|
Blasticidin S
Blasticidin S is an antibiotic that is used in biology research for selecting cells in cell culture. Cells of interest can express the blasticidin resistance genes BSD or bsr, and can then survive treatment with the antibiotic. Blasticidin S is a nucleoside analogue antibiotic, resembling the nucleoside cytidine. Blasticidin works against human cells, fungi, and bacteria, all by disrupting protein translation. It was originally described by Japanese researchers in the 1950s seeking antibiotics for rice blast fungus. Chemistry A nucleoside analog, blasticidin S resembles the nucleoside cytidine. The chemical structure consists of a cytosine molecule, linked to a glucuronic acid-derived ring, linked in turn to the peptide N-methyl β-arginine. Uses Blasticidin S is widely used in cell culture for selecting and maintaining genetically manipulated cells. Cells of interest express the blasticidin S resistance genes BSD or bsr, and can then survive blasticidin S being added ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention of such infections. They may either kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria. A limited number of antibiotics also possess antiprotozoal activity. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses such as the common cold or influenza; drugs which inhibit viruses are termed antiviral drugs or antivirals rather than antibiotics. Sometimes, the term ''antibiotic''—literally "opposing life", from the Greek roots ἀντι ''anti'', "against" and βίος ''bios'', "life"—is broadly used to refer to any substance used against microbes, but in the usual medical usage, antibiotics (such as penicillin) are those produced naturally (by one microorganism fighting another), whereas non-antibiotic antibacterials (such as sulfonamides and antiseptics) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Translation (genetics)
In molecular biology and genetics, translation is the process in which ribosomes in the cytoplasm or endoplasmic reticulum synthesize proteins after the process of transcription of DNA to RNA in the cell's nucleus. The entire process is called gene expression. In translation, messenger RNA (mRNA) is decoded in a ribosome, outside the nucleus, to produce a specific amino acid chain, or polypeptide. The polypeptide later folds into an active protein and performs its functions in the cell. The ribosome facilitates decoding by inducing the binding of complementary tRNA anticodon sequences to mRNA codons. The tRNAs carry specific amino acids that are chained together into a polypeptide as the mRNA passes through and is "read" by the ribosome. Translation proceeds in three phases: # Initiation: The ribosome assembles around the target mRNA. The first tRNA is attached at the start codon. # Elongation: The last tRNA validated by the small ribosomal subunit (''accommodation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungus
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''true f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
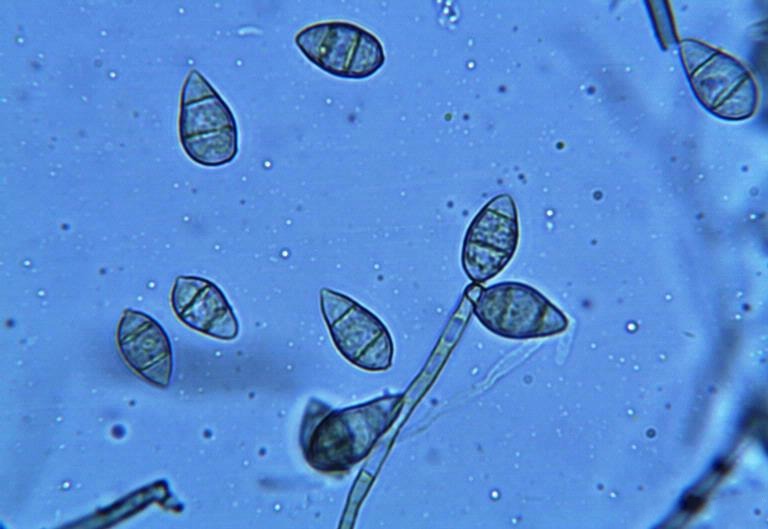
Magnaporthe Grisea
''Magnaporthe grisea'', also known as rice blast fungus, rice rotten neck, rice seedling blight, blast of rice, oval leaf spot of graminea, pitting disease, ryegrass blast, Johnson spot, neck blast, wheat blast, and Imochi (Japanese:稲熱) is a plant-pathogenic fungus and model organism that causes a serious disease affecting rice. It is now known that ''M. grisea'' consists of a cryptic species complex containing at least two biological species that have clear genetic differences and do not interbreed. Complex members isolated from ''Digitaria'' have been more narrowly defined as ''M. grisea''. The remaining members of the complex isolated from rice and a variety of other hosts have been renamed ''Magnaporthe oryzae'', within the same ''M. grisea'' complex. Confusion on which of these two names to use for the rice blast pathogen remains, as both are now used by different authors. Members of the ''Magnaporthe grisea'' complex can also infect other agriculturally important cereal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north toward the East China Sea, Philippine Sea, and Taiwan in the south. Japan is a part of the Ring of Fire, and spans Japanese archipelago, an archipelago of List of islands of Japan, 6852 islands covering ; the five main islands are Hokkaido, Honshu (the "mainland"), Shikoku, Kyushu, and Okinawa Island, Okinawa. Tokyo is the Capital of Japan, nation's capital and largest city, followed by Yokohama, Osaka, Nagoya, Sapporo, Fukuoka, Kobe, and Kyoto. Japan is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eleventh most populous country in the world, as well as one of the List of countries and dependencies by population density, most densely populated and Urbanization by country, urbanized. About three-fourths of Geography of Japan, the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillus Cereus
''Bacillus cereus'' is a Gram-positive rod-shaped bacterium commonly found in soil, food, and marine sponges. The specific name, ''cereus'', meaning "waxy" in Latin, refers to the appearance of colonies grown on blood agar. Some strains are harmful to humans and cause foodborne illness due to their spore-forming nature, while other strains can be beneficial as probiotics for animals, and even exhibit mutualism with certain plants. ''B. cereus'' bacteria may be anaerobes or facultative anaerobes, and like other members of the genus ''Bacillus'', can produce protective endospores. They have a wide range of virulence factors, including phospholipase C, cereulide, sphingomyelinase, metalloproteases, and cytotoxin K, many of which are regulated via quorum sensing. ''B. cereus'' strains exhibit flagellar motility. The ''Bacillus cereus'' group comprises seven closely related species: ''B. cereus'' ''sensu stricto'' (referred to herein as ''B. cereus''), '' B. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspergillus Terreus
''Aspergillus terreus'', also known as ''Aspergillus terrestris'', is a fungus (mold) found worldwide in soil. Although thought to be strictly asexual until recently, ''A. terreus'' is now known to be capable of sexual reproduction. This saprotrophic fungus is prevalent in warmer climates such as tropical and subtropical regions. Aside from being located in soil, ''A. terreus'' has also been found in habitats such as decomposing vegetation and dust. ''A. terreus'' is commonly used in industry to produce important organic acids, such as itaconic acid and ''cis''-aconitic acid, as well as enzymes, like xylanase. It was also the initial source for the drug mevinolin (lovastatin), a drug for lowering serum cholesterol. ''Aspergillus terreus'' can cause opportunistic infection in people with deficient immune systems. It is relatively resistant to amphotericin B, a common antifungal drug. ''Aspergillus terreus'' also produces aspterric acid and 6-hydroxymellein, inhibitors of pollen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deaminase
Deamination is the removal of an amino group from a molecule. Enzymes that catalyse this reaction are called deaminases. In the human body, deamination takes place primarily in the liver, however it can also occur in the kidney. In situations of excess protein intake, deamination is used to break down amino acids for energy. The amino group is removed from the amino acid and converted to ammonia. The rest of the amino acid is made up of mostly carbon and hydrogen, and is recycled or oxidized for energy. Ammonia is toxic to the human system, and enzymes convert it to urea or uric acid by addition of carbon dioxide molecules (which is not considered a deamination process) in the urea cycle, which also takes place in the liver. Urea and uric acid can safely diffuse into the blood and then be excreted in urine. Deamination reactions in DNA Cytosine Spontaneous deamination is the hydrolysis reaction of cytosine into uracil, releasing ammonia in the process. This can occur in vitro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antimicrobial Resistance
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) occurs when microbes evolve mechanisms that protect them from the effects of antimicrobials. All classes of microbes can evolve resistance. Fungi evolve antifungal resistance. Viruses evolve antiviral resistance. Protozoa evolve antiprotozoal resistance, and bacteria evolve antibiotic resistance. Those bacteria that are considered extensively drug resistant (XDR) or totally drug-resistant (TDR) are sometimes called "superbugs".A.-P. Magiorakos, A. Srinivasan, R. B. Carey, Y. Carmeli, M. E. Falagas, C. G. Giske, S. Harbarth, J. F. Hinndler ''et al''Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria... Clinical Microbiology and Infection, Vol 8, Iss. 3 first published 27 July 2011 ia Wiley Online Library Retrieved 28 August 2020 Although antimicrobial resistance is a naturally-occurring process, it is often the result of improper usage of the drugs and management of the infections. Antibiotic resistance is a major subset o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streptomyces Lividans
Snapalysin (, ''small neutral protease'', ''SnpA gene product (Streptomyces lividans)'') is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the IUPAC nomenclature for organic transformations, chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the pos ... : Hydrolyses proteins with a preference for Tyr or Phe in the P1' position. Has no action on amino-acid p-nitroanilides This enzyme belongs to the peptidase family M7. References External links * {{Portal bar, Biology, border=no EC 3.4.24 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streptomyces Griseochromogenes
''Streptomyces griseochromogenes'' is a bacterium species from the genus of ''Streptomyces'' which has been isolated from soil.Deutsche Sammlung von Mikroorganismen und Zellkulturenbr>/ref> ''Streptomyces griseochromogenes'' produces blasticidin A, blasticidin B, blasticidin C, blasticidin S Blasticidin S is an antibiotic that is used in biology research for selecting cells in cell culture. Cells of interest can express the blasticidin resistance genes BSD or bsr, and can then survive treatment with the antibiotic. Blasticidin S is ..., pentalenene and cytomycin. See also * List of ''Streptomyces'' species References External linksType strain of ''Streptomyces griseochromogenes'' at Bac''Dive'' – the Bacterial Diversity Metadatabase griseochromogenes Bacteria described in 1955 {{Streptomyces-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CGA Synthase
CGA may refer to: Companies and organizations * Canadian Gemmological Association * Coast Guard Administration of Taiwan * Controller General of Accounts of Pakistan * Central of Georgia Railway, in 1833, a.k.a. Central Rail Road and Banking Company of Georgia * Community of the Glorious Ascension, a Christian monastic community * Compressed Gas Association * Connecticut General Assembly, the bicameral legislative body of the American state of Connecticut * United States Coast Guard Academy, the military academy of the US Coast Guard * United States Coast Guard Auxiliary, a civilian branch of the US Coast Guard * , the Education Workforce Council of Wales * Casual Games Association, an industry group for casual video game developers and publishers * Coordination of Anarchist Groups, a French anarchist organization Computing * Color Graphics Adapter, IBM's first graphics display card * Computer animation, a.k.a. computer-generated animation * Cryptographically Generated Addre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |