|
Bombus
A bumblebee (or bumble bee, bumble-bee, or humble-bee) is any of over 250 species in the genus ''Bombus'', part of Apidae, one of the bee families. This genus is the only extant group in the tribe Bombini, though a few extinct related genera (e.g., '' Calyptapis'') are known from fossils. They are found primarily in higher altitudes or latitudes in the Northern Hemisphere, although they are also found in South America, where a few lowland tropical species have been identified. European bumblebees have also been introduced to New Zealand and Tasmania. Female bumblebees can sting repeatedly, but generally ignore humans and other animals. Most bumblebees are social insects that form colonies with a single queen. The colonies are smaller than those of honey bees, growing to as few as 50 individuals in a nest. Cuckoo bumblebees are brood parasitic and do not make nests or form colonies; their queens aggressively invade the nests of other bumblebee species, kill the resident ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psithyrus
Cuckoo bumblebees are members of the subgenus ''Psithyrus'' in the bumblebee genus ''Bombus''. Until recently, the 28 species of ''Psithyrus'' were considered to constitute a separate genus. They are a specialized socially parasitic lineage which parasitises the nests of 'true' bumblebees, resulting in the loss of the ability to collect pollen and establish their own nests. Cuckoo bumblebees do not create a worker caste and produce only male and female reproductives. They are considered inquilines in the colonies of 'true' bumblebees. Cuckoo bumblebee females emerge from hibernation later than their host species to ensure that their host has had sufficient time to establish a nest. Before finding and invading a host colony, a ''Psithyrus'' female feeds directly from flowers until her ovaries are sufficiently developed, at which time she begins seeking a nest to invade. Once she has located and infiltrated a host colony, the ''Psithyrus'' female usurps the nest by killing or su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
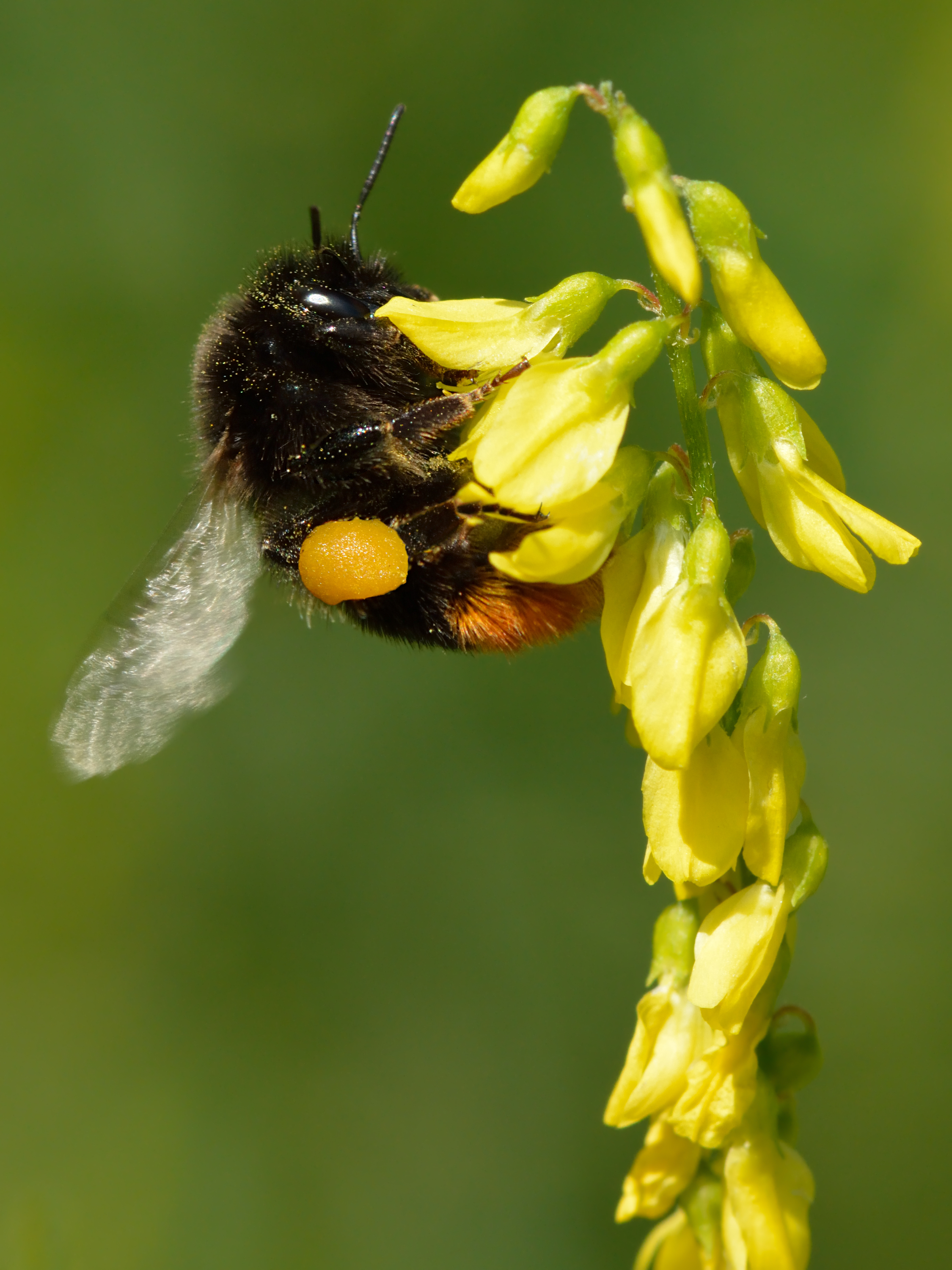
Bombus Lapidarius
''Bombus lapidarius'' is a species of bumblebee in the subgenus ''Melanobombus''. Commonly known as the red-tailed bumblebee, ''B. lapidarius'' can be found throughout much of Central Europe. Known for its distinctive black and red body, this social bee is important in pollination. Taxonomy and phylogeny The red-tailed bumblebee is a part of the order Hymenoptera, family Apidae, and the genus '' Bombus'', which includes many species including ''Bombus terrestris '', '' Bombus lucorum'', and ''Bombus hypnorum''. Description and identification The red-tailed bumblebee is typically distinguished by its black body with red markings around the abdomen. Worker females and the queen look similar, except the queen is much larger than the worker females. Males typically have both the red and black coloration along with a yellow band around the abdomen and yellow markings on the face. Further, ''B. lapidarius'' tend to have a medium-sized proboscis, which is significant in that it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
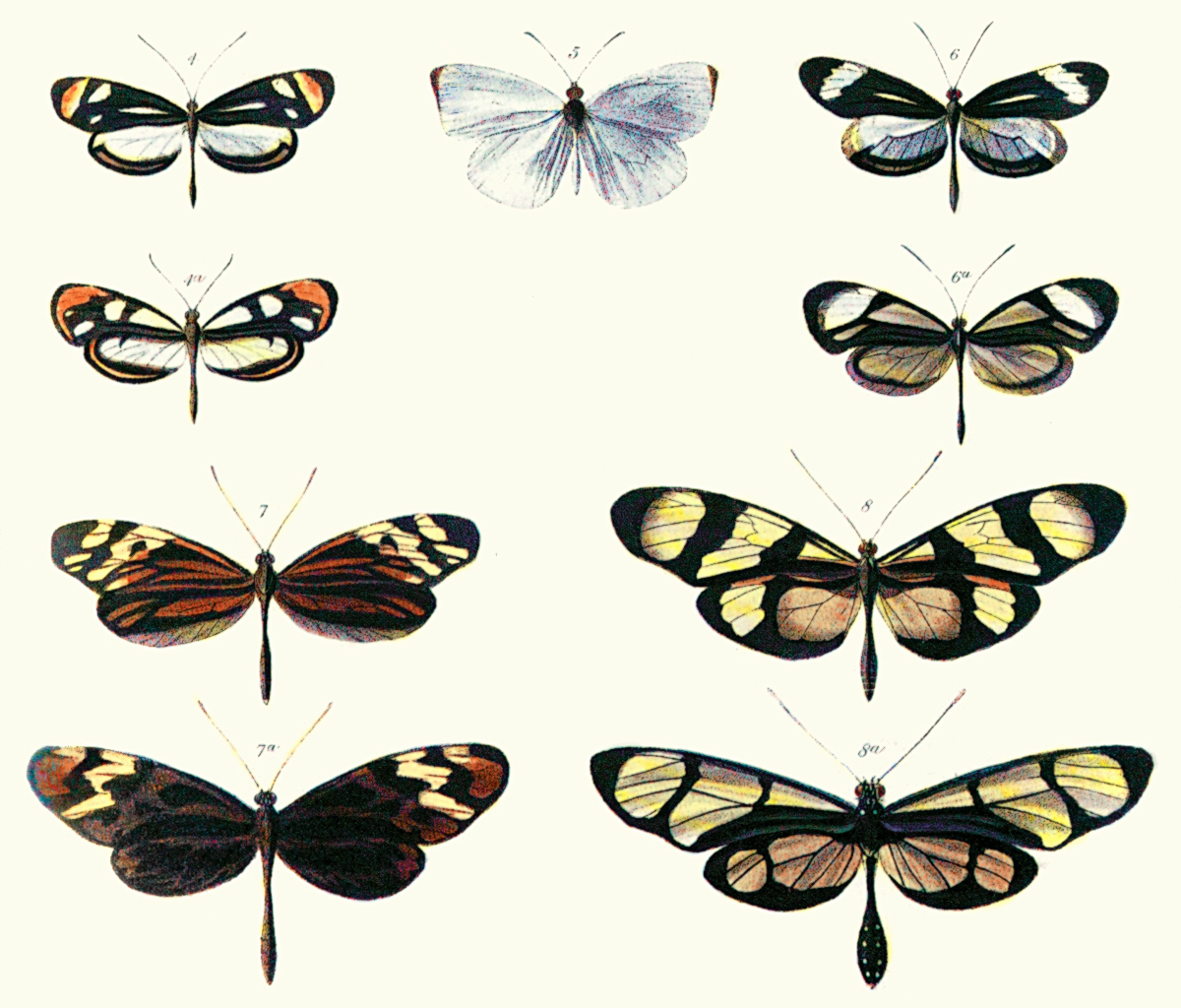
Müllerian Mimicry
Müllerian mimicry is a natural phenomenon in which two or more well-defended species, often foul-tasting and sharing common predators, have come to mimicry, mimic each other's honest signal, honest aposematism, warning signals, to their mutualism (biology), mutual benefit. The benefit to Müllerian mimics is that predators only need one unpleasant encounter with one member of a set of Müllerian mimics, and thereafter avoid all similar coloration, whether or not it belongs to the same species as the initial encounter. It is named after the German naturalist Fritz Müller, who first proposed the concept in 1878, supporting his theory with the first mathematical model of frequency-dependent selection, one of the first such models anywhere in biology. Müllerian mimicry was first identified in tropical butterfly, butterflies that shared colourful wing patterns, but it is found in many groups of insects such as bumblebees, and other animals including Ranitomeya, poison frogs and co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bombini
The Bombini are a tribe of large bristly apid bees which feed on pollen or nectar. Many species are social, forming nests of up to a few hundred individuals; other species, formerly classified as '' Psithyrus'' cuckoo bees, are brood parasites of nest-making species. The tribe contains a single living genus, '' Bombus'', the bumblebees, and some extinct genera such as '' Calyptapis'' and '' Oligobombus''. The tribe was described by Pierre André Latreille in 1802. Fossils '' Bombus cerdanyensis'' was described from Late Miocene lacustrine beds of La Cerdanya, Spain in 2014. '' Calyptapis florissantensis'' was described by Theodore Dru Alison Cockerell in 1906 from the Chadronian ( Eocene) lacustrine – large shale of Florissant in the US. '' Oligobombus cuspidatus'' was described by Antropov ''et al'' (2014) from the Late Eocene Insect Bed of the Bembridge Marls on the Isle of Wight, England. The holotype fossil was described by re-examining a specimen in the Smith ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nectar Robbing
Nectar robbing is a foraging behavior utilized by some organisms that feed on floral nectar, carried out by feeding from holes bitten in flowers, rather than by entering through the flowers' natural openings. "Nectar robbers" usually feed in this way, avoiding contact with the floral reproductive structures, and therefore do not facilitate plant reproduction via pollination. Because many species that act as pollinators also act as nectar robbers, nectar robbing is considered to be a form of exploitation of plant-pollinator mutualism. While there is variation in the dependency on nectar for robber species, most species rob facultatively. Nectar robbers vary greatly in species diversity and include species of carpenter bees, bumblebees, stingless '' Trigona'' bees, solitary bees, wasps, ants, hummingbirds, and some passerine birds, including flowerpiercers. Nectar robbing mammals include a fruit bat and Swinhoe's striped squirrel, which robs nectar from the ginger plant. Hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pollen Basket
The pollen basket or corbicula (plural corbiculae) is part of the tibia on the hind legs of certain species of bees. They use the structure in harvesting pollen and carrying it to the nest or hive. Other species of bees have scopae instead. Etymology There was little formal description of the corbicula before Carl Linnaeus explained the biological function of pollen in the mid-18th century. In English the first edition of ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' described the structure in 1771 without giving it any special name. The second edition, 1777, refers to the corbicula simply as the "basket". By 1802 William Kirby had introduced the New Latin term into English. He had borrowed it, with acknowledgement, from Réaumur. Like other Latin anatomical terms, this had the advantages of specificity, international acceptability, and culture neutrality. By 1820 the term ''pollen-basket'' seems to have gained acceptance in beekeeping, extracted in though a century later a compendium of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Batesian Mimicry
Batesian mimicry is a form of mimicry where a harmless species has evolved to imitate the warning signals of a harmful species directed at a predator of them both. It is named after the English naturalist Henry Walter Bates, after his work on butterflies in the rainforests of Brazil. Batesian mimicry is the most commonly known and widely studied of mimicry complexes, such that the word mimicry is often treated as synonymous with Batesian mimicry. There are many other forms however, some very similar in principle, others far separated. It is often contrasted with Müllerian mimicry, a form of mutually beneficial convergence between two or more harmful species. However, because the mimic may have a degree of protection itself, the distinction is not absolute. It can also be contrasted with functionally different forms of mimicry. Perhaps the sharpest contrast here is with aggressive mimicry where a predator or parasite mimics a harmless species, avoiding detection and improving it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pollinator Decline
Pollinator decline is the reduction in abundance of insect and other animal pollinators in many ecosystems worldwide that began being recorded at the end of the 20th century. Multiple lines of evidence exist for the reduction of wild pollinator populations at the regional level, especially within Europe and North America. Similar findings from studies in South America, China and Japan make it reasonable to suggest that declines are occurring around the globe. The majority of studies focus on bees, particularly honeybee and bumblebee species, with a smaller number involving hoverflies and lepidopterans. The picture for domesticated pollinator species is less clear. Although the number of managed honey bee colonies in Europe and North America declined by 25% and 59% between 1985-2005 and 1947-2005 respectively, overall global stocks increased due to major hive number increases in countries such as China and Argentina. Nevertheless, in the time managed honeybee hives increased by 4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
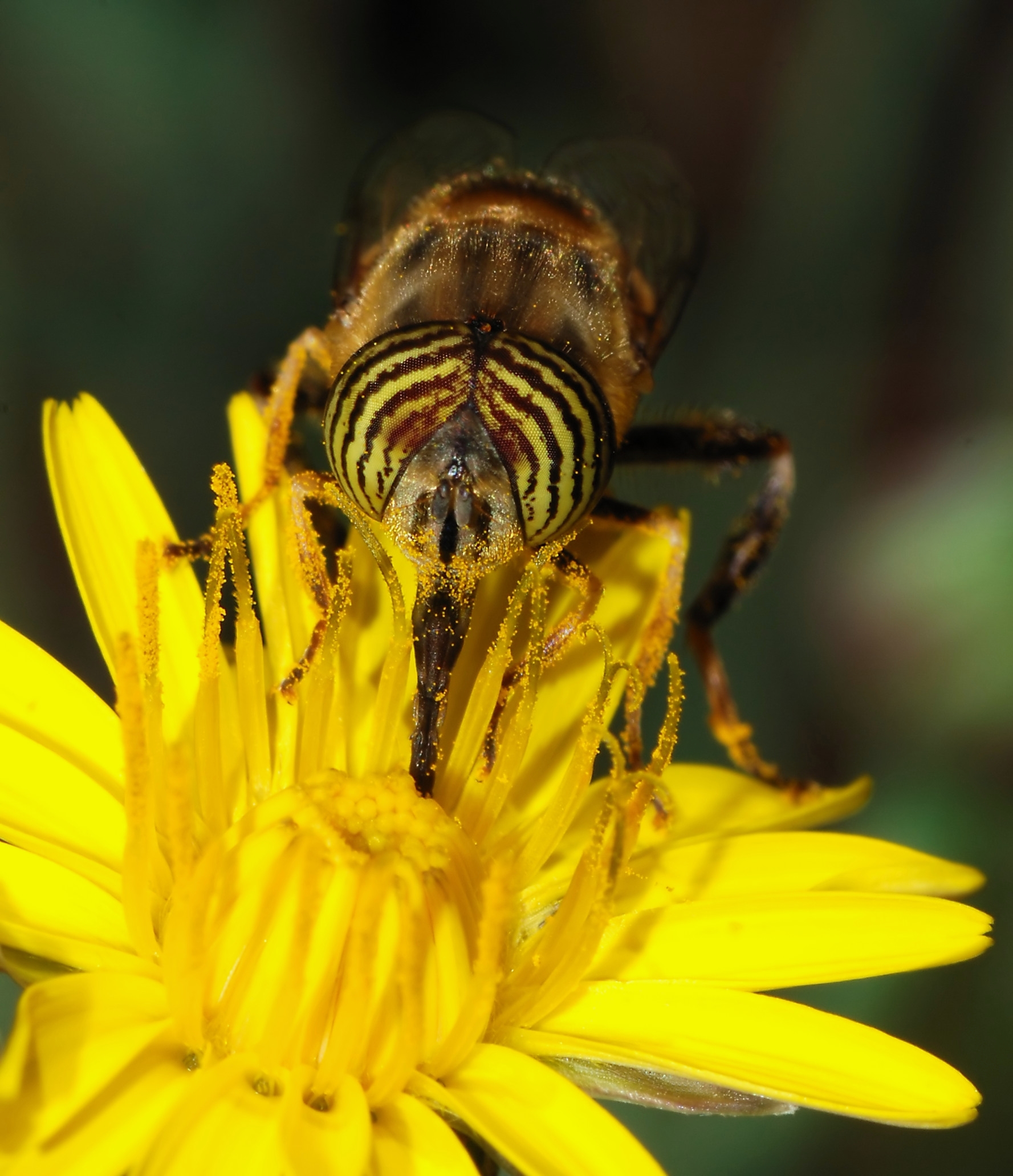
Pollinator
A pollinator is an animal that moves pollen from the male anther of a flower to the female stigma of a flower. This helps to bring about fertilization of the ovules in the flower by the male gametes from the pollen grains. Insects are the major pollinators of most plants, and insect pollinators include all families of bees and most families of aculeate wasps; ants; many families of flies; many lepidopterans (both butterflies and moths); and many families of beetles. Vertebrates, mainly bats and birds, but also some non-bat mammals (monkeys, lemurs, possums, rodents) and some lizards pollinate certain plants. Among the pollinating birds are hummingbirds, honeyeaters and sunbirds with long beaks; they pollinate a number of deep-throated flowers. Humans may also carry out artificial pollination. A pollinator is different from a pollenizer, a plant that is a source of pollen for the pollination process. Background Plants fall into pollination syndromes that reflect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calyptapis
''Calyptapis'' is an extinct bombini genus related to bumblebees with one described species ''Calyptapis florissantensis''. It is known only from the Late Eocene Chadronian age shales of the Florissant Formation in Colorado. the genus and species were described by Theodore Dru Alison Cockerell in 1906. References † A dagger, obelisk, or obelus is a typographical mark that usually indicates a footnote if an asterisk has already been used. The symbol is also used to indicate death (of people) or extinction (of species). It is one of the modern descendan ... Eocene insects Fossil bee taxa Fossil taxa described in 1906 Insects described in 1906 Prehistoric insects of North America Fossil bee genera {{paleo-insect-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honey Bee
A honey bee (also spelled honeybee) is a eusocial flying insect within the genus ''Apis'' of the bee clade, all native to Afro-Eurasia. After bees spread naturally throughout Africa and Eurasia, humans became responsible for the current cosmopolitan distribution of honey bees, introducing multiple subspecies into South America (early 16th century), North America (early 17th century), and Australia (early 19th century). Honey bees are known for their construction of wiktionary:perennial, perennial Colony (biology), colonial nests from Beeswax, wax, the large size of their colonies, and surplus production and storage of honey, distinguishing their hives as a prized foraging target of many animals, including honey badgers, bears and human hunter-gatherers. Only eight surviving species of honey bee are recognized, with a total of 43 subspecies, though historically 7 to 11 species are recognized. Honey bees represent only a small fraction of the roughly 20,000 known species of bees ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brood Parasite
Brood parasites are animals that rely on others to raise their young. The strategy appears among birds, insects and fish. The brood parasite manipulates a host, either of the same or of another species, to raise its young as if it were its own, usually using egg mimicry, with eggs that resemble the host's. The evolutionary strategy relieves the parasitic parents from the investment of rearing young. This benefit comes at the cost of provoking an evolutionary arms race between parasite and host as they coevolve: many hosts have developed strong defenses against brood parasitism, such as recognizing and ejecting parasitic eggs, or abandoning parasitized nests and starting over. It is less obvious why most hosts do care for parasite nestlings, given that for example cuckoo chicks differ markedly from host chicks in size and appearance. One explanation, the mafia hypothesis, proposes that parasitic adults retaliate by destroying host nests where rejection has occurred; there ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)

_e_(_Zonotrichia_Capensis_).jpg)