|
Bjerkandera Adusta
''Bjerkandera adusta'', commonly known as the smoky polypore or smoky bracket, is a species of fungus in the family Meruliaceae. It is a plant pathogen that causes Wood-decay fungus#White rot, white rot in live trees, but most commonly appears on dead wood. It was first species description, described scientifically as ''Boletus adustus'' by Carl Ludwig Willdenow in 1787. The Whole genome sequencing, genome sequence of ''Bjerkandera adusta'' was reported in 2013. The species is inedible. Description The fungus grows in shelflike fruit bodies which often overlap. The caps are tomentose to hairy and buff in colour. The species is often found on decaying wood. ''Bjerkandera fumosa'' is similar; its flesh has a dark line near the base of the tubes. Some members of the genera ''Stereum'' and ''Trametes'' are similar as well. Chemistry Because ''Bjerkandera adusta'' produces enzymes that can degrade polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, such as those used in synthetic textile dyeing, dy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fruit Bodies
The sporocarp (also known as fruiting body, fruit body or fruitbody) of fungi is a multicellular structure on which spore-producing structures, such as basidia or asci, are borne. The fruitbody is part of the sexual phase of a fungal life cycle, while the rest of the life cycle is characterized by vegetative mycelial growth and asexual spore production. The sporocarp of a basidiomycete is known as a ''basidiocarp'' or ''basidiome'', while the fruitbody of an ascomycete is known as an '' ascocarp''. Many shapes and morphologies are found in both basidiocarps and ascocarps; these features play an important role in the identification and taxonomy of fungi. Fruitbodies are termed ''epigeous'' if they grow on the ground, while those that grow underground are ''hypogeous''. Epigeous sporocarps that are visible to the naked eye, especially fruitbodies of a more or less agaricoid morphology, are often called mushrooms. Epigeous sporocarps have mycelia that extend underground far ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi Described In 1787
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''true fungi' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungal Plant Pathogens And Diseases
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''true f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi Of Europe
A fungus (plural, : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of Eukaryote, eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and Mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a Kingdom (biology), kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of motility, mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
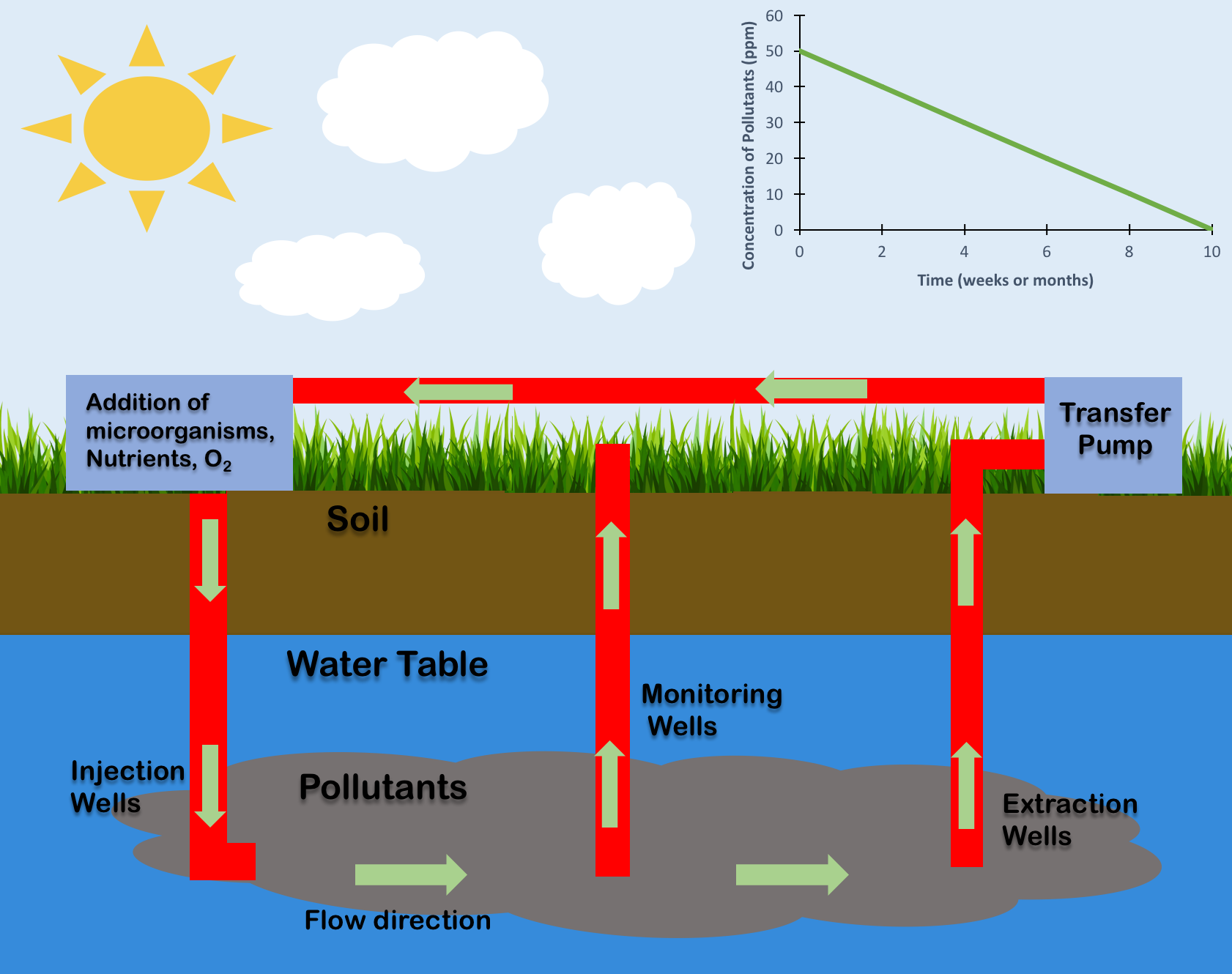
Bioremediation
Bioremediation broadly refers to any process wherein a biological system (typically bacteria, microalgae, fungi, and plants), living or dead, is employed for removing environmental pollutants from air, water, soil, flue gasses, industrial effluents etc., in natural or artificial settings. The natural ability of organisms to adsorb, accumulate, and degrade common and emerging pollutants has attracted the use of biological resources in treatment of contaminated environment. In comparison to conventional physicochemical treatment methods bioremediation may offer considerable advantages as it aims to be sustainable, eco-friendly, cheap, and scalable. Most bioremediation is inadvertent, involving native organisms. Research on bioremediation is heavily focused on stimulating the process by inoculation of a polluted site with organisms or supplying nutrients to promote the growth. In principle, bioremediation could be used to reduce the impact of byproducts created from anthropogenic acti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyeing
Dyeing is the application of dyes or pigments on textile materials such as fibers, yarns, and fabrics with the goal of achieving color with desired color fastness. Dyeing is normally done in a special solution containing dyes and particular chemical material. Dye molecules are fixed to the fiber by absorption, diffusion, or bonding with temperature and time being key controlling factors. The bond between dye molecule and fiber may be strong or weak, depending on the dye used. Dyeing and printing are different applications; in printing, color is applied to a localized area with desired patterns. In dyeing, it is applied to the entire textile. The primary source of dye, historically, has been nature, with the dyes being extracted from animals or plants. Since the mid-19th century, however, humans have produced artificial dyes to achieve a broader range of colors and to render the dyes more stable to washing and general use. Different classes of dyes are used for different types ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon
A polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) is a class of organic compounds that is composed of multiple aromatic rings. The simplest representative is naphthalene, having two aromatic rings and the three-ring compounds anthracene and phenanthrene. PAHs are uncharged, non-polar and planar. Many are colorless. Many of them are found in coal and in oil deposits, and are also produced by the combustion of organic matter—for example, in engines and incinerators or when biomass burns in forest fires. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons are discussed as possible starting materials for abiotic syntheses of materials required by the earliest forms of life. Nomenclature and structure The terms polyaromatic hydrocarbon or polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbon are also used for this concept. By definition, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons have multiple rings, precluding benzene from being considered a PAH. Some sources, such as the US EPA and CDC, consider naphthalene to be the simplest PAH. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trametes
''Trametes'' is a genus of fungi that is distinguished by a pileate basidiocarp, di- to trimitic hyphal systems, smooth non-dextrinoid spores, and a hymenium usually without true hymenial cystidia.Ryvarden L. (1991). "Genera of polypores: Nomenclature and taxonomy." ''Syn. Fung.'' 5: 1–363. The genus has a widespread distribution and contains about fifty species. The genus was circumscribed by Elias Magnus Fries in 1836. ''Trametes'' fungi are food for caterpillars of certain Lepidoptera, mainly fungus moths (Tineidae) such as ''Triaxomera parasitella''. Biotechnology Several species of ''Trametes'' have been investigated for biotechnological application of their lignin-degrading enzymes (particularly laccase and manganese peroxidase) for analytical, industrial or environmental sciences. Selected species *''Trametes gibbosa'' – Lumpy bracket *''Trametes hirsuta'' – Hairy bracket *''Trametes nivosa'' *''Trametes pubescens'' *''Trametes versicolor ''Trametes versicol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stereum
''Stereum'' is the type genus of the Stereaceae family of fungi, in the Russulales order. Until recently, the genus was classified in the Corticiaceae family, of the Corticiales order. However, it was given its own family as a result of the split-up of the Corticiales. Common names for species of this genus include leaf fungus, wax fungus, and shelf fungus. Fungi having a shape similar to a ''Stereum'' are said to have a stereoid shape. ''Stereum'' contains 27 species that have a widespread distribution. Habitat ''Stereum'' species are found to live on all kinds of deadwood or hardwood or dead leaves (they are therefore said to be saprobic). Sometimes they are also found on living leaves. Characteristics ''Stereum'' species are wood decay fungi. Their simple, shelving fruiting bodies have a smooth hymenium, lacking gills or tubes. Like most members or the family Stereaceae, ''Stereum'' fruiting bodies lack clamp connections and produce amyloid basidiospores. The species can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genera
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus '' Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants of an ancestral taxon are grouped together (i.e. phylogenetic analysis should clearly demons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)


