|
Binary XML
Various binary formats have been proposed as compact representations for XML (''Extensible Markup Language''). Using a binary XML format generally reduces the verbosity of XML documents thereby also reducing the cost of parsing, but hinders the use of ordinary text editors and third-party tools to view and edit the document. There are several competing formats, but none has yet emerged as a ''de facto standard'', although the World Wide Web Consortium adopted EXI as a Recommendation on 10 March 2011. Binary XML is typically used in applications where the performance of standard XML is insufficient, but the ability to convert the document to and from a form (XML) which ''is'' easily viewed and edited is valued. Other advantages may include enabling random access and indexing of XML documents. The major challenge for binary XML is to create a single, widely adopted standard. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Telecommunication Union (I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary File
A binary file is a computer file that is not a text file. The term "binary file" is often used as a term meaning "non-text file". Many binary file formats contain parts that can be interpreted as text; for example, some computer document files containing formatted text, such as older Microsoft Word document files, contain the text of the document but also contain formatting information in binary form. Structure Binary files are usually thought of as being a sequence of bytes, which means the binary digits (bits) are grouped in eights. Binary files typically contain bytes that are intended to be interpreted as something other than text characters. Compiled computer programs are typical examples; indeed, compiled applications are sometimes referred to, particularly by programmers, as binaries. But binary files can also mean that they contain images, sounds, compressed versions of other files, etc. – in short, any type of file content whatsoever. Some binary files contain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extensible Binary Meta Language
Extensible Binary Meta Language (EBML) is a generalized file format for any kind of data, aiming to be a binary equivalent to XML. It provides a basic framework for storing data in XML-like tags. It was originally developed for the Matroska audio/video container format. EBML is not extensible in the same way that XML is, as the XML schema (e.g., DTD) must be known in advance. See also *Binary XML *WBXML *Matroska *WebM *XML *IFF In logic and related fields such as mathematics and philosophy, "if and only if" (shortened as "iff") is a biconditional logical connective between statements, where either both statements are true or both are false. The connective is bicon ..., an older structured binary format widely adopted for multimedia References External linksThe EBML website [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CBOR
Concise Binary Object Representation (CBOR) is a binary data serialization format loosely based on JSON authored by C. Bormann. Like JSON it allows the transmission of data objects that contain name–value pairs, but in a more concise manner. This increases processing and transfer speeds at the cost of human readability. It is defined in IETF . Amongst other uses, it is the recommended data serialization layer for the CoAP Internet of Things protocol suite and the data format on which COSE messages are based. It is also used in the Client-to-Authenticator Protocol (CTAP) within the scope of the FIDO2 project. CBOR was inspired by MessagePack, which was developed and promoted by Sadayuki Furuhashi. CBOR extended MessagePack, particularly by allowing to distinguish text strings from byte strings, which was implemented in 2013 in MessagePack. Specification of the CBOR encoding CBOR encoded data is seen as a stream of data items. Each data item consists of a header byte con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MessagePack
MessagePack is a computer data interchange format. It is a binary form for representing simple data structures like arrays and associative arrays. MessagePack aims to be as compact and simple as possible. The official implementation is available in a variety of languages such as C, C++, C#, D, Erlang, Go, Haskell, Java, JavaScript (NodeJS), Lua, OCaml, Perl, PHP, Python, Ruby, Scala, Smalltalk, and Swift. Data types and syntax Data structures processed by MessagePack loosely correspond to those used in JSON format. They consist of the following element types: * nil * bool, boolean (true and false) * int, integer (up to 64 bits signed or unsigned) * float, floating point numbers (IEEE single/double precision) * str, UTF-8 string * bin, binary data (up to 232 − 1 bytes) * array * map, an associative array * ext (arbitrary data of an application-defined format, up to 232 − 1 bytes) * timestamp (ext type = −1) (up to 32-bit seconds and 64-bit nanoseconds) Comparison ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BSON
BSON () is a computer data interchange format. The name "BSON" is based on the term JSON and stands for "Binary JSON". It is a binary form for representing simple or complex data structures including associative arrays (also known as name-value pairs), integer indexed arrays, and a suite of fundamental scalar types. BSON originated in 2009 at MongoDB. Several scalar data types are of specific interest to MongoDB and the format is used both as a data storage and network transfer format for the MongoDB database, but it can be used independently outside of MongoDB. Implementations are available in a variety of languages such as C, C++, C#, D, Delphi, Erlang, Go, Haskell, Java, JavaScript, Julia, Lua, OCaml, Perl, PHP, Python, Ruby, Rust, Scala, Smalltalk, and Swift. Data types and syntax BSON has a published specification. The topmost element in the structure must be of type BSON object and contains 1 or more elements, where an element consists of a field name, a type, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apache Avro
Avro is a row-oriented remote procedure call and data serialization framework developed within Apache's Hadoop project. It uses JSON for defining data types and protocols, and serializes data in a compact binary format. Its primary use is in Apache Hadoop, where it can provide both a serialization format for persistent data, and a wire format for communication between Hadoop nodes, and from client programs to the Hadoop services. Avro uses a schema to structure the data that is being encoded. It has two different types of schema languages; one for human editing (Avro IDL) and another which is more machine-readable based on JSON. It is similar to Thrift and Protocol Buffers, but does not require running a code-generation program when a schema changes (unless desired for statically-typed languages). Apache Spark SQL can access Avro as a data source. Avro Object Container File An Avro Object Container File consists of: * A file header, followed by * one or more file dat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Object Management Group
The Object Management Group (OMG) is a computer industry standardization, standards consortium. OMG Task Forces develop enterprise integration standards for a range of technologies. Business activities The goal of the OMG was a common portable and interoperable object model with methods and data that work using all types of development environments on all types of platforms. The group provides only specifications, not implementations. But before a specification can be accepted as a standard by the group, the members of the submitter team must guarantee that they will bring a conforming product to market within a year. This is an attempt to prevent unimplemented (and unimplementable) standards. Other private companies or open source groups are encouraged to produce conforming products and OMG is attempting to develop mechanisms to enforce true interoperability. OMG hosts four technical meetings per year for its members and interested nonmembers. The Technical Meetings provide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
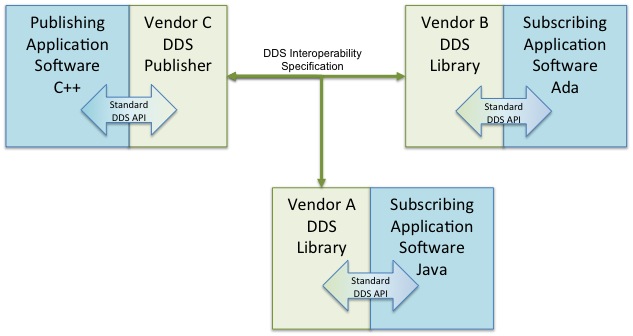
Data Distribution Service
The Data Distribution Service (DDS) for real-time systems is an Object Management Group (OMG) machine-to-machine (sometimes called middleware or connectivity framework) standard that aims to enable dependable, high-performance, interoperable, real-time, scalable data exchanges using a publish–subscribe pattern. DDS addresses the needs of applications like aerospace and defense, air-traffic control, autonomous vehicles, medical devices, robotics, power generation, simulation and testing, smart grid management, transportation systems, and other applications that require real-time data exchange. Architecture Model DDS is a networking middleware that simplifies complex computer network programming, network programming. It implements a publish–subscribe pattern for sending and receiving data, events, and commands among the node (networking), nodes. Nodes that produce information (publishers) create "topics" (e.g., temperature, location, pressure) and publish "samples". DDS d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apache Thrift
Thrift is an interface definition language and binary communication protocol used for defining and creating services for numerous programming languages. It was developed at Facebook for "scalable cross-language services development" and as of 2020 is an open source project in the Apache Software Foundation. With a remote procedure call (RPC) framework it combines a software stack with a code generation engine to build cross-platform services which can connect applications written in a variety of languages and frameworks, including ActionScript, C, C++, C#, Cappuccino, Cocoa, Delphi, Erlang, Go, Haskell, Java, JavaScript, Objective-C, OCaml, Perl, PHP, Python, Ruby, Elixir, Rust, Scala, Smalltalk and Swift. The implementation was described in an April 2007 technical paper released by Facebook, now hosted on Apache. Architecture Thrift includes a complete stack for creating clients and servers. The top part is generated code from the Thrift definition. From this file, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protocol Buffers
Protocol Buffers (Protobuf) is a free and open-source cross-platform data format used to serialize structured data. It is useful in developing programs to communicate with each other over a network or for storing data. The method involves an interface description language that describes the structure of some data and a program that generates source code from that description for generating or parsing a stream of bytes that represents the structured data. Overview Google developed Protocol Buffers for internal use and provided a code generator for multiple languages under an open-source license (see below). The design goals for Protocol Buffers emphasized simplicity and performance. In particular, it was designed to be smaller and faster than XML. Protocol Buffers are widely used at Google for storing and interchanging all kinds of structured information. The method serves as a basis for a custom remote procedure call (RPC) system that is used for nearly all inter-machine comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NET Framework
The .NET Framework (pronounced as "''dot net"'') is a proprietary software framework developed by Microsoft that runs primarily on Microsoft Windows. It was the predominant implementation of the Common Language Infrastructure (CLI) until being superseded by the cross-platform .NET project. It includes a large class library called Framework Class Library (FCL) and provides language interoperability (each language can use code written in other languages) across several programming languages. Programs written for .NET Framework execute in a software environment (in contrast to a computer hardware, hardware environment) named the Common Language Runtime (CLR). The CLR is an process virtual machine, application virtual machine that provides services such as security, memory management, and exception handling. As such, computer code written using .NET Framework is called "managed code". FCL and CLR together constitute the .NET Framework. FCL provides the user interface, data access, d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |