|
Bleed Screw
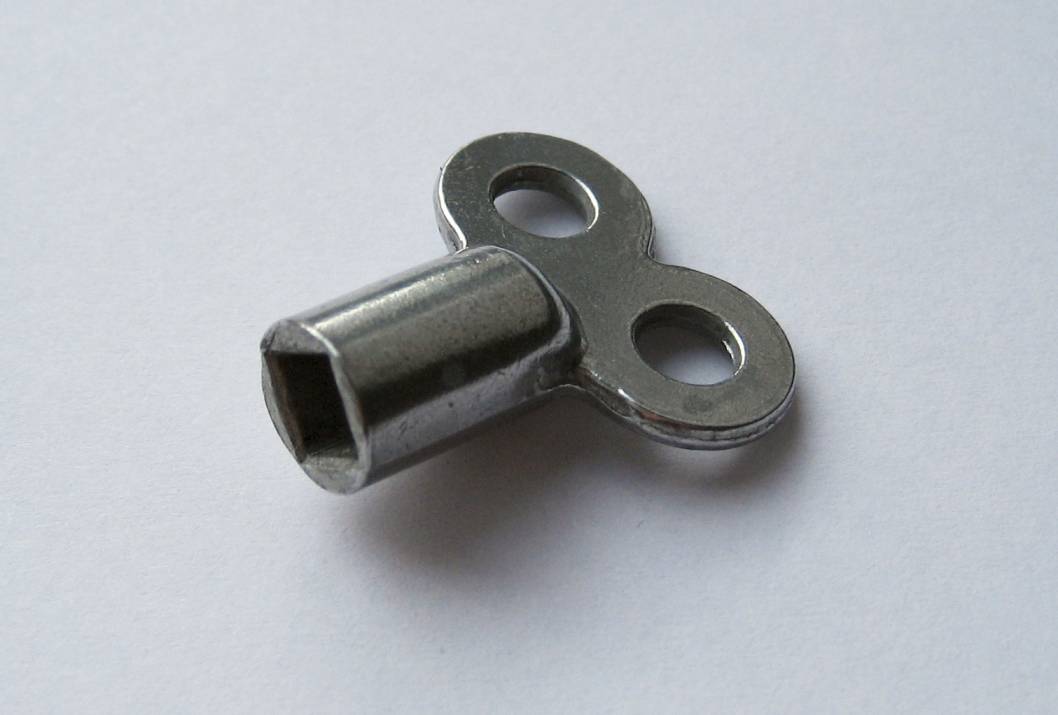
A bleed screw is a device used to create a temporary opening in an otherwise closed hydraulic system, which facilitates the removal of air or another substance from the system by way of pressure and density differences. Applications Domestic heating radiators On a home radiator unit, the bleed screw can be opened, usually by means of a key, to allow unwanted air to escape from the unit. Bleed screws are also found on some pump types fulfilling a similar purpose. They are most often located at the top of the radiator on the side of the inflow pipe. The screw itself, usually a hexagonal or square knob, is inside a small round protrusion. The key looks similar to that used to wind a clock. It is inserted into the protrusion, mates with the bleed screw and turns it. Opening the bleed screw then allows air which has risen to the top of the radiator system (the top of the radiator itself) to escape and new water to take its place. Removing the air and allowing water to displace it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haynes Manual
The Haynes Owner's Workshop Manuals (commonly known as Haynes Manuals) are a series of practical manuals from the British publisher Haynes Publishing Group. The series primarily focuses upon the maintenance and repair of automotive vehicles, covering a wide range of makes and models (300 models of car and 130 models of motorcycle); the manuals are aimed mainly at DIY enthusiasts rather than professional garage mechanics, as they lack the depth of coverage on particular vehicles or problems. The series includes a range of 'practical lifestyle' manuals in the same style for a range of topics, including domestic appliances and personal computers, digital photography, model railways, sport, animal care, men, babies, sex, and women. They also now publish the Bluffer's Guides collection. Additionally, Haynes have released manuals based on popular fictional series including '' Star Trek'' and ''Thomas and Friends''. History The Haynes manuals are named after John Harold Haynes (1938& ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brake Fluid
Brake fluid is a type of hydraulic fluid used in hydraulic brake and hydraulic clutch applications in automobiles, motorcycles, light trucks, and some bicycles. It is used to transfer force into pressure, and to amplify braking force. It works because liquids are not appreciably compressible. Most brake fluids used today are glycol-ether based, but mineral oil (''Citroën/Rolls-Royce liquide hydraulique minéral'' ( LHM)) and silicone-based (DOT 5) fluids are also available. Standards Most Brake fluids are manufactured to meet standards set by international, national, or local organizations or government agencies. International The International Standards Organisation has published its standard ISO 4925, defining classes 3, 4, and 5, as well as class 5.1, class 6 and class 7 reflecting progressively higher performance for brake fluids. SAE The Society of Automotive Engineers SAE has published standards J1703, J1704, and J1705, reflecting progressively higher performance for b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydraulics
Hydraulics (from Greek: Υδραυλική) is a technology and applied science using engineering, chemistry, and other sciences involving the mechanical properties and use of liquids. At a very basic level, hydraulics is the liquid counterpart of pneumatics, which concerns gases. Fluid mechanics provides the theoretical foundation for hydraulics, which focuses on the applied engineering using the properties of fluids. In its fluid power applications, hydraulics is used for the generation, control, and transmission of power by the use of pressurized liquids. Hydraulic topics range through some parts of science and most of engineering modules, and cover concepts such as pipe flow, dam design, fluidics and fluid control circuitry. The principles of hydraulics are in use naturally in the human body within the vascular system and erectile tissue. Free surface hydraulics is the branch of hydraulics dealing with free surface flow, such as occurring in rivers, canals, lakes, estuar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Residential Heating
A residential area is a land used in which housing predominates, as opposed to industrial and commercial areas. Housing may vary significantly between, and through, residential areas. These include single-family housing, multi-family residential, or mobile homes. Zoning for residential use may permit some services or work opportunities or may totally exclude business and industry. It may permit high density land use or only permit low density uses. Residential zoning usually includes a smaller FAR (floor area ratio) than business, commercial or industrial/manufacturing zoning. The area may be large or small. Overview In certain residential areas, especially rural, large tracts of land may have no services whatever, such that residents seeking services must use a motor vehicle or other transportation, so the need for transportation has resulted in land development following existing or planned transport infrastructure such as rail and road. Development patterns may be regu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Degasification
Degassing, also known as degasification, is the removal of dissolved gases from liquids, especially water or aqueous solutions. There are numerous methods for removing gases from liquids. Gases are removed for various reasons. Chemists remove gases from solvents when the compounds they are working on are possibly air- or oxygen-sensitive (air-free technique), or when bubble formation at solid-liquid interfaces becomes a problem. The formation of gas bubbles when a liquid is frozen can also be undesirable, necessitating degassing beforehand. Pressure reduction The solubility of gas obeys Henry's law, that is, the amount of a dissolved gas in a liquid is proportional to its partial pressure. Therefore, placing a solution under reduced pressure makes the dissolved gas less soluble. Sonication and stirring under reduced pressure can usually enhance the efficiency. This technique is often referred to as ''vacuum degasification''. Specialized vacuum chambers, called vacuum degassers, ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiator (heating)
Radiators and convectors are heat exchangers designed to transfer thermal energy from one medium to another for the purpose of space heating. Denison Olmsted of New Haven, Connecticut, appears to have been the earliest person to use the term 'radiator' to mean a heating appliance in an 1834 patent for a stove with a heat exchanger which then radiated heat. In the patent he wrote that his invention was ''a peculiar kind of apparatus, which I call a radiator''. The heating radiator was invented by Franz San Galli in 1855, a Kingdom of Prussia-born Russian businessman living in St. Petersburg. In the late 1800s, companies, such as the American Radiator Company, promoted cast iron radiators over previous fabricated steel designs in order to lower costs and expand the market. Radiation vs. convection In practice, the term ''radiator'' refers to any of a number of devices in which a fluid circulates through exposed pipes (often with fins or other means of increasing surface area), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automatic Bleeding Valve
An automatic bleeding valve or air release valve (ARV) is a plumbing valve used to automatically release trapped air from a heating system. Air, or other gas, may collect within plumbing. For water delivery systems to taps and basins, particularly with good main supply pressure, this air is usually flushed through with the water flow and does not cause a problem, although in some hot-water systems (particularly Gravity systems) air locks can be problematic. In a closed heating system though, it has no other means of escape and builds up. An air bubble trapped within a radiator means that no hot water circulates in the upper part and so the heating power of the radiator is reduced. If air is trapped within the boiler this may cause pump cavitation or boiling and overheating within the heat exchanger. Installation and use Automatic valves are used to release trapped air as it collects. They are not a substitute for bleeding a system manually when it is first filled during commi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slave Cylinder
In automotive engineering, the master cylinder is a control device that converts force (commonly from a driver's foot) into hydraulic pressure. This device controls slave cylinders located at the other end of the hydraulic brake system. As piston(s) move along the bore of the master cylinder, this movement is transferred through the hydraulic fluid, to result in a movement of the slave cylinder(s). The hydraulic pressure created by moving a piston (inside the bore of the master cylinder) toward the slave cylinder(s) compresses the fluid evenly, but by varying the comparative surface area of the master cylinder and each slave cylinder, one can vary the amount of force and displacement applied to each slave cylinder, relative to the amount of force and displacement applied to the master cylinder. Vehicle applications The most common vehicle uses of master cylinders are in brake and clutch systems. In brake systems, the operated devices are cylinders inside brake calipers and/or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
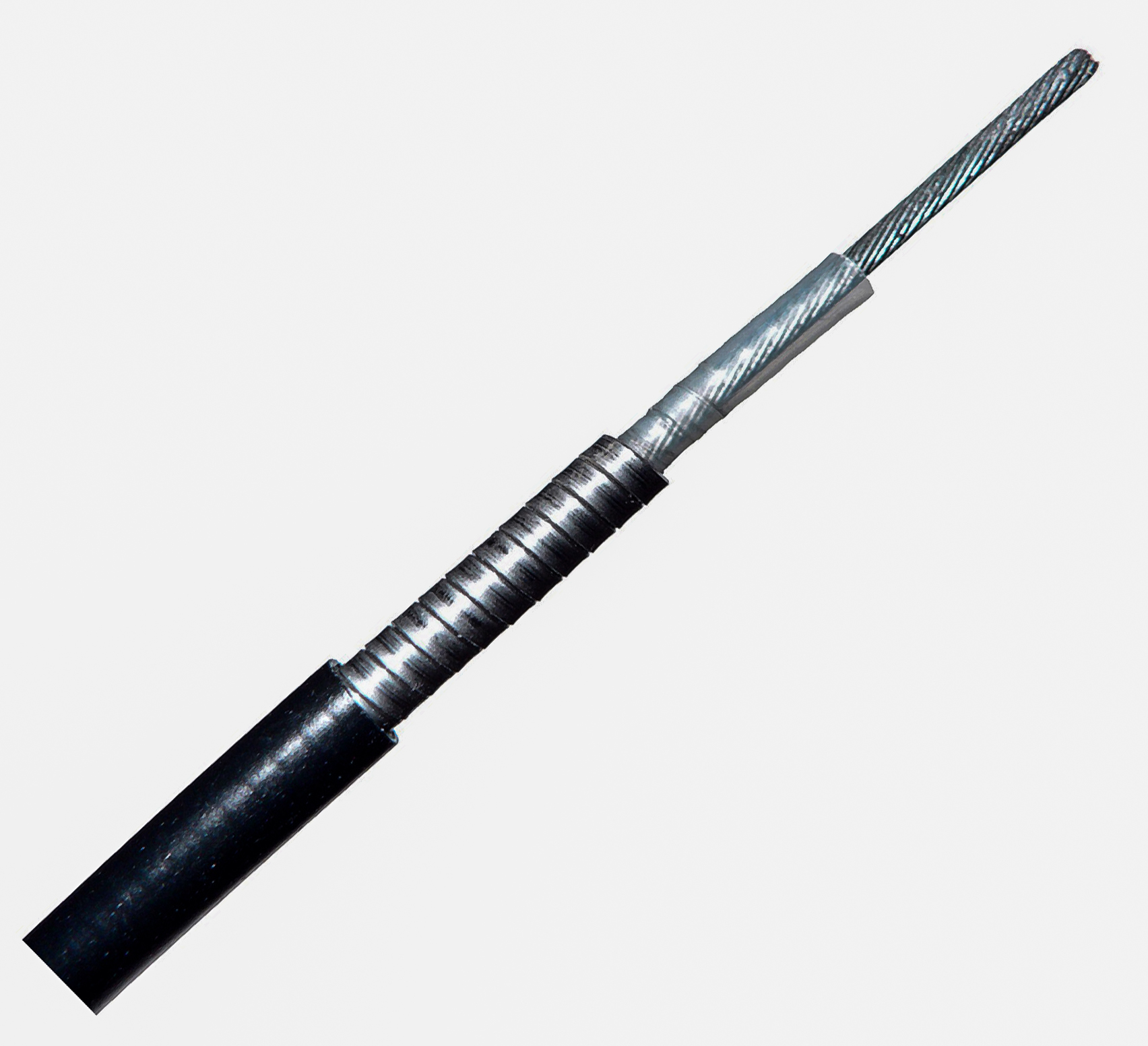
Bowden Cable
A Bowden cable ( ) is a type of flexible cable used to transmit mechanical force or energy by the movement of an inner cable relative to a hollow outer cable housing. The housing is generally of composite construction, consisting of an inner lining, a longitudinally incompressible layer such as a helical winding or a sheaf of steel wire, and a protective outer covering. The linear movement of the inner cable is most often used to transmit a pulling force, although push/pull cables have gained popularity in recent years e.g. as gear shift cables. Many light aircraft use a push/pull Bowden cable for the throttle control, and here it is normal for the inner element to be a solid wire, rather than a multi-strand cable. Usually, provision is made for adjusting the cable tension using an inline hollow bolt (often called a "barrel adjuster"), which lengthens or shortens the cable housing relative to a fixed anchor point. Lengthening the housing (turning the barrel adjuster out) ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clutch
A clutch is a mechanical device that engages and disengages power transmission, especially from a drive shaft to a driven shaft. In the simplest application, clutches connect and disconnect two rotating shafts (drive shafts or line shafts). In these devices, one shaft is typically attached to an engine or other power unit (the driving member), while the other shaft (the driven member) provides output power for work. Typically the motions involved are rotary, but linear clutches also exist. In a motor vehicle, the clutch acts as a mechanical linkage between the engine and transmission, and briefly disconnects, or separates the engine from the transmission system. This disconnects the drive wheels whenever the clutch pedal is depressed, allowing the driver to smoothly change gears. In a torque-controlled drill, for instance, one shaft is driven by a motor, and the other drives a drill chuck. The clutch connects the two shafts so they may be locked together and spin at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gearbox
Propulsion transmission is the mode of transmitting and controlling propulsion power of a machine. The term ''transmission'' properly refers to the whole drivetrain, including clutch, gearbox, prop shaft (for rear-wheel drive vehicles), differential, and final drive shafts. In the United States the term is sometimes used in casual speech to refer more specifically to the gearbox alone, and detailed usage differs. The transmission reduces the higher engine speed to the slower wheel speed, increasing torque in the process. Transmissions are also used on pedal bicycles, fixed machines, and where different rotational speeds and torques are adapted. Often, a transmission has multiple gear ratios (or simply "gears") with the ability to switch between them as the speed varies. This switching may be done manually (by the operator) or automatically (by a control unit). Directional (forward and reverse) control may also be provided. Single-ratio transmissions also exist, which simply chan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bleeder Valve Entlüftungsventil IMG 6446
Bleeding usually means the leakage or loss of blood from the body. Bleeding, bleed, or bleeder may also refer to: *Bleed (printing), intentionally printing across the expected trim line or edge of the sheet *Bleed, or spill (audio), when audio from one source is picked up by a microphone intended for a different source *Bleed, the presence of surface water on concrete *Bleed air, compressed air taken from gas turbine compressor stages * Bleeder, baseball term for a weakly hit ground ball that goes for a base hit *Bleeder resistor, which passively discharges a capacitor when it is disconnected or equipment is powered off * Bleeding (computer graphics), a computer graphics term for when a graphic object passes through another in an unwanted manner *Bleeding (roads), a type of pavement distress common in asphalt roads *Bleeding, or capillary action, the ability of a substance (such as blood, ink, or water) to flow in narrow spaces without the assistance of, and in opposition to externa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |