|
Bismuth
Bismuth is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Bi and atomic number 83. It is a post-transition metal and one of the pnictogens, with chemical properties resembling its lighter group 15 siblings arsenic and antimony. Elemental bismuth occurs naturally, and its sulfide and oxide forms are important commercial ores. The free element is 86% as dense as lead. It is a brittle metal with a silvery-white color when freshly produced. Passivation (chemistry), Surface oxidation generally gives samples of the metal a somewhat rosy cast. Further oxidation under heat can give bismuth a vividly Iridescence, iridescent appearance due to thin-film interference. Bismuth is both the most Diamagnetism, diamagnetic element and one of the least Thermal conductivity, thermally conductive metals known. Bismuth was long considered the element with the highest atomic mass whose nuclei do not spontaneously decay. However, in 2003 it was discovered to be extremely weakly radioactive. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pnictogen
A pnictogen ( or ; from grc, πνῑ́γω "to choke" and -gen, "generator") is any of the chemical elements in group 15 of the periodic table. Group 15 is also known as the nitrogen group or nitrogen family. Group 15 consists of the elements nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), bismuth (Bi), and moscovium (Mc). Since 1988, IUPAC calls it Group 15. Before that, in America it was called Group VA, owing to a text by H. C. Deming and the Sargent-Welch Scientific Company, while in Europe it was called Group VB and IUPAC recommended that in 1970. (Pronounced "group five A" and "group five B"; "V" is the Roman numeral 5). In semiconductor physics, it is still usually called Group V. The "five" ("V") in the historical names comes from the " pentavalency" of nitrogen, reflected by the stoichiometry of compounds such as N2O5. They have also been called the pentels. Characteristics Chemical Like other groups, the members of this family show similar patterns ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Group 15
A pnictogen ( or ; from grc, πνῑ́γω "to choke" and -gen, "generator") is any of the chemical elements in group 15 of the periodic table. Group 15 is also known as the nitrogen group or nitrogen family. Group 15 consists of the elements nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), bismuth (Bi), and moscovium (Mc). Since 1988, IUPAC calls it Group 15. Before that, in America it was called Group VA, owing to a text by H. C. Deming and the Sargent-Welch Scientific Company, while in Europe it was called Group VB and IUPAC recommended that in 1970. (Pronounced "group five A" and "group five B"; "V" is the Roman numeral 5). In semiconductor physics, it is still usually called Group V. The "five" ("V") in the historical names comes from the " pentavalency" of nitrogen, reflected by the stoichiometry of compounds such as N2O5. They have also been called the pentels. Characteristics Chemical Like other groups, the members of this family show similar patter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bismuth Subsalicylate
Bismuth subsalicylate, sold generically as pink bismuth and under the brand names Pepto-Bismol and BisBacter, is an antacid medication used to treat temporary discomforts of the stomach and gastrointestinal tract, such as nausea, heartburn, indigestion, upset stomach, and diarrhea. Bismuth subsalicylate has the empirical chemical formula of C7H5BiO4, and it is a colloidal substance obtained by hydrolysis of bismuth salicylate (Bi(C6H4(OH)CO2)3). Medical uses As a derivative of salicylic acid, bismuth subsalicylate displays anti-inflammatory and bactericidal action. It also acts as an antacid. Adverse effects There are some adverse effects. It can cause a black tongue and black stools in some users of the drug when it combines with trace amounts of sulfur in saliva and the colon to form bismuth sulfide. Bismuth sulfide is a highly insoluble black salt, and the discoloration seen is temporary and harmless. Long-term use (greater than six weeks) may lead to accumulation and tox ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bismuth-209
Bismuth-209 (209Bi) is the isotope of bismuth with the longest known half-life of any radioisotope that undergoes α-decay (alpha decay). It has 83 protons and a magic number of 126 neutrons, and an atomic mass of 208.9803987 amu (atomic mass units). Primordial bismuth consists entirely of this isotope. Decay properties Bismuth-209 was long thought to have the heaviest stable nucleus of any element, but in 2003, a research team at the Institut d’Astrophysique Spatiale in Orsay, France, discovered that 209Bi undergoes alpha decay with a half-life of approximately 19 exayears (1.9×1019, approximately 19 quintillion years), over a billion times longer than the current estimated age of the universe. The heaviest nucleus considered to be stable is now lead-208 and the heaviest stable monoisotopic element is gold as the 197Au isotope. Theory had previously predicted a half-life of 4.6 years. It had been suspected to be radioactive for a long time. The decay event produces a 3.1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post-transition Metal
The metallic elements in the periodic table located between the transition metals and the chemically weak nonmetallic metalloids have received many names in the literature, such as ''post-transition metals'', ''poor metals'', ''other metals'', ''p-block metals'' and ''chemically weak metals''; none have been recommended by IUPAC. The most common name, ''post-transition metals'', is generally used in this article. Depending on where the adjacent sets of transition metals and metalloids are judged to begin and end, there are at least five competing proposals for which elements to count as post-transition metals: the three most common contain six, ten and thirteen elements, respectively (see image). All proposals include gallium, indium, tin, thallium, lead, and bismuth. Physically, these metals are soft (or brittle), have poor mechanical strength, and usually have melting points lower than those of the transition metals. Being close to the metal-nonmetal border, their crystallin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element with the symbol As and atomic number 33. Arsenic occurs in many minerals, usually in combination with sulfur and metals, but also as a pure elemental crystal. Arsenic is a metalloid. It has various allotropes, but only the gray form, which has a metallic appearance, is important to industry. The primary use of arsenic is in alloys of lead (for example, in car batteries and ammunition). Arsenic is a common n-type dopant in semiconductor electronic devices. It is also a component of the III-V compound semiconductor gallium arsenide. Arsenic and its compounds, especially the trioxide, are used in the production of pesticides, treated wood products, herbicides, and insecticides. These applications are declining with the increasing recognition of the toxicity of arsenic and its compounds. A few species of bacteria are able to use arsenic compounds as respiratory metabolites. Trace quantities of arsenic are an essential dietary element in rats, ham ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symbol (chemistry)
Chemical symbols are the abbreviations used in chemistry for chemical elements, functional groups and chemical compounds. Element symbols for chemical elements normally consist of one or two letters from the Latin alphabet and are written with the first letter capitalised. History Earlier symbols for chemical elements stem from classical Latin and Greek vocabulary. For some elements, this is because the material was known in ancient times, while for others, the name is a more recent invention. For example, Pb is the symbol for lead (''plumbum'' in Latin); Hg is the symbol for mercury (''hydrargyrum'' in Greek); and He is the symbol for helium (a new Latin name) because helium was not known in ancient Roman times. Some symbols come from other sources, like W for tungsten (''Wolfram'' in German) which was not known in Roman times. A three-letter temporary symbol may be assigned to a newly synthesized (or not yet synthesized) element. For example, "Uno" was the temporary symbol fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primordial Isotope
In geochemistry, geophysics and nuclear physics, primordial nuclides, also known as primordial isotopes, are nuclides found on Earth that have existed in their current form since before Earth was formed. Primordial nuclides were present in the interstellar medium from which the solar system was formed, and were formed in, or after, the Big Bang, by nucleosynthesis in stars and supernovae followed by mass ejection, by cosmic ray spallation, and potentially from other processes. They are the stable nuclides plus the long-lived fraction of radionuclides surviving in the primordial solar nebula through planet accretion until the present; 286 such nuclides are known. Stability All of the known 251 stable nuclides, plus another 35 nuclides that have half-lives long enough to have survived from the formation of the Earth, occur as primordial nuclides. These 35 primordial radionuclides represent isotopes of 28 separate elements. Cadmium, tellurium, xenon, neodymium, samarium, osmium, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radioactive
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is considered radioactive. Three of the most common types of decay are alpha decay ( ), beta decay ( ), and gamma decay ( ), all of which involve emitting one or more particles. The weak force is the mechanism that is responsible for beta decay, while the other two are governed by the electromagnetism and nuclear force. A fourth type of common decay is electron capture, in which an unstable nucleus captures an inner electron from one of the electron shells. The loss of that electron from the shell results in a cascade of electrons dropping down to that lower shell resulting in emission of discrete X-rays from the transitions. A common example is iodine-125 commonly used in medical settings. Radioactive decay is a stochastic (i.e. random) process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
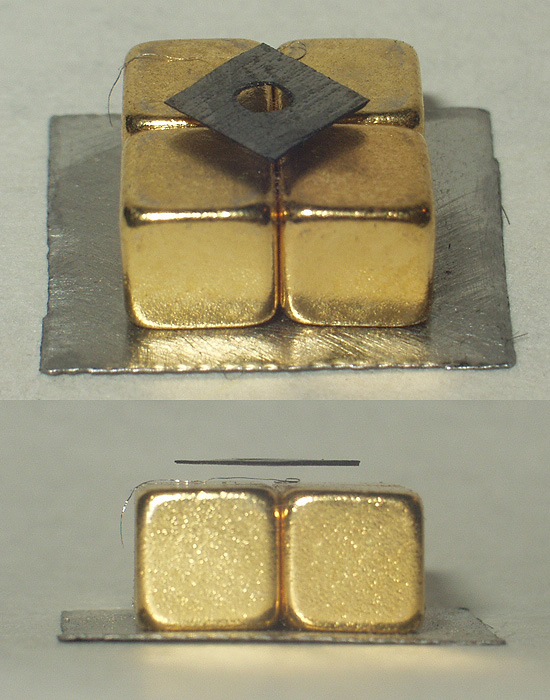
Diamagnetism
Diamagnetic materials are repelled by a magnetic field; an applied magnetic field creates an induced magnetic field in them in the opposite direction, causing a repulsive force. In contrast, paramagnetic and ferromagnetic materials are attracted by a magnetic field. Diamagnetism is a quantum mechanical effect that occurs in all materials; when it is the only contribution to the magnetism, the material is called diamagnetic. In paramagnetic and ferromagnetic substances, the weak diamagnetic force is overcome by the attractive force of magnetic dipoles in the material. The magnetic permeability of diamagnetic materials is less than the permeability of vacuum, ''μ''0. In most materials, diamagnetism is a weak effect which can be detected only by sensitive laboratory instruments, but a superconductor acts as a strong diamagnet because it repels a magnetic field entirely from its interior. Diamagnetism was first discovered when Anton Brugmans observed in 1778 that bismuth was repel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Element
A chemical element is a species of atoms that have a given number of protons in their nuclei, including the pure substance consisting only of that species. Unlike chemical compounds, chemical elements cannot be broken down into simpler substances by any chemical reaction. The number of protons in the nucleus is the defining property of an element, and is referred to as its atomic number (represented by the symbol ''Z'') – all atoms with the same atomic number are atoms of the same element. Almost all of the baryonic matter of the universe is composed of chemical elements (among rare exceptions are neutron stars). When different elements undergo chemical reactions, atoms are rearranged into new compounds held together by chemical bonds. Only a minority of elements, such as silver and gold, are found uncombined as relatively pure native element minerals. Nearly all other naturally occurring elements occur in the Earth as compounds or mixtures. Air is primarily a mixture o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cut, lead is a shiny gray with a hint of blue. It tarnishes to a dull gray color when exposed to air. Lead has the highest atomic number of any stable element and three of its isotopes are endpoints of major nuclear decay chains of heavier elements. Lead is toxic, even in small amounts, especially to children. Lead is a relatively unreactive post-transition metal. Its weak metallic character is illustrated by its amphoteric nature; lead and lead oxides react with acids and bases, and it tends to form covalent bonds. Compounds of lead are usually found in the +2 oxidation state rather than the +4 state common with lighter members of the carbon group. Exceptions are mostly limited to organolead compounds. Like the lighter members of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



%2C_black_and_white.png)
