|
Bootstrap Aggregating
Bootstrap aggregating, also called bagging (from bootstrap aggregating), is a machine learning ensemble meta-algorithm designed to improve the stability and accuracy of machine learning algorithms used in statistical classification and regression. It also reduces variance and helps to avoid overfitting. Although it is usually applied to decision tree methods, it can be used with any type of method. Bagging is a special case of the model averaging approach. Description of the technique Given a standard training set D of size ''n'', bagging generates ''m'' new training sets D_i, each of size ''n′'', by sampling from ''D'' uniformly and with replacement. By sampling with replacement, some observations may be repeated in each D_i. If ''n ′''=''n'', then for large ''n'' the set D_i is expected to have the fraction (1 - 1/'' e'') (≈63.2%) of the unique examples of ''D'', the rest being duplicates. This kind of sample is known as a bootstrap sample. Sampling with replacement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ensemble Learning
In statistics and machine learning, ensemble methods use multiple learning algorithms to obtain better predictive performance than could be obtained from any of the constituent learning algorithms alone. Unlike a statistical ensemble in statistical mechanics, which is usually infinite, a machine learning ensemble consists of only a concrete finite set of alternative models, but typically allows for much more flexible structure to exist among those alternatives. Overview Supervised learning algorithms perform the task of searching through a hypothesis space to find a suitable hypothesis that will make good predictions with a particular problem. Even if the hypothesis space contains hypotheses that are very well-suited for a particular problem, it may be very difficult to find a good one. Ensembles combine multiple hypotheses to form a (hopefully) better hypothesis. The term ''ensemble'' is usually reserved for methods that generate multiple hypotheses using the same base learne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Neural Networks
Artificial neural networks (ANNs), usually simply called neural networks (NNs) or neural nets, are computing systems inspired by the biological neural networks that constitute animal brains. An ANN is based on a collection of connected units or nodes called artificial neurons, which loosely model the neurons in a biological brain. Each connection, like the synapses in a biological brain, can transmit a signal to other neurons. An artificial neuron receives signals then processes them and can signal neurons connected to it. The "signal" at a connection is a real number, and the output of each neuron is computed by some non-linear function of the sum of its inputs. The connections are called ''edges''. Neurons and edges typically have a ''weight'' that adjusts as learning proceeds. The weight increases or decreases the strength of the signal at a connection. Neurons may have a threshold such that a signal is sent only if the aggregate signal crosses that threshold. Typically, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neural Network
A neural network is a network or circuit of biological neurons, or, in a modern sense, an artificial neural network, composed of artificial neurons or nodes. Thus, a neural network is either a biological neural network, made up of biological neurons, or an artificial neural network, used for solving artificial intelligence (AI) problems. The connections of the biological neuron are modeled in artificial neural networks as weights between nodes. A positive weight reflects an excitatory connection, while negative values mean inhibitory connections. All inputs are modified by a weight and summed. This activity is referred to as a linear combination. Finally, an activation function controls the amplitude of the output. For example, an acceptable range of output is usually between 0 and 1, or it could be −1 and 1. These artificial networks may be used for predictive modeling, adaptive control and applications where they can be trained via a dataset. Self-learning resulting from e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
E-commerce
E-commerce (electronic commerce) is the activity of electronically buying or selling of products on online services or over the Internet. E-commerce draws on technologies such as mobile commerce, electronic funds transfer, supply chain management, Internet marketing, online transaction processing, electronic data interchange (EDI), inventory management systems, and automated data collection systems. E-commerce is in turn driven by the technological advances of the semiconductor industry, and is the largest sector of the electronics industry. Defining e-commerce The term was coined and first employed by Dr. Robert Jacobson, Principal Consultant to the California State Assembly's Utilities & Commerce Committee, in the title and text of California's Electronic Commerce Act, carried by the late Committee Chairwoman Gwen Moore (D-L.A.) and enacted in 1984. E-commerce typically uses the web for at least a part of a transaction's life cycle although it may also use other techno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
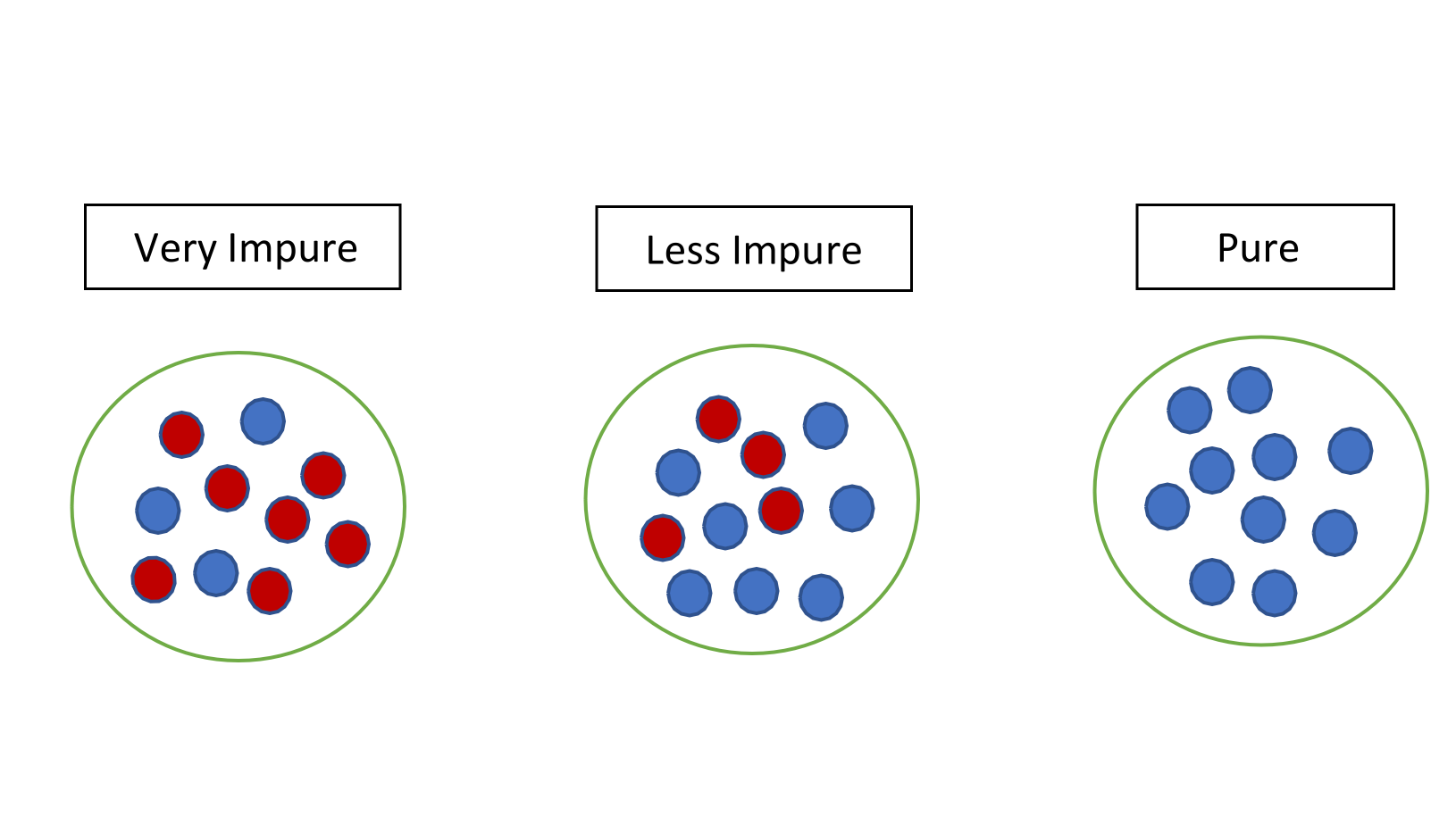
Overfitting
mathematical modeling, overfitting is "the production of an analysis that corresponds too closely or exactly to a particular set of data, and may therefore fail to fit to additional data or predict future observations reliably". An overfitted model is a mathematical model that contains more parameters than can be justified by the data. The essence of overfitting is to have unknowingly extracted some of the residual variation (i.e., the noise) as if that variation represented underlying model structure. Underfitting occurs when a mathematical model cannot adequately capture the underlying structure of the data. An under-fitted model is a model where some parameters or terms that would appear in a correctly specified model are missing. Under-fitting would occur, for example, when fitting a linear model to non-linear data. Such a model will tend to have poor predictive performance. The possibility of over-fitting exists because the criterion used for selecting the model is no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Random Forest Diagram Extra Wide
In common usage, randomness is the apparent or actual lack of pattern or predictability in events. A random sequence of events, symbols or steps often has no order and does not follow an intelligible pattern or combination. Individual random events are, by definition, unpredictable, but if the probability distribution is known, the frequency of different outcomes over repeated events (or "trials") is predictable.Strictly speaking, the frequency of an outcome will converge almost surely to a predictable value as the number of trials becomes arbitrarily large. Non-convergence or convergence to a different value is possible, but has probability zero. For example, when throwing two dice, the outcome of any particular roll is unpredictable, but a sum of 7 will tend to occur twice as often as 4. In this view, randomness is not haphazardness; it is a measure of uncertainty of an outcome. Randomness applies to concepts of chance, probability, and information entropy. The fields ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Random Forest
Random forests or random decision forests is an ensemble learning method for classification, regression and other tasks that operates by constructing a multitude of decision trees at training time. For classification tasks, the output of the random forest is the class selected by most trees. For regression tasks, the mean or average prediction of the individual trees is returned. Random decision forests correct for decision trees' habit of overfitting to their training set. Random forests generally outperform decision trees, but their accuracy is lower than gradient boosted trees. However, data characteristics can affect their performance. The first algorithm for random decision forests was created in 1995 by Tin Kam Ho using the random subspace method, which, in Ho's formulation, is a way to implement the "stochastic discrimination" approach to classification proposed by Eugene Kleinberg. An extension of the algorithm was developed by Leo Breiman and Adele Cutler, who reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decision Tree Depth 2
Decision may refer to: Law and politics *Judgment (law), as the outcome of a legal case * Landmark decision, the outcome of a case that sets a legal precedent * ''Per curiam'' decision, by a court with multiple judges Books * ''Decision'' (novel), a 1983 political novel by Allen Drury * ''The Decision'' (novel), a 1998 book in the ''Animorphs'' series Sports *Decision (baseball), a statistical credit earned by a baseball pitcher * Decisions in combat sports *Decisions (professional wrestling), by which a wrestler scores a point against his opponent Film and TV * ''Decision'' (TV series), an American anthology TV series * ''The Decision'' (play), by the 20th-century German dramatist Bertolt Brecht * ''The Decision'' (TV special), in which NBA player LeBron James announced that he would switch teams * "The Decision" (song), by English indie rock band Young Knives Music Albums * ''Decisions'' (George Adams and Don Pullen album), 1984 * ''Decisions'' (The Winans album), 1987 Song ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Gain In Decision Trees
In information theory and machine learning, information gain is a synonym for ''Kullback–Leibler divergence''; the amount of information gained about a random variable or signal from observing another random variable. However, in the context of decision trees, the term is sometimes used synonymously with mutual information, which is the conditional expected value of the Kullback–Leibler divergence of the univariate probability distribution of one variable from the conditional distribution of this variable given the other one. The information gain of a random variable ''X'' obtained from an observation of a random variable ''A'' taking value is defined IG_ = D_\text, the Kullback–Leibler divergence of the prior distribution P_ for x from the posterior distribution P_ for ''x'' given ''a''. The expected value of the information gain is the mutual information of ''X'' and ''A'' – i.e. the reduction in the entropy of ''X'' achieved by learning the state of the random ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confusion Matrix
In the field of machine learning and specifically the problem of statistical classification, a confusion matrix, also known as an error matrix, is a specific table layout that allows visualization of the performance of an algorithm, typically a supervised learning one (in unsupervised learning it is usually called a matching matrix). Each row of the matrix represents the instances in an actual class while each column represents the instances in a predicted class, or vice versa – both variants are found in the literature. The name stems from the fact that it makes it easy to see whether the system is confusing two classes (i.e. commonly mislabeling one as another). It is a special kind of contingency table, with two dimensions ("actual" and "predicted"), and identical sets of "classes" in both dimensions (each combination of dimension and class is a variable in the contingency table). __TOC__ Example Given a sample of 12 individuals, 8 that have been diagnosed with cancer an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decision Tree
A decision tree is a decision support tool that uses a tree-like model of decisions and their possible consequences, including chance event outcomes, resource costs, and utility. It is one way to display an algorithm that only contains conditional control statements. Decision trees are commonly used in operations research, specifically in decision analysis, to help identify a strategy most likely to reach a goal, but are also a popular tool in machine learning. Overview A decision tree is a flowchart-like structure in which each internal node represents a "test" on an attribute (e.g. whether a coin flip comes up heads or tails), each branch represents the outcome of the test, and each leaf node represents a class label (decision taken after computing all attributes). The paths from root to leaf represent classification rules. In decision analysis, a decision tree and the closely related influence diagram are used as a visual and analytical decision support tool, where t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complete Example 2
Complete may refer to: Logic * Completeness (logic) * Completeness of a theory, the property of a theory that every formula in the theory's language or its negation is provable Mathematics * The completeness of the real numbers, which implies that there are no "holes" in the real numbers * Complete metric space, a metric space in which every Cauchy sequence converges * Complete uniform space, a uniform space where every Cauchy net in converges (or equivalently every Cauchy filter converges) * Complete measure, a measure space where every subset of every null set is measurable * Completion (algebra), at an ideal * Completeness (cryptography) * Completeness (statistics), a statistic that does not allow an unbiased estimator of zero * Complete graph, an undirected graph in which every pair of vertices has exactly one edge connecting them * Complete category, a category ''C'' where every diagram from a small category to ''C'' has a limit; it is ''cocomplete'' if every such functor ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |