211 families; there are also 1,317 naturalised alien or invasive plant species more commonly known as weeds. There are an estimated 150,000 cryptogam species or nonvascular plants which include lichens, and fungi although only 1,786 species have been published, with 948 algae and 672 lichen the majority. History Indigenous Australians have a long history with the flora of Western Australia. They have for over 50,000 years obtained detailed information on most plants. The information includes its uses as sources for food, shelter, tools and medicine. As Indigenous Australians passed the knowledge along orally or by example, most of this information has been lost, along many of the names they gave the flora. It was not until Europeans started to explore Western Australia that systematic written details of the flora comme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floristic Regions
A phytochorion, in phytogeography, is a geographic area with a relatively uniform composition of plant species. Adjacent phytochoria do not usually have a sharp boundary, but rather a soft one, a transitional area in which many species from both regions overlap. The region of overlap is called a vegetation tension zone. In traditional schemes, areas in phytogeography are classified hierarchically, according to the presence of endemic families, genera or species, e.g., in floral (or floristic, phytogeographic) zones and regions, or also in kingdoms, regions and provinces, sometimes including the categories empire and domain. However, some authors prefer not to rank areas, referring to them simply as "areas", "regions" (in a non hierarchical sense) or "phytochoria". Systems used to classify vegetation can be divided in two major groups: those that use physiognomic-environmental parameters and characteristics and those that are based on floristic (i.e. shared genera and species) rela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation For Australia
The Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia (IBRA) is a biogeographic regionalisation of Australia developed by the Australian government's Department of Sustainability, Environment, Water, Population, and Communities. It was developed for use as a planning tool, for example for the establishment of a national reserve system. The first version of IBRA was developed in 1993–94 and published in 1995. Within the broadest scale, Australia is a major part of the Australasia biogeographic realm, as developed by the World Wide Fund for Nature. Based on this system, the world is also split into 14 terrestrial habitats, of which eight are shared by Australia. The Australian land mass is divided into 89 bioregions and 419 subregions. Each region is a land area made up of a group of interacting ecosystems that are repeated in similar form across the landscape. IBRA is updated periodically based on new data, mapping improvements, and review of the existing scheme. The most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southwest Australia
Southwest Australia is a biogeographic region in Western Australia. It includes the Mediterranean-climate area of southwestern Australia, which is home to a diverse and distinctive flora and fauna. The region is also known as the Southwest Australia Global Diversity Hotspot, as well as Kwongan. Geography The region includes the Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub ecoregions of Western Australia. The region covers 356,717 km2, consisting of a broad coastal plain 20-120 kilometres wide, transitioning to gently undulating uplands made up of weathered granite, gneiss and laterite. Bluff Knoll in the Stirling Range is the highest peak in the region, at 1,099 metres (3,606 ft) elevation. Desert and xeric shrublands lie to the north and east across the centre of Australia, separating Southwest Australia from the other Mediterranean and humid-climate regions of the continent. Climate The region has a wet-winter, dry-summer Mediterranean climate, one of five such regio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regions Of Western Australia
Western Australia (WA) is divided into regions according to a number of systems. The most common system is the WA Government division of the state into regions for economic development purposes, which comprises nine defined regions; however, there are a number of other systems, including those made for purposes of land management (such as agriculture and conservation), information gathering (such as statistical and meteorological), and election for political office. The various different systems were defined for different purposes, and give specific boundaries, but although many of the different systems' regions have similar names, they have different boundaries; the names and boundaries of regions can and do vary between systems. The ''Regional Development Commissions Act'' regions The Western Australian system of regions defined by the Government of Western Australia for purposes of economic development administration, which excludes the Perth metropolitan region, is a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warren (biogeographic Region)
Warren, also known as Karri Forest Region and the Jarrah-Karri forest and shrublands ecoregion, is a biogeographic region in southern Western Australia. Located in the southwest corner of Western Australia between Cape Naturaliste and Albany, it is bordered to the north and east by the Jarrah Forest region. Its defining characteristic is an extensive tall forest of ''Eucalyptus diversicolor'' (karri). This occurs on dissected, hilly ground, with a moderately wet climate. Karri is a valuable timber and much of the karri forest has been logged over, but less than a third has been cleared for agriculture. Recognised as a region under the Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia (IBRA), and as a terrestrial ecoregion by the World Wide Fund for Nature, it was first defined by Ludwig Diels in 1906. Geography and geology The Warren region is defined as the coastal sandplain between Cape Naturaliste and Albany. Extending from the ocean to the edge of the Yilgarn craton p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Stanley Beard
John Stanley Beard (15 February 1916 – 17 February 2011) was a British-born forester and ecologist who resided in Australia. Beard studied at the University of Oxford where he completed his doctoral thesis on tropical forestry. While working with the Forestry Division in Trinidad and Tobago during the 1940s, Beard developed a system of forest classification for Tropical America and described the forests of Trinidad, Tobago, and the Lesser Antilles; these descriptions remain standard references on the topics. After leaving Trinidad, Beard moved to South Africa and then to Australia, where he produced an extensive series of vegetation maps covering much of the country. His extensive surveys of Western Australia set standards for understanding regional floristic zones and biogeographical areas for the whole state. He was the main author of the 1964–1981 explanatory notes to the mapping project of the '' Vegetation Survey of Western Australia'', which involved travelling some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBRA Regions
The Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia (IBRA) is a biogeographic regionalisation of Australia developed by the Australian government's Department of Sustainability, Environment, Water, Population, and Communities. It was developed for use as a planning tool, for example for the establishment of a national reserve system. The first version of IBRA was developed in 1993–94 and published in 1995. Within the broadest scale, Australia is a major part of the Australasia biogeographic realm, as developed by the World Wide Fund for Nature. Based on this system, the world is also split into 14 terrestrial habitats, of which eight are shared by Australia. The Australian land mass is divided into 89 bioregions and 419 subregions. Each region is a land area made up of a group of interacting ecosystems that are repeated in similar form across the landscape. IBRA is updated periodically based on new data, mapping improvements, and review of the existing scheme. The most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |