|
Boehmeria
''Boehmeria'' is a genus of 47 species of flowering plants in the nettle family Urticaceae. Of the species, 33 are indigenous to the Old World and 14 to the New World; no species is indigenous to both the Old and New Worlds. The species include herbaceous perennials, shrubs and small trees. Although related to the similar-looking species of the stinging nettles of genus ''Urtica'', species of ''Boehmeria'' do not have stinging hairs. Because of the similarity in appearance, some species are commonly called "false nettles". This genus is named in honor of the German botanist, Georg Rudolf Boehmer. Fossil record 14 fossil fruits of †''Boehmeria sibirica'' have been extracted from borehole samples of the Middle Miocene fresh water deposits in Nowy Sacz Basin, West Carpathians, Poland. Cultivation and uses One species, ramie (''Boehmeria nivea'') is an important fibre crop. Some are also used as ornamental plants. ''Boehmeria'' species are used as food plants by the larvae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boehmeria Celtidifolia
''Boehmeria'' is a genus of 47 species of flowering plants in the nettle family Urticaceae. Of the species, 33 are indigenous to the Old World and 14 to the New World; no species is indigenous to both the Old and New Worlds. The species include herbaceous perennials, shrubs and small trees. Although related to the similar-looking species of the stinging nettles of genus ''Urtica'', species of ''Boehmeria'' do not have stinging hairs. Because of the similarity in appearance, some species are commonly called "false nettles". This genus is named in honor of the German botanist, Georg Rudolf Boehmer. Fossil record 14 fossil fruits of †''Boehmeria sibirica'' have been extracted from borehole samples of the Middle Miocene fresh water deposits in Nowy Sacz Basin, West Carpathians, Poland. Cultivation and uses One species, ramie (''Boehmeria nivea'') is an important fibre crop. Some are also used as ornamental plants. ''Boehmeria'' species are used as food plants by the larvae o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boehmeria Brevirostris
''Boehmeria'' is a genus of 47 species of flowering plants in the nettle family Urticaceae. Of the species, 33 are indigenous to the Old World and 14 to the New World; no species is indigenous to both the Old and New Worlds. The species include herbaceous perennials, shrubs and small trees. Although related to the similar-looking species of the stinging nettles of genus ''Urtica'', species of ''Boehmeria'' do not have stinging hairs. Because of the similarity in appearance, some species are commonly called "false nettles". This genus is named in honor of the German botanist, Georg Rudolf Boehmer. Fossil record 14 fossil fruits of †''Boehmeria sibirica'' have been extracted from borehole samples of the Middle Miocene fresh water deposits in Nowy Sacz Basin, West Carpathians, Poland. Cultivation and uses One species, ramie (''Boehmeria nivea'') is an important fibre crop. Some are also used as ornamental plants. ''Boehmeria'' species are used as food plants by the larvae o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boehmeria Aspera
''Boehmeria'' is a genus of 47 species of flowering plants in the nettle family Urticaceae. Of the species, 33 are indigenous to the Old World and 14 to the New World; no species is indigenous to both the Old and New Worlds. The species include herbaceous perennials, shrubs and small trees. Although related to the similar-looking species of the stinging nettles of genus ''Urtica'', species of ''Boehmeria'' do not have stinging hairs. Because of the similarity in appearance, some species are commonly called "false nettles". This genus is named in honor of the German botanist, Georg Rudolf Boehmer. Fossil record 14 fossil fruits of †''Boehmeria sibirica'' have been extracted from borehole samples of the Middle Miocene fresh water deposits in Nowy Sacz Basin, West Carpathians, Poland. Cultivation and uses One species, ramie (''Boehmeria nivea'') is an important fibre crop. Some are also used as ornamental plants. ''Boehmeria'' species are used as food plants by the larvae o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boehmeria Ramiflora
''Boehmeria'' is a genus of 47 species of flowering plants in the nettle family Urticaceae. Of the species, 33 are indigenous to the Old World and 14 to the New World; no species is indigenous to both the Old and New Worlds. The species include herbaceous perennials, shrubs and small trees. Although related to the similar-looking species of the stinging nettles of genus ''Urtica'', species of ''Boehmeria'' do not have stinging hairs. Because of the similarity in appearance, some species are commonly called "false nettles". This genus is named in honor of the German botanist, Georg Rudolf Boehmer. Fossil record 14 fossil fruits of †''Boehmeria sibirica'' have been extracted from borehole samples of the Middle Miocene fresh water deposits in Nowy Sacz Basin, West Carpathians, Poland. Cultivation and uses One species, ramie (''Boehmeria nivea'') is an important fibre crop. Some are also used as ornamental plants. ''Boehmeria'' species are used as food plants by the larvae o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boehmeria Bullata
''Boehmeria'' is a genus of 47 species of flowering plants in the nettle family Urticaceae. Of the species, 33 are indigenous to the Old World and 14 to the New World; no species is indigenous to both the Old and New Worlds. The species include herbaceous perennials, shrubs and small trees. Although related to the similar-looking species of the stinging nettles of genus ''Urtica'', species of ''Boehmeria'' do not have stinging hairs. Because of the similarity in appearance, some species are commonly called "false nettles". This genus is named in honor of the German botanist, Georg Rudolf Boehmer. Fossil record 14 fossil fruits of †''Boehmeria sibirica'' have been extracted from borehole samples of the Middle Miocene fresh water deposits in Nowy Sacz Basin, West Carpathians, Poland. Cultivation and uses One species, ramie (''Boehmeria nivea'') is an important fibre crop. Some are also used as ornamental plants. ''Boehmeria'' species are used as food plants by the larvae o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boehmeria Caudata
''Boehmeria'' is a genus of 47 species of flowering plants in the nettle family Urticaceae. Of the species, 33 are indigenous to the Old World and 14 to the New World; no species is indigenous to both the Old and New Worlds. The species include herbaceous perennials, shrubs and small trees. Although related to the similar-looking species of the stinging nettles of genus ''Urtica'', species of ''Boehmeria'' do not have stinging hairs. Because of the similarity in appearance, some species are commonly called "false nettles". This genus is named in honor of the German botanist, Georg Rudolf Boehmer. Fossil record 14 fossil fruits of †''Boehmeria sibirica'' have been extracted from borehole samples of the Middle Miocene fresh water deposits in Nowy Sacz Basin, West Carpathians, Poland. Cultivation and uses One species, ramie (''Boehmeria nivea'') is an important fibre crop. Some are also used as ornamental plants. ''Boehmeria'' species are used as food plants by the larvae o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urticaceae
The Urticaceae are a family, the nettle family, of flowering plants. The family name comes from the genus '' Urtica''. The Urticaceae include a number of well-known and useful plants, including nettles in the genus ''Urtica'', ramie (''Boehmeria nivea''), māmaki ('' Pipturus albidus''), and ajlai ('' Debregeasia saeneb''). The family includes about 2,625 species, grouped into 53 genera according to the database of the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew and Christenhusz and Byng (2016). The largest genera are '' Pilea'' (500 to 715 species), '' Elatostema'' (300 species), '' Urtica'' (80 species), and '' Cecropia'' (75 species). '' Cecropia'' contains many myrmecophytes. Urticaceae species can be found worldwide, apart from the polar regions. Description Urticaceae species can be shrubs (e.g. '' Pilea''), lianas, herbs (e.g. '' Urtica'', '' Parietaria''), or, rarely, trees ('' Dendrocnide'', '' Cecropia''). Their leaves are usually entire and bear stipules. Urticating (stinging) h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
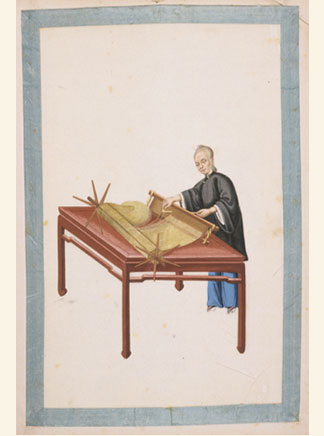
Ramie
Ramie (pronounced: , ; from Malay ) is a flowering plant in the nettle family Urticaceae, native to eastern Asia. It is a herbaceous perennial growing to tall;Ramie: Old Fiber - New Image at the (September 17, 2002). |
Bedellia
Bedelliidae is a small family of small, narrow-winged moths; most authorities recognize just a single genus, ''Bedellia'', previously included in the family Lyonetiidae. The family is still included in the Lyonetiidae Lyonetiidae is a family of moths with some 200 described species. These are small, slender moths, the wingspan rarely exceeding 1 cm. The very narrow forewings, held folded backwards covering the hindwings and abdomen, often have pointed ap ... as the subfamily Bedelliinae by some authors. Species References External linksMicrolepsU.S.A. (Nearctic)Images of imagines, larva and pupa Moth genera Taxa named by Henry Tibbats Stainton {{Yponomeutoidea-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georg Rudolf Boehmer
Georg Rudolf Boehmer (German: Böhmer) (1 October 1723 – 4 April 1803) was a German botanist and physician born in Liegnitz. He studied botany at the University of Leipzig under Christian Gottlieb Ludwig (1709–1773). In 1752, he succeeded Abraham Vater (1684–1751) as professor of botany and anatomy at the University of Wittenberg, where in 1782 became a professor of therapy. During his career he also had part-time duties as city physician () in Wittenberg, later serving a similar function in Kemberg. Among his publications was a five-volume work on natural history called ''Bibliotheca scriptorum historiae naturalis''. The plant genus ''Boehmeria'' from the family Urticaceae is named in his honor. He is also known as an entomologist. Selected publications * ''Lexicon rei Herbaria'' * ''Technische Geschichte der Pflanzen'' (Technical history of plants) * ''Bibliotheca scriptorum historiae naturalis'', five volumes 1785–1789. * ''Systematisch-literarische Handbuch der ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Carpathians
The Western Carpathians are a mountain range and geomorphological province that forms the western part of the Carpathian Mountains. The mountain belt stretches from the Low Beskids range of the Eastern Carpathians along the border of Poland with Slovakia toward the Moravian region of the Czech Republic and the Austrian Weinviertel. In the south the North Hungarian Mountains cover northern Hungary. The area of the Western Carpathians comprises about 70,000 km². The highest elevation is the Gerlachovský štít (2,655m). Geographical definition Most of the perimeter of the Western Carpathians is quite sharply defined by valleys. To the northwest and north they are separated from the Bohemian Massif by the Forecarpathian Lowland and the Lesser Poland Upland; to the west the Moravian Gate leads over to the Sudetes. To the south the mountain chain falls away towards the Pannonian Plain, a large plain situated between the Alps, the Dinaric Alps, and the main mass of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larva
A larva (; plural larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into adults. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle. The larva's appearance is generally very different from the adult form (''e.g.'' caterpillars and butterflies) including different unique structures and organs that do not occur in the adult form. Their diet may also be considerably different. Larvae are frequently adapted to different environments than adults. For example, some larvae such as tadpoles live almost exclusively in aquatic environments, but can live outside water as adult frogs. By living in a distinct environment, larvae may be given shelter from predators and reduce competition for resources with the adult population. Animals in the larval stage will consume food to fuel their transition into the adult form. In some organisms like polychaetes and barnacles, adults are im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |