|
Biozone
In biostratigraphy, biostratigraphic units or biozones are intervals of geological strata that are defined on the basis of their characteristic fossil taxa, as opposed to a lithostratigraphic unit which is defined by the lithological properties of the surrounding rock. A biostratigraphic unit is defined by the zone fossils it contains. These may be a single taxon or combinations of taxa if the taxa are relatively abundant, or variations in features related to the distribution of fossils. The same strata may be zoned differently depending on the diagnostic criteria or fossil group chosen, so there may be several, sometimes overlapping, biostratigraphic units in the same interval. Like lithostratigraphic units, biozones must have a type section designated as a stratotype. These stratotypes are named according to the typical taxon (or taxa) that are found in that particular biozone. The boundary of two distinct biostratigraphic units is called a ''biohorizon''. Biozones can be furthe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biostratigraphic Index Fossils 02
Biostratigraphy is the branch of stratigraphy which focuses on correlating and assigning relative ages of rock strata by using the fossil assemblages contained within them.Hine, Robert. “Biostratigraphy.” ''Oxford Reference: Dictionary of Biology'', 8th ed., Oxford University Press, 2019. The primary objective of biostratigraphy is ''correlation'', demonstrating that a particular horizon in one geological section represents the same period of time as another horizon at a different section. Fossils within these strata are useful because sediments of the same age can look completely different, due to local variations in the sedimentary environment. For example, one section might have been made up of clays and marls, while another has more chalky limestones. However, if the fossil species recorded are similar, the two sediments are likely to have been laid down around the same time. Ideally these fossils are used to help identify biozones, as they make up the basic biostratigraphy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biostratigraphy
Biostratigraphy is the branch of stratigraphy which focuses on correlating and assigning relative ages of rock Stratum, strata by using the fossil assemblages contained within them.Hine, Robert. “Biostratigraphy.” ''Oxford Reference: Dictionary of Biology'', 8th ed., Oxford University Press, 2019. The primary objective of biostratigraphy is ''correlation'', demonstrating that a particular Horizon (geology), horizon in one geological section represents the same period of time as another horizon at a different section. Fossils within these strata are useful because sediments of the same age can look completely different, due to local variations in the Sedimentary depositional environment, sedimentary environment. For example, one section might have been made up of clays and marls, while another has more chalky limestones. However, if the fossil species recorded are similar, the two sediments are likely to have been laid down around the same time. Ideally these fossils are used to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teilzone
In biostratigraphy, a local-range zone, topozone or teilzone (German ''teil'' = part + Greek ''zone'') is the stratigraphic range of the rock unit between the first and last appearance datum of a particular taxon in a local area. It is a subset of the global biozone for that taxon. For the teilzone data to be meaningful, the local area must be identified. The term was coined in 1914 by German paleontologist and geologist Josef Felix Pompeckj. See also *Biozone *Acme zone In biostratigraphy, an acme zone, abundance zone, or peak zone is the area of a teilzone where a particular fossil taxon reaches a higher level of abundance. See also *Biozone In biostratigraphy, biostratigraphic units or biozones are intervals of ... References Biostratigraphy {{geology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biochronology
In paleontology, biochronology is the correlation in time of biological events using fossils. In its strict sense, it refers to the use of assemblages of fossils that are not tied to stratigraphic sections (in contrast to biostratigraphy, where they are). Collections of land mammal ages have been defined for every continent except Antarctica, and most are correlated with each other indirectly through known evolutionary lineages. A combination of argon–argon dating and magnetostratigraphy, magnetic stratigraphy allows a direct temporal comparison of terrestrial events with climate variability, climate variations and Extinction event, mass extinctions. Comparison with biostratigraphy In sedimentary rocks, fossils are the only widely applicable tool for time correlation. Evolution leaves a record of progressive change, sequential and nonrepeating. A rock unit has a characteristic Faunal assemblage, assemblage of fossils, independent of its lithology. Thus, the fossils can be use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signor–Lipps Effect
The Signor–Lipps effect is a paleontological principle proposed in 1982 by Philip W. Signor and Jere H. Lipps which states that, since the fossil record of organisms is never complete, neither the first nor the last organism in a given taxon will be recorded as a fossil. The Signor–Lipps effect is often applied specifically to cases of the youngest-known fossils of a taxon failing to represent the last appearance of an organism. The inverse, regarding the oldest-known fossils failing to represent the first appearance of a taxon, is alternatively called the Jaanusson effect after researcher Valdar Jaanusson, or the Sppil–Rongis effect (''Signor–Lipps'' spelled backwards). One famous example is the coelacanth, which was thought to have become extinct in the very late Cretaceous—until a live specimen was caught in 1938. The animals known as " Burgess Shale-type fauna" are best known from rocks of the Early and Middle Cambrian periods. Since 2006, though, a few fossils of s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hominids
The Hominidae (), whose members are known as the great apes or hominids (), are a taxonomic family of primates that includes eight extant species in four genera: '' Pongo'' (the Bornean, Sumatran and Tapanuli orangutan); ''Gorilla'' (the eastern and western gorilla); '' Pan'' (the chimpanzee and the bonobo); and ''Homo'', of which only modern humans remain. Several revisions in classifying the great apes have caused the use of the term ''"hominid"'' to vary over time. The original meaning of "hominid" referred only to humans (''Homo'') and their closest extinct relatives. However, by the 1990s humans, apes, and their ancestors were considered to be "hominids". The earlier restrictive meaning has now been largely assumed by the term ''"hominin"'', which comprises all members of the human clade after the split from the chimpanzees (''Pan''). The current meaning of "hominid" includes all the great apes including humans. Usage still varies, however, and some scientists and laypers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannabis
''Cannabis'' () is a genus of flowering plants in the family Cannabaceae. The number of species within the genus is disputed. Three species may be recognized: ''Cannabis sativa'', '' C. indica'', and '' C. ruderalis''. Alternatively, ''C. ruderalis'' may be included within ''C. sativa'', all three may be treated as subspecies of ''C. sativa'', or ''C. sativa'' may be accepted as a single undivided species. The genus is widely accepted as being indigenous to and originating from Asia. The plant is also known as hemp, although this term is often used to refer only to varieties of ''Cannabis'' cultivated for non-drug use. Cannabis has long been used for hemp fibre, hemp seeds and their oils, hemp leaves for use as vegetables and as juice, medicinal purposes, and as a recreational drug. Industrial hemp products are made from cannabis plants selected to produce an abundance of fibre. Various cannabis strains have been bred, often selectively to pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
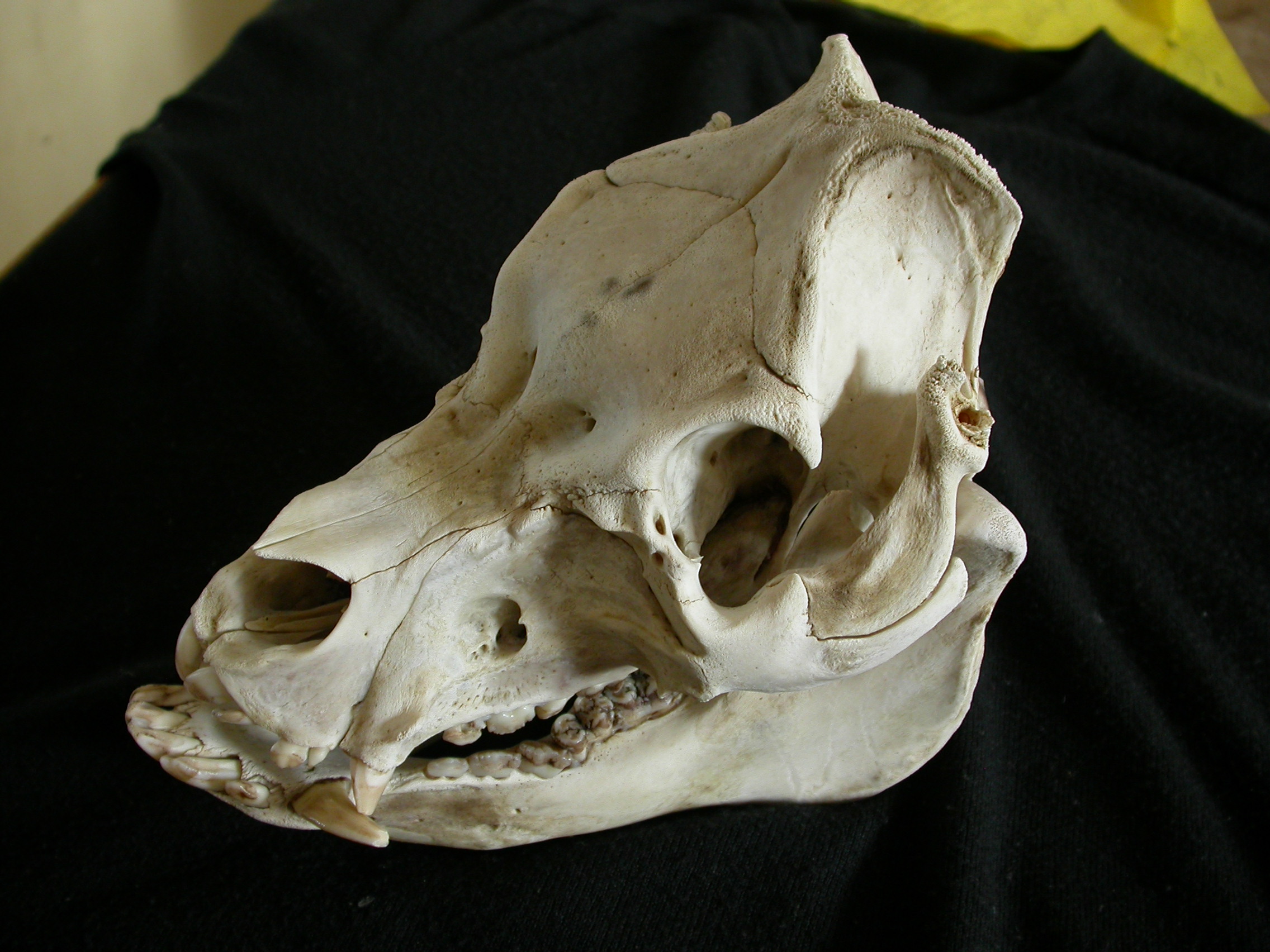
Pigs
The pig (''Sus domesticus''), often called swine, hog, or domestic pig when distinguishing from other members of the genus '' Sus'', is an omnivorous, domesticated, even-toed, hoofed mammal. It is variously considered a subspecies of ''Sus scrofa'' (the wild boar or Eurasian boar) or a distinct species. The pig's head-plus-body length ranges from , and adult pigs typically weigh between , with well-fed individuals even exceeding this range. The size and weight of hogs largely depends on their breed. Compared to other artiodactyls, a pig's head is relatively long and pointed. Most even-toed ungulates are herbivorous, but pigs are omnivores, like their wild relative. Pigs grunt and make snorting sounds. When used as livestock, pigs are farmed primarily for the production of meat, called pork. A group of pigs is called a ''passel'', a ''team'', or a ''sounder''. The animal's bones, hide, and bristles are also used in products. Pigs, especially miniature breeds, are kept as pets ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palynology
Palynology is the "study of dust" (from grc-gre, παλύνω, palynō, "strew, sprinkle" and '' -logy'') or of "particles that are strewn". A classic palynologist analyses particulate samples collected from the air, from water, or from deposits including sediments of any age. The condition and identification of those particles, organic and inorganic, give the palynologist clues to the life, environment, and energetic conditions that produced them. The term is commonly used to refer to a subset of the discipline, which is defined as "the study of microscopic objects of macromolecular organic composition (i.e., compounds of carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen and oxygen), not capable of dissolution in hydrochloric or hydrofluoric acids". It is the science that studies contemporary and fossil palynomorphs (paleopalynology), including pollen, spores, orbicules, dinocysts, acritarchs, chitinozoans and scolecodonts, together with particulate organic matter (POM) and kerogen found in sedimen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foraminifera
Foraminifera (; Latin for "hole bearers"; informally called "forams") are single-celled organisms, members of a phylum or class of amoeboid protists characterized by streaming granular Ectoplasm (cell biology), ectoplasm for catching food and other uses; and commonly an external shell (called a "Test (biology), test") of diverse forms and materials. Tests of chitin (found in some simple genera, and Textularia in particular) are believed to be the most primitive type. Most foraminifera are marine, the majority of which live on or within the seafloor sediment (i.e., are benthos, benthic), while a smaller number float in the water column at various depths (i.e., are planktonic), which belong to the suborder Globigerinina. Fewer are known from freshwater or brackish conditions, and some very few (nonaquatic) soil species have been identified through molecular analysis of small subunit ribosomal DNA. Foraminifera typically produce a test (biology), test, or shell, which can have eithe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinoflagellates
The dinoflagellates (Greek δῖνος ''dinos'' "whirling" and Latin ''flagellum'' "whip, scourge") are a monophyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes constituting the phylum Dinoflagellata and are usually considered algae. Dinoflagellates are mostly marine plankton, but they also are common in freshwater habitats. Their populations vary with sea surface temperature, salinity, and depth. Many dinoflagellates are photosynthetic, but a large fraction of these are in fact mixotrophic, combining photosynthesis with ingestion of prey (phagotrophy and myzocytosis). In terms of number of species, dinoflagellates are one of the largest groups of marine eukaryotes, although substantially smaller than diatoms. Some species are endosymbionts of marine animals and play an important part in the biology of coral reefs. Other dinoflagellates are unpigmented predators on other protozoa, and a few forms are parasitic (for example, ''Oodinium'' and ''Pfiesteria''). Some dinoflagellates prod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micropaleontology
Micropaleontology (American spelling; spelled micropalaeontology in European usage) is the branch of paleontology (palaeontology) that studies microfossils, or fossils that require the use of a microscope to see the organism, its morphology and its characteristic details. Microfossils Microfossils are fossils that are generally between 0.001mm and 1 mm in size, the study of which requires the use of light or electron microscopy. Fossils which can be studied by the naked eye or low-powered magnification, such as a hand lens, are referred to as macrofossils. For example, some colonial organisms, such as Bryozoa (especially the Cheilostomata) have relatively large colonies, but are classified by fine skeletal details of the small individuals of the colony. In another example, many fossil genera of Foraminifera, which are protists are known from shells (called "tests") that were as big as coins, such as the genus '' Nummulites''. Microfossils are a common feature of the g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |