|
Born And Wolf
''Principles of Optics'', colloquially known as ''Born and Wolf'', is an optics textbook written by Max Born and Emil Wolf that was initially published in 1959 by Pergamon Press. After going through six editions with Pergamon Press, the book was transferred to Cambridge University Press who issued an expanded seventh edition in 1999. A 60th anniversary edition was published in 2019 with a foreword by Sir Peter Knight. It is considered a classic science book and one of the most influential optics books of the twentieth century. Background In 1933, Springer published Max Born's book “Optik”; this dealt with all optical phenomena for which the methods of classical physics, and Maxwell's equations in particular, were applicable. In 1950, with encouragement from Sir Edward Appleton, the principal of Edinburgh University, Born decided to produce an updated version of his “Optik” book in English. He was partly motivated by the need to make money, as he had not been worki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
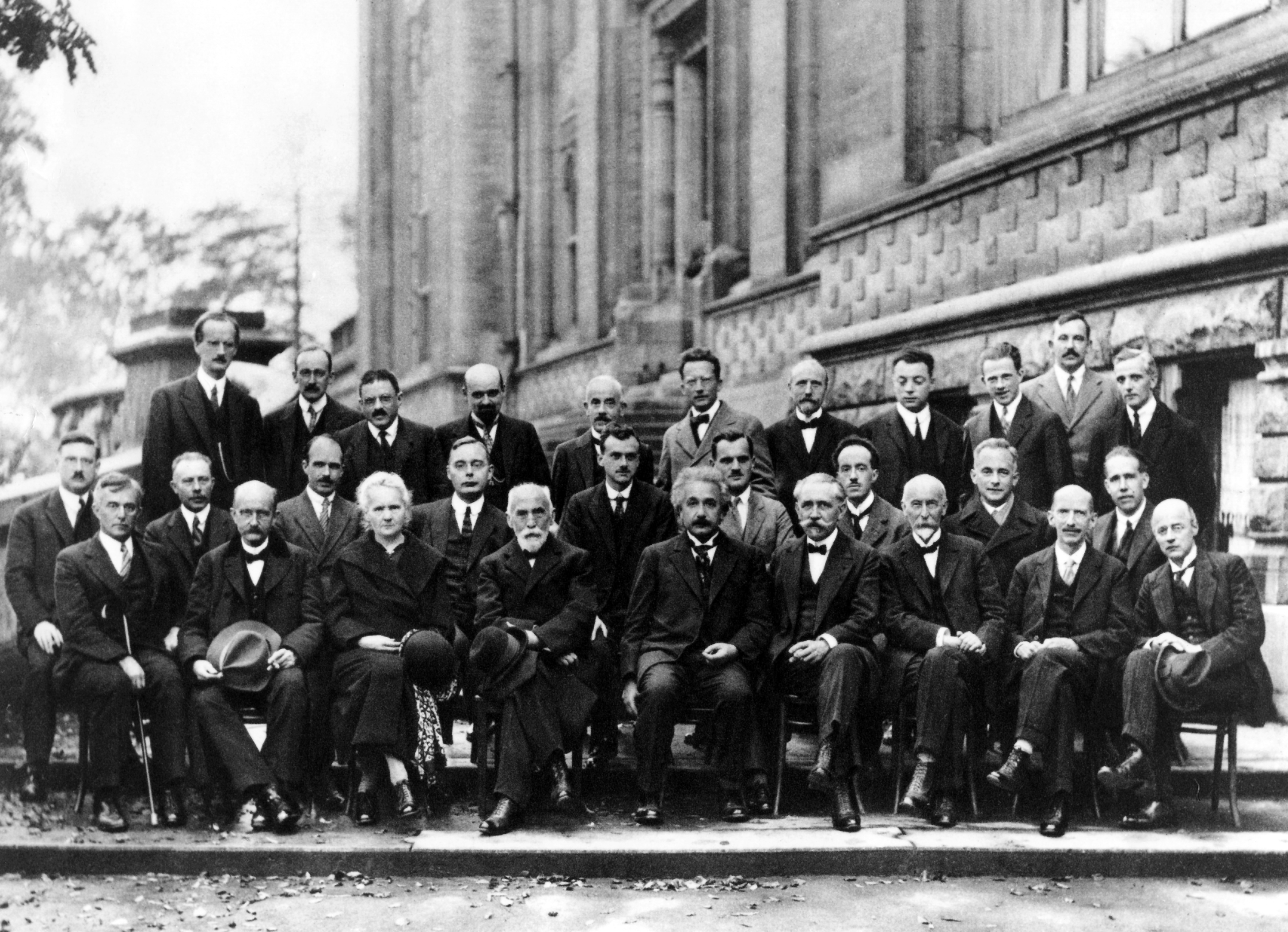
Max Born
Max Born (; 11 December 1882 – 5 January 1970) was a German physicist and mathematician who was instrumental in the development of quantum mechanics. He also made contributions to solid-state physics and optics and supervised the work of a number of notable physicists in the 1920s and 1930s. Born won the 1954 Nobel Prize in Physics for his "fundamental research in quantum mechanics, especially in the statistical interpretation of the wave function". Born entered the University of Göttingen in 1904, where he met the three renowned mathematicians Felix Klein, David Hilbert, and Hermann Minkowski. He wrote his PhD thesis on the subject of "Stability of Elastica in a Plane and Space", winning the university's Philosophy Faculty Prize. In 1905, he began researching special relativity with Minkowski, and subsequently wrote his habilitation thesis on the Thomson model of the atom. A chance meeting with Fritz Haber in Berlin in 1918 led to discussion of how an ionic compou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
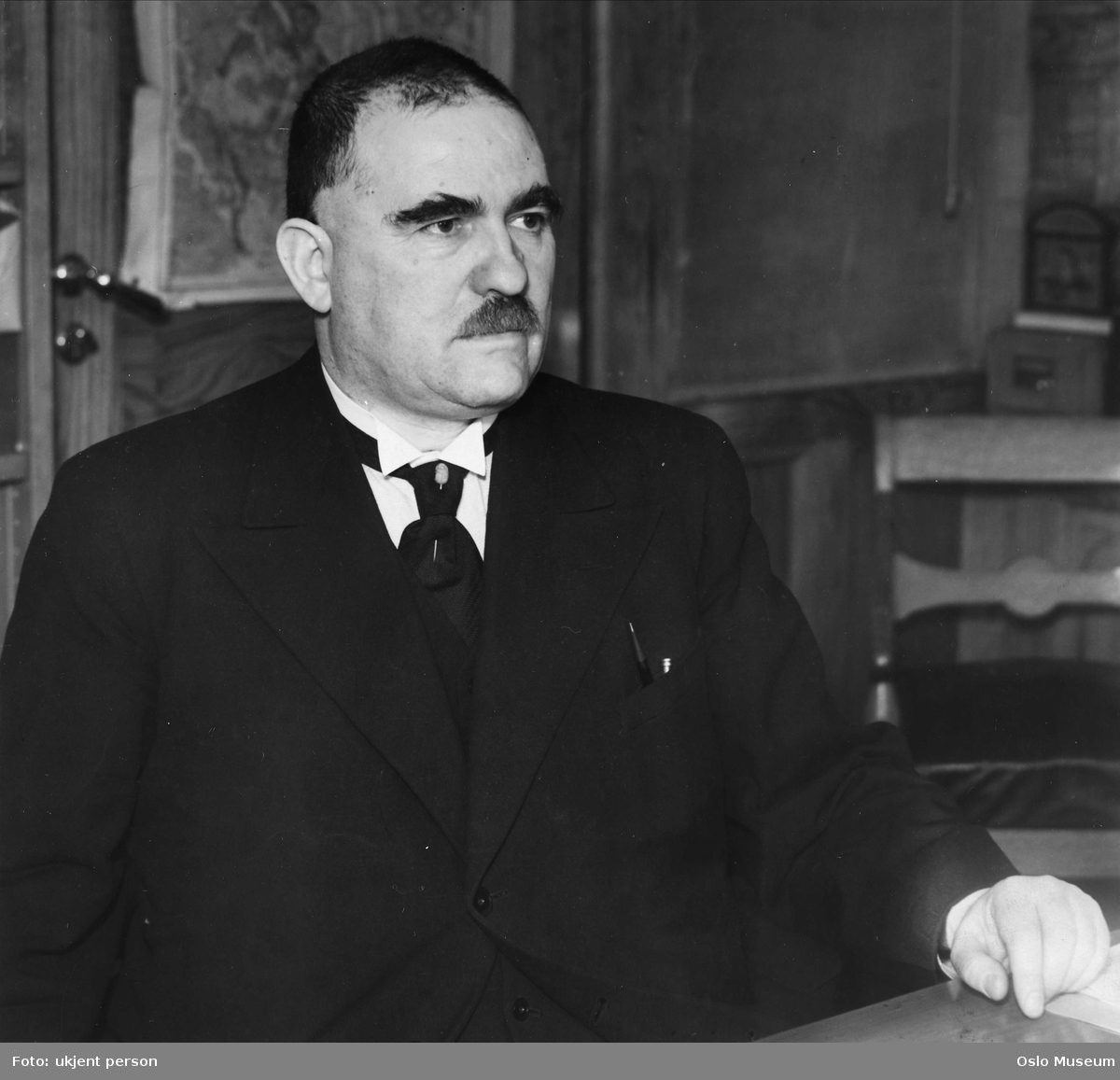
Paul Rosbaud
Paul Rosbaud (18 November 1896 – 28 January 1963), was a metallurgist and scientific adviser for Springer Verlag in Germany before and during World War II. He continued in science publishing after the war with Pergamon Press in Oxford, England. In 1986 Arnold Kramish revealed the undercover work of Rosbaud for the British during the war in the book ''The Griffin''. It was Rosbaud who dispelled anxiety over a "German atom bomb". Education Paul Rosbaud was born in Graz, Austria. He was an illegitimate son.N/ Riehl and F. Seitz, ''Stalin's Captive: Nikolaus Riehl and the Soviet Race for the Bomb'', p.47 His mother taught piano lessons, and Paul's brother Hans Rosbaud became a famous conductor. Rosbaud served in the Austrian army during World War I from 1915 to 1918. After the war ended his unit was taken as prisoner of war by British forces; this experience ended up giving him a liking of the British. He studied chemistry at Darmstadt Technische Hochschule beginning in 1920. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foundations Of Physics
''Foundations of Physics'' is a monthly journal "devoted to the conceptual bases and fundamental theories of modern physics and cosmology, emphasizing the logical, methodological, and philosophical premises of modern physical theories and procedures". The journal publishes results and observations based on fundamental questions from all fields of physics, including: quantum mechanics, quantum field theory, special relativity, general relativity, string theory, M-theory, cosmology, thermodynamics, statistical physics, and quantum gravity ''Foundations of Physics'' has been published since 1970. Its founding editors were Henry Margenau and Wolfgang Yourgrau. The 1999 Nobel laureate Gerard 't Hooft was editor-in-chief from January 2007. At that stage, it absorbed the associated journal for shorter submissions ''Foundations of Physics Letters'', which had been edited by Alwyn Van der Merwe since its foundation in 1988. Past editorial board members (which include several Nobel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter W
Peter may refer to: People * List of people named Peter, a list of people and fictional characters with the given name * Peter (given name) ** Saint Peter (died 60s), apostle of Jesus, leader of the early Christian Church * Peter (surname), a surname (including a list of people with the name) Culture * Peter (actor) (born 1952), stage name Shinnosuke Ikehata, Japanese dancer and actor * ''Peter'' (album), a 1993 EP by Canadian band Eric's Trip * ''Peter'' (1934 film), a 1934 film directed by Henry Koster * ''Peter'' (2021 film), Marathi language film * "Peter" (''Fringe'' episode), an episode of the television series ''Fringe'' * ''Peter'' (novel), a 1908 book by Francis Hopkinson Smith * "Peter" (short story), an 1892 short story by Willa Cather Animals * Peter, the Lord's cat, cat at Lord's Cricket Ground in London * Peter (chief mouser), Chief Mouser between 1929 and 1946 * Peter II (cat), Chief Mouser between 1946 and 1947 * Peter III (cat), Chief Mouser between 1947 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Problems With Pergamon Press And Robert Maxwell
A problem is a difficulty which may be resolved by problem solving. Problem(s) or The Problem may also refer to: People * Problem (rapper), (born 1985) American rapper Books * ''Problems'' (Aristotle), an Aristotelian (or pseudo-Aristotelian) collection of problems in question and answer form * ''The Problem'' (play), by A. R. Gurney Film and TV * ''Problems'' (TV series), a 2012 Australian comedy television series. * ''The Problem with Jon Stewart'', an American current affairs television series. Music Albums * ''The Problem'' (album), by Mathematics * ''Problems'' (album), a 2019 album by The Get Up Kids Songs * "Problem" (Ariana Grande song), 2014 * "Problem" (Natalia Kills song), 2013 * "Problems" (song), a 1958 song by The Everly Brothers * "Fuckin' Problems", sometimes known as "Problems", a 2012 song by A$AP Rocky * "Problem", by Becky G * "Problem", by Erin Bowman * "Problem", by Šarlo Akrobata from '' Bistriji ili tuplji čovek biva kad...'' * "Problems", by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contents
Content or contents may refer to: Media * Content (media), information or experience provided to audience or end-users by publishers or media producers ** Content industry, an umbrella term that encompasses companies owning and providing mass media and media metadata ** Content provider, a provider of non-core services in the telecommunications industry ** Free content, published material that can be used, copied, and modified without significant legal restriction ** Open content, published material licensed to authorize copying and modification by anyone ** Web content, information published on the World Wide Web * Content format, an encoded format for converting a specific type of data to displayable information * Digital content * Table of contents, a list of chapters or sections in a document Places * Content (Centreville, Maryland) also known as C.C. Harper Farm, a historic home located at Centreville, Maryland * Content (Upper Marlboro, Maryland) also known as the Bow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
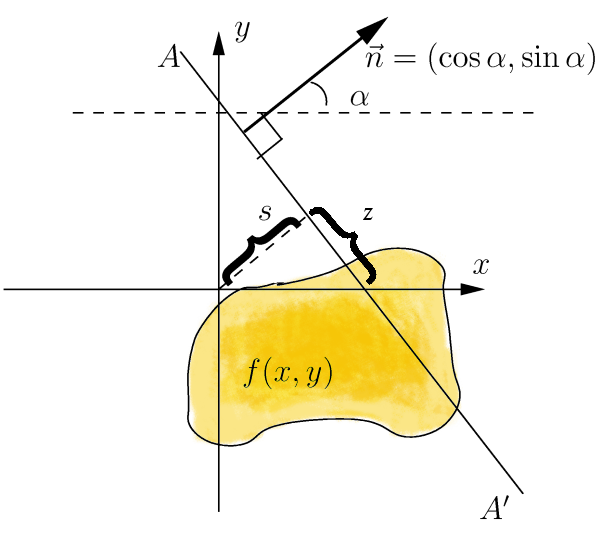
Radon Transform
In mathematics, the Radon transform is the integral transform which takes a function ''f'' defined on the plane to a function ''Rf'' defined on the (two-dimensional) space of lines in the plane, whose value at a particular line is equal to the line integral of the function over that line. The transform was introduced in 1917 by Johann Radon, who also provided a formula for the inverse transform. Radon further included formulas for the transform in three dimensions, in which the integral is taken over planes (integrating over lines is known as the X-ray transform). It was later generalized to higher-dimensional Euclidean spaces, and more broadly in the context of integral geometry. The complex analogue of the Radon transform is known as the Penrose transform. The Radon transform is widely applicable to tomography, the creation of an image from the projection data associated with cross-sectional scans of an object. Explanation If a function f represents an unknown density, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juris Upatnieks
Juris Upatnieks (born 7 May 1936 in Riga) is a Latvian-American physicist and inventor, and pioneer in the field of holography. Upatnieks fled the Latvia with his parents at the close of World War II, seeking asylum in Germany. In 1951 the family emigrated to the United States. He attended high school in Akron, Ohio, and studied electrical engineering at the University of Akron, where he was awarded a bachelor's degree in 1960. Thereafter he studied at the Institute of Science and Technology of the University of Michigan, where he earned a master's degree in electrical engineering in 1965. From 1973 to 1993 he worked at the Environmental Research Institute of Michigan and was an Adjunct Professor, Electrical and Computer Engineering Department at University of Michigan in Ann Arbor. There he taught a laboratory course in optics until 1996. From 1993 to 2001 he was a consultant with Applied Optics in Ann Arbor. From 1996 to 2001 he was also a researcher with the faculty of Mec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emmett Leith
Emmett Norman Leith (March 12, 1927 in Detroit, Michigan – December 23, 2005 in Ann Arbor, Michigan) was a professor of electrical engineering at the University of Michigan and, with Juris Upatnieks of the University of Michigan, the co-inventor of three-dimensional holography. Leith received his B.S. in physics from Wayne State University in 1949 and his M.S. in physics in 1952. He received his Ph.D. in electrical engineering from Wayne State in 1978. Much of Leith's holographic work was an outgrowth of his research on synthetic aperture radar (SAR) performed while a member of the Radar Laboratory of the University of Michigan's Willow Run Laboratory beginning in 1952. Leith joined the University of Michigan as a research assistant and was promoted to graduate research assistant in 1955, research associate in 1956, research engineer in 1960, associate professor in 1965, and full professor in 1968. Professor Leith and his coworker Juris Upatnieks at the University of Michigan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Hilbert
David Hilbert (; ; 23 January 1862 – 14 February 1943) was a German mathematician, one of the most influential mathematicians of the 19th and early 20th centuries. Hilbert discovered and developed a broad range of fundamental ideas in many areas, including invariant theory, the calculus of variations, commutative algebra, algebraic number theory, the foundations of geometry, spectral theory of operators and its application to integral equations, mathematical physics, and the foundations of mathematics (particularly proof theory). Hilbert adopted and defended Georg Cantor's set theory and transfinite numbers. In 1900, he presented a collection of problems that set the course for much of the mathematical research of the 20th century. Hilbert and his students contributed significantly to establishing rigor and developed important tools used in modern mathematical physics. Hilbert is known as one of the founders of proof theory and mathematical logic. Life Early life and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Young (scientist)
Thomas Young FRS (13 June 177310 May 1829) was a British polymath who made notable contributions to the fields of vision, light, solid mechanics, energy, physiology, language, musical harmony, and Egyptology. He was instrumental in the decipherment of Egyptian hieroglyphs, specifically the Rosetta Stone. Young has been described as " The Last Man Who Knew Everything". His work influenced that of William Herschel, Hermann von Helmholtz, James Clerk Maxwell, and Albert Einstein. Young is credited with establishing the wave theory of light, in contrast to the particle theory of Isaac Newton. Young's work was subsequently supported by the work of Augustin-Jean Fresnel. Personal life Young belonged to a Quaker family of Milverton, Somerset, where he was born in 1773, the eldest of ten children. At the age of fourteen Young had learned Greek and Latin. Young began to study medicine in London at St Bartholomew's Hospital in 1792, moved to the University of Edinburgh Medical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |