|
Bird Behavior
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to birds: Birds (class Aves) – winged, bipedal, endothermic (warm-blooded), egg-laying, vertebrate animals. There are around 10,000 living species, making them the most varied of tetrapod vertebrates. They inhabit ecosystems across the globe, from the Arctic, to the Antarctic. Extant birds range in size from the bee hummingbird to the ostrich. What ''type'' of thing is a bird A bird can be described as all of the following: * Life form – entity or being that is living or alive. ** Animal – multicellular, eukaryotic organisms of the kingdom Animalia (also called Metazoa). Their body plan eventually becomes fixed as they develop, although some undergo a process of metamorphosis later on in their lives. Most animals are motile, meaning they can move spontaneously and independently. Biological classification * Kingdom: Animalia * Phylum: Chordata * Class: Aves Nature of birds Bir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Life Form
Life form (also spelled life-form or lifeform) is an entity that is living, such as plants (flora) and animals (fauna). It is estimated that more than 99% of all species that ever existed on Earth, amounting to over five billion species, are extinct. Earth is the only celestial body known to harbor life forms. No form of extraterrestrial life has ever been discovered. Archaea * Archaea – a domain of single-celled microorganisms, morphologically similar to bacteria, but they possess genes and several metabolic pathways that are more closely related to those of eukaryotes, notably the enzymes involved in transcription and translation. Many archaea are extremophiles, which means living in harsh environments, such as hot springs and salt lakes, but they have since been found in a broad range of habitats. ** Thermoproteota – a phylum of the Archaea kingdom. Initially *** Thermoprotei **** Sulfolobales – grow in terrestrial volcanic hot springs with optimum growth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barb (feather)
Feathers are epidermal growths that form a distinctive outer covering, or plumage, on both avian (bird) and some non-avian dinosaurs and other archosaurs. They are the most complex integumentary structures found in vertebrates and a premier example of a complex evolutionary novelty. They are among the characteristics that distinguish the extant birds from other living groups. Although feathers cover most of the bird's body, they arise only from certain well-defined tracts on the skin. They aid in flight, thermal insulation, and waterproofing. In addition, coloration helps in communication and protection. Plumology (or plumage science) is the name for the science that is associated with the study of feathers. Feathers have a number of utilitarian, cultural, and religious uses. Feathers are both soft and excellent at trapping heat; thus, they are sometimes used in high-class bedding, especially pillows, blankets, and mattresses. They are also used as filling for winter clothin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alula
The alula , or bastard wing, (plural ''alulae'') is a small projection on the anterior edge of the wing of modern birds and a few non-avian dinosaurs. The word is Latin and means "winglet"; it is the diminutive of ''ala'', meaning "wing". The alula is the freely moving first digit, a bird's "thumb", and typically bears three to five small flight feathers, with the exact number depending on the species. There also are minor covert feathers overlying the flight feathers. Like the larger flight feathers found on the wing's trailing edge, these alula feathers are asymmetrical, with the shaft running closer to anterior edge. Function In most situations, the alula is held flush against the wing; however, it can be manipulated. When flying at slow speeds or landing, the bird moves its alula slightly upwards and forward, which creates a small slot on the wing's leading edge. This functions in the same way as the slats on the wing of an aircraft, allowing the wing to achieve a higher tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feather
Feathers are epidermal growths that form a distinctive outer covering, or plumage, on both avian (bird) and some non-avian dinosaurs and other archosaurs. They are the most complex integumentary structures found in vertebrates and a premier example of a complex evolutionary novelty. They are among the characteristics that distinguish the extant birds from other living groups. Although feathers cover most of the bird's body, they arise only from certain well-defined tracts on the skin. They aid in flight, thermal insulation, and waterproofing. In addition, coloration helps in communication and protection. Plumology (or plumage science) is the name for the science that is associated with the study of feathers. Feathers have a number of utilitarian, cultural, and religious uses. Feathers are both soft and excellent at trapping heat; thus, they are sometimes used in high-class bedding, especially pillows, blankets, and mattresses. They are also used as filling for winter cloth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comb (anatomy)
A comb is a fleshy growth or crest on the top of the head of some gallinaceous birds, such as domestic chickens. The alternative name cockscomb (with several spelling variations) reflects the fact that combs are generally larger on cock birds than on hens. The comb is one of several fleshy protuberances on the heads of chickens, the others being the wattles and earlobes, which collectively are called caruncles. In turkeys, the caruncles are the fleshy nodules on the head and throat. Chicken combs are most commonly red, but may also be black or dark purple in breeds such as the Silkie or the Sebright. In other species the color may vary from light grey to deep blue or red. The comb may be a reliable indicator of health or vigor and is used for mate-assessment in some poultry species. Types of chicken comb Comb shape varies considerably depending on the breed or species of bird. Of the many types and shapes seen in chicken cocks the principal ones are: * the single comb, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
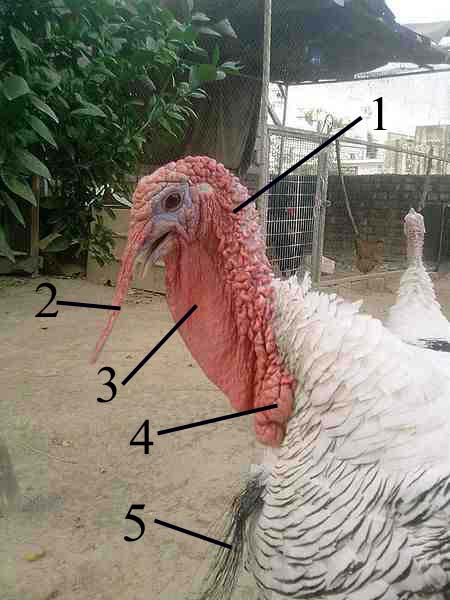
Caruncle (bird Anatomy)
A caruncle is defined as 'a small, fleshy excrescence that is a normal part of an animal's anatomy'. Within this definition, caruncles in birds include wattles (or dewlaps), combs, snoods, and earlobes. The term ''caruncle'' is derived from Latin ''caruncula'', the diminutive of ''carō'', "flesh". Taxonomy Caruncles are carnosities, often of bright colors such as red, blue, yellow or white. They can be present on the head, neck, throat, cheeks or around the eyes of some birds. They may be present as combs or crests and other structures near the beak, or, hanging from the throat or neck. Caruncles may be featherless, or, have small scattered feathers. In some species, they may form pendulous structures of erectile tissue, such as the snood of the domestic turkey. Caruncles are sometimes secondary sexual characteristics, having a more intense color or even a different color, developing as the male reaches sexual maturity. Function Caruncles are also ornamental elements used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beak
The beak, bill, or rostrum is an external anatomical structure found mostly in birds, but also in turtles, non-avian dinosaurs and a few mammals. A beak is used for eating, preening, manipulating objects, killing prey, fighting, probing for food, courtship, and feeding young. The terms ''beak'' and ''rostrum'' are also used to refer to a similar mouth part in some ornithischians, pterosaurs, cetaceans, dicynodonts, anuran tadpoles, monotremes (i.e. echidnas and platypuses, which have a beak-like structure), sirens, pufferfish, billfishes and cephalopods. Although beaks vary significantly in size, shape, color and texture, they share a similar underlying structure. Two bony projections – the upper and lower mandibles – are covered with a thin keratinized layer of epidermis known as the rhamphotheca. In most species, two holes called ''nares'' lead to the respiratory system. Etymology Although the word "beak" was, in the past, generally restricted to the sharpened bills o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Terms Used In Bird Topography
The following is a list of terms used in bird topography: Plumage features * Back * Belly * Breast * Cheek * Chin * Crest * Crown * Crown patch * Ear-coverts * Eye-ring * Eyestripe (or eye line) * Feather, see category: :Feathers * Flanks * Forecrown * Gorget * Hood (or half-hood) * Lateral throat stripe * Lores * Malar * Mantle * Mask * Moustachial stripe * Nape * Nuchal collar * Operculum (on pigeons). * Pennaceous feathers * Postocular stripe * Remiges * Rump * Spectacles * Submoustachial stripe * Supercilium * Supraloral * Parts of the tail include: **Rectrices ** Tail corner ** Terminal band ***Subterminal band * Throat * Undertail coverts * Upper mandible (or maxilla) * Uppertail coverts * Vent, crissum or cloaca ** Vent band *Parts of the wings include: ** Alula ** Apical spot ** Axillar ** Bend of wing ** Carpal covert ** Emargination ** Greater coverts ** Leading edge of wing ** Lesser coverts ** Marginal coverts ** Median coverts ** Mirror (on gulls) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bird Anatomy
Bird anatomy, or the physiological structure of birds' bodies, shows many unique adaptations, mostly aiding flight. Birds have a light skeletal system and light but powerful musculature which, along with circulatory and respiratory systems capable of very high metabolic rates and oxygen supply, permit the bird to fly. The development of a beak has led to evolution of a specially adapted digestive system. Skeletal system Birds have many bones that are hollow ( pneumatized) with criss-crossing struts or trusses for structural strength. The number of hollow bones varies among species, though large gliding and soaring birds tend to have the most. Respiratory air sacs often form air pockets within the semi-hollow bones of the bird's skeleton. The bones of diving birds are often less hollow than those of non-diving species. Penguins, loons, and puffins are without pneumatized bones entirely. Flightless birds, such as ostriches and emus, have pneumatized femurs and, in the case of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aves
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight skeleton. Birds live worldwide and range in size from the bee hummingbird to the ostrich. There are about ten thousand living species, more than half of which are passerine, or "perching" birds. Birds have whose development varies according to species; the only known groups without wings are the extinct moa and elephant birds. Wings, which are modified forelimbs, gave birds the ability to fly, although further evolution has led to the loss of flight in some birds, including ratites, penguins, and diverse endemic island species. The digestive and respiratory systems of birds are also uniquely adapted for flight. Some bird species of aquatic environments, particularly seabirds and some waterbirds, have further evolved for swimming. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)
.jpg)