|
Blood Mountain
Blood Mountain is the highest peak on the Georgia section of the Appalachian Trail and the sixth-tallest mountain in Georgia, with an elevation of .Brown (1996), p.93 It is located on the border of Lumpkin County with Union County and is within the boundaries of the Chattahoochee National Forest and the Blood Mountain Wilderness. There are several waterfalls, hiking trails and other recreational areas in the vicinity. Blood Mountain is the high point of the Apalachicola River watershed via the Chattahoochee River. History There are various theories on the origin of the mountain's name. Some believe that the name of the mountain comes from a bloody battle between the Cherokee and Muscogee Native Americans. Some people believe that it got its name from the reddish color of the lichen and Catawba growing near the summit. Hiking and recreation This peak has scenic views from the large rock formations that top the mountain. There is a hiker's shelter at the top of the mountai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vogel State Park
Vogel State Park is a or 94 hectares state park located at the base of Blood Mountain in the Chattahoochee National Forest. It became one of the first two parks in Georgia when it founded a state park system in 1931. Much of the park was constructed by the Civilian Conservation Corps during the 1930s. The park features streams, a waterfall, and Lake Trahlyta. At elevation it is one of Georgia's highest altitude state parks. The mountainous habitats surrounding the lake support a wide assortment of plants and animals. Within the park are a series of hiking trails. These include the Bear Hair Gap Trail and the more strenuous Coosa Backcountry Trail, which leads up toward Blood Mountain and the Appalachian Trail near Neel Gap. Vogel Park features camping sites, cabins, swimming, boating and other recreational activities. Description and history Vogel State Park is located south of Blairsville on US Highway 19 in the north Georgia mountains. At nearly altitude, Vogel State ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgia Appalachian Trail Club
The Georgia Appalachian Trail Club, Inc. (GATC) is a non-profit organization that was organized in 1930 in Dahlonega, Georgia (U.S. state), GA. Its membership consists of individual volunteers who share a love for the Appalachian Trail, Appalachian Trail (AT). The GATC is responsible for the management and maintenance of the Appalachian Trail, AT in Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia. This is accomplished through cooperation with the Appalachian Trail Conservancy, Appalachian Trail Conservancy (ATC) and the U.S. Forest Service, U.S. Forest Service (USFS). The GATC is active in the Conservation ethic, conservation community on issues relating to the protection of the Appalachian Trail. It also conducts a wide range of outdoor recreational events for its membership. See also *List of Peaks on Appalachian Trail in Georgia (U.S.), Georgia Peaks on the Appalachian Trail External linksGeorgia Appalachian Trail Club [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountains Of Lumpkin County, Georgia
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least 300 metres (1,000 feet) above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DeSoto Falls (Georgia)
The DeSoto Falls of Georgia are located in Lumpkin County, Georgia along Frogtown Creek. There are actually three waterfalls on Frogtown Creek, called Upper DeSoto Falls, Middle Desoto Falls and Lower DeSoto Falls. The upper waterfall drops , the middle waterfall drops and the lower waterfall drops . The overall height of the falls, as measured inclusive of non-vertical falls, cascades and steep stream bed, is . DeSoto Falls are located at an elevation of on Rocky Mountain. The DeSoto Falls are named for Spanish explorer Hernando deSoto, who passed through Georgia around 1540. According to a sign posted on the DeSoto Falls Trail, a ''in and out'' hiking trail to the falls, a plate of armor was discovered at the base of the falls in the 1880s. The falls are part of the Chattahoochee National Forest and located in a area designated the Desoto Falls Scenic Area. There is also a campground located along the banks of Frogtown Creek. DeSoto Falls is one of four popular waterfa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liriodendron Tulipifera
''Liriodendron tulipifera''—known as the tulip tree, American tulip tree, tulipwood, tuliptree, tulip poplar, whitewood, fiddletree, and yellow-poplar—is the North American representative of the two-species genus ''Liriodendron'' (the other member is ''Liriodendron chinense''), and the tallest eastern hardwood. It is native to eastern North America from Southern Ontario and possibly southern Quebec to Illinois eastward to southwestern Massachusetts and Rhode Island, and south to central Florida and Louisiana. It can grow to more than in virgin cove forests of the Appalachian Mountains, often with no limbs until it reaches in height, making it a very valuable timber tree. The tallest individual at the present time (2021) is one called the Fork Ridge Tulip Tree at a secret location in the Great Smoky Mountains of North Carolina. Repeated measurements by laser and tape-drop have shown it to be in height. This is the tallest known individual tree in eastern North America. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aesculus
The genus ''Aesculus'' ( or ), with species called buckeye and horse chestnut, comprises 13–19 species of flowering plants in the family Sapindaceae. They are trees and shrubs native plant, native to the temperateness, temperate Northern Hemisphere, with six species native to North America and seven to 13 species native to Eurasia. Several Hybrid (biology), hybrids occur. ''Aesculus'' exhibits a classical Arcto-Tertiary Geoflora, Arcto-Tertiary distribution. Ungnadia, Mexican buckeye seedpods resemble the ''Aesculus'' seedpods, but belong to a different genus. Carl Linnaeus named the genus ''Aesculus'' after the Roman name for an edible acorn. Common names for these trees include "buckeye" and "horse chestnut", though they are not in the same order as the true chestnuts, ''Castanea'' in the Fagales. Some are also called white chestnut or red chestnut. In Britain, they are sometimes called conker trees because of their link with the game of conkers, played with the seeds, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Winfield Scott
Lake Winfield Scott is an mountain lake located south of Blairsville, Georgia in Union County. The lake, which is owned and managed by the U.S. Forest Service, is the source of Cooper Creek. It is the centerpiece of the Forest Service's Lake Winfield Scott Recreation Area, a park which features hiking, fishing, boating and other outdoor activities. At elevation it is one of Georgia's highest altitude lakes. The various habitats surrounding the lake support a wide assortment of plants and animals. History Completed in early 1942, Lake Winfield Scott is a man-made reservoir created as part of the Civilian Conservation Corps' efforts to establish recreational areas in north Georgia. It was the final CCC project in Georgia and one of the last in the nation, completed just after the United States' entry into World War II. It is located in the southern Blue Ridge Mountains near Blood Mountain. The lake was named after General Winfield Scott, a 19th-century United States Army general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hairpin Turn
A hairpin turn (also hairpin bend or hairpin corner) is a bend in a road with a very acute inner angle, making it necessary for an oncoming vehicle to turn about 180° to continue on the road. It is named for its resemblance to a bent metal hairpin. Such turns in ramps and trails may be called switchbacks in American English, by analogy with switchback railways. Description Hairpin turns are often built when a route climbs up or down a steep slope, so that it can travel mostly across the slope with only moderate steepness, and are often arrayed in a zigzag pattern. Highways with repeating hairpin turns allow easier, safer ascents and descents of mountainous terrain than a direct, steep climb and descent, at the price of greater distances of travel and usually lower speed limits, due to the sharpness of the turn. Highways of this style are also generally less costly to build and maintain than highways with tunnels. On occasion, the road may loop completely, using a tunnel or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
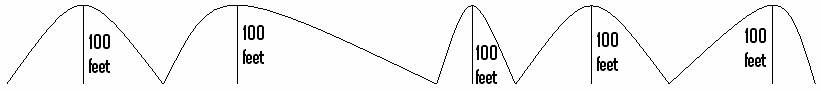
Elevation Gain
In running, cycling, and mountaineering, cumulative elevation gain refers to the sum of every gain in elevation throughout an entire trip. It is sometimes also known as cumulative gain or elevation gain, or often in the context of mountain travel, simply gain. Another commonly used phrase is total ascent. Elevation losses are not counted in this measure. Cumulative elevation gain, along with round-trip distance, is arguably the most important value used in quantifying the strenuousness of a trip. This is because hiking on flat land (zero elevation gain) is significantly easier than hiking up and down a large mountain with the same round-trip distance. Computation In the simplest case of a trip where hikers only travel ''up'' on their way to a single summit, the cumulative elevation gain is simply given by the difference in the summit elevation and the starting elevation. For example, if one starts hiking at a trailhead with elevation , and continues up to a summit of , the cumu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Mountain CCC Shelter
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in the circulatory system is also known as ''peripheral blood'', and the blood cells it carries, ''peripheral blood cells''. Blood is composed of blood cells suspended in blood plasma. Plasma, which constitutes 55% of blood fluid, is mostly water (92% by volume), and contains proteins, glucose, mineral ions, hormones, carbon dioxide (plasma being the main medium for excretory product transportation), and blood cells themselves. Albumin is the main protein in plasma, and it functions to regulate the colloidal osmotic pressure of blood. The blood cells are mainly red blood cells (also called RBCs or erythrocytes), white blood cells (also called WBCs or leukocytes) and platelets (also called thrombocytes). The most abundant cells in vertebrate blo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Park Service
The National Park Service (NPS) is an agency of the United States federal government within the U.S. Department of the Interior that manages all national parks, most national monuments, and other natural, historical, and recreational properties with various title designations. The U.S. Congress created the agency on August 25, 1916, through the National Park Service Organic Act. It is headquartered in Washington, D.C., within the main headquarters of the Department of the Interior. The NPS employs approximately 20,000 people in 423 individual units covering over 85 million acres in all 50 states, the District of Columbia, and US territories. As of 2019, they had more than 279,000 volunteers. The agency is charged with a dual role of preserving the ecological and historical integrity of the places entrusted to its management while also making them available and accessible for public use and enjoyment. History Yellowstone National Park was created as the first national par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Register Of Historic Places
The National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) is the United States federal government's official list of districts, sites, buildings, structures and objects deemed worthy of preservation for their historical significance or "great artistic value". A property listed in the National Register, or located within a National Register Historic District, may qualify for tax incentives derived from the total value of expenses incurred in preserving the property. The passage of the National Historic Preservation Act (NHPA) in 1966 established the National Register and the process for adding properties to it. Of the more than one and a half million properties on the National Register, 95,000 are listed individually. The remainder are contributing resources within historic districts. For most of its history, the National Register has been administered by the National Park Service (NPS), an agency within the U.S. Department of the Interior. Its goals are to help property owners and inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |