|
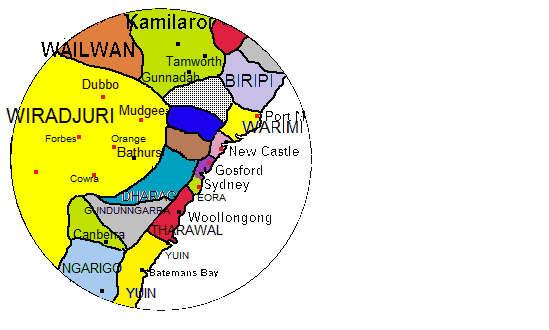
Bigambal Language
Bigambal (also ''Bigambul'', ''Bigumbil'', ''Pikambul'', or ''Pikumbul'') is an extinct and unclassified Australian Aboriginal language from the Pama–Nyungan language family. The Bigambul language region includes the landscape within the local government boundaries of the Goondiwindi Regional Council, including the towns of Goondiwindi, Yelarbon and Texas extending north towards Moonie and Millmerran. The AUSTLANG database maintained by the Australian Institute of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Studies states that the Bigambal language was spoken by the Bigambul people, with Gambuwal and Kwiambal (or Gujambal) known dialects. However, it is likely that the Gamilaraay (or Yuwaaliyaay) language was used by those peoples living in southern Bigambul territory. Classification Dixon (2002) groups Bigambal together with the Bundjalung languages while O'Grady, Voegelin and Voegelin classify it as a 'Wiradjuric' language. Glottolog states that Wafer and Lissarrague (2008) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bigambul People
The Bigambul people are an Aboriginal Australian people of the Northern Tablelands and Border Rivers regions of New South Wales and Queensland. Name In the traditional language, the name of this group is derived from the Bigambul word ''biga'' or ''pika'' which translates in English to ''yes''. The Bigambul are bounded to the south–east by the Ngarabal, the Kamilaroi to the south, the Kooma to the west, the Mandandanji and Kabi to the north, and the Baruŋgam to the north–east. Country Norman Tindale ascribed to the Bigambul a traditional territory spreading over east of Nindigully, on the Weir and Moonie rivers, north to Tara; at Talwood; on the Macintyre River from east of Boomi to Texas; at Yetman, Boggabilla, and at Middle Creek. Alternate names * ''Bigabul'' * ''Pikambul'' * ''Bigambal'' * ''Bigambel'' * ''Bee-gum-bul'' * ''Bigumble'' * ''Pikumbul,'Pikumpal, Pikambal'' * ''Pikum-bul, Pickum-bul, Pickimbul'' * ''Pickumble, Picumbul, Pikumbil'' * ''Begumble'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bigambul
The Bigambul people are an Aboriginal Australian people of the Northern Tablelands and Border Rivers regions of New South Wales and Queensland. Name In the traditional language, the name of this group is derived from the Bigambul word ''biga'' or ''pika'' which translates in English to ''yes''. The Bigambul are bounded to the south–east by the Ngarabal, the Kamilaroi to the south, the Kooma to the west, the Mandandanji and Kabi to the north, and the Baruŋgam to the north–east. Country Norman Tindale ascribed to the Bigambul a traditional territory spreading over east of Nindigully, on the Weir and Moonie rivers, north to Tara; at Talwood; on the Macintyre River from east of Boomi to Texas; at Yetman, Boggabilla, and at Middle Creek. Alternate names * ''Bigabul'' * ''Pikambul'' * ''Bigambal'' * ''Bigambel'' * ''Bee-gum-bul'' * ''Bigumble'' * ''Pikumbul,'Pikumpal, Pikambal'' * ''Pikum-bul, Pickum-bul, Pickimbul'' * ''Pickumble, Picumbul, Pikumbil'' * ''Begumble'' * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Institute Of Aboriginal And Torres Strait Islander Studies
The Australian Institute of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Studies (AIATSIS), established as the Australian Institute of Aboriginal Studies (AIAS) in 1964, is an independent Australian Government statutory authority. It is a collecting, publishing and research institute and is considered to be Australia's premier resource for information about the cultures and societies of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples. The institute is a leader in ethical research and the handling of culturally sensitive material'Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Library, Information and Resource Network (ATSILIRN) Protocols for Libraries, Archives and Information Services', http://atsilirn.aiatsis.gov.au/protocols.php, retrieved 12 March 2015‘'AIATSIS Collection Development Policy 2013 – 2016'’, AIATSIS website, http://aiatsis.gov.au/sites/default/files/docs/about-us/collection-development-policy.pdf, retrieved 12 March 2015 and holds in its collections many unique and irrepla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glottolog
''Glottolog'' is a bibliographic database of the world's lesser-known languages, developed and maintained first at the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology in Leipzig, Germany (between 2015 and 2020 at the Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History in Jena, Germany). Its main curators include Harald Hammarström and Martin Haspelmath. Overview Sebastian Nordhoff and Harald Hammarström created the Glottolog/Langdoc project in 2011. The creation of ''Glottolog'' was partly motivated by the lack of a comprehensive language bibliography, especially in ''Ethnologue''. Glottolog provides a catalogue of the world's languages and language families and a bibliography on the world's less-spoken languages. It differs from the similar catalogue '' Ethnologue'' in several respects: * It tries to accept only those languages that the editors have been able to confirm both exist and are distinct. Varieties that have not been confirmed, but are inherited from anothe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wiradhuric Languages
The Wiradhuric languages or Central (Inland) New South Wales, are a family of Pama–Nyungan languages of Australia. There are three languages: *Gamilaraay (northeast) *Wiradhuri–Ngiyambaa ** Wiradhuri (south) **Ngiyambaa (west) All are now moribund Moribund refers to a literal or figurative state near death. Moribund may refer to: * ''Moribund'' (album), a 2006 album by the Norwegian black metal band Koldbrann * " Le Moribond", a song by Jacques Brel known in English as "Seasons in the Sun .... Wiradhuri and Ngiyambaa appear to be more closely related to each other than to Gamilaraay, as they show some common features that Gamilaraay lacks. The languages are close enough to be accepted as related in the conservative classification of Dixon (2002). Bowern (2011) lists the Yuwaaliyaay and Yuwaalaraay varieties of Gamilaraay as separate languages.Bowern, Claire. 2011.How Many Languages Were Spoken in Australia?, ''Anggarrgoon: Australian languages on the web'', December 23, 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yugambeh–Bundjalung Languages
Yugambeh–Bundjalung, also known as Bandjalangic, is a branch of the Pama–Nyungan languages, Pama–Nyungan language family, that is spoken in north-eastern New South Wales and South-East Queensland. Yugambeh–Bundjalung was historically a dialect continuum consisting of a number of dialect, varieties, including Yugambeh dialect, Yugambeh, Nganduwal, Minjangbal, Njangbal (Nyangbal), Biriin, Baryulgil, Waalubal, Dinggabal, Wiyabal, Gidabal, Galibal, and Wudjeebal. Language varieties in the group vary in degree of mutual intelligibility, with varieties at different ends of the continuum being mostly unintelligible. These dialects formed four clusters: * Yugambeh Language, Tweed-Albert Language (Yugambeh) * Githabul language, Condamine-Upper Clarence (Githabul) * Lower Richmond (Eastern Bundjalung – Nyangbal, Minyangbal and Bandjalang proper) * Wahlubal, Middle Clarence (Western Bundjalung) Bowern (2011) lists Yugambeh, Githabul, Minyangbal, and Bandjalang as separate ''Ban ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamilaraay Language
The Gamilaraay or Kamilaroi language is a Pama–Nyungan languages, Pama–Nyungan language of the Wiradhuric languages, Wiradhuric subgroup found mostly in south-eastern Australia. It is the traditional language of the Gamilaraay, Gamilaraay (Kamilaroi), an Aboriginal Australian people. It has been noted as endangered, but the number of speakers grew from 87 in the 2011 Australian Census to 105 in the 2016 Australian Census. Thousands of Australians identify as Gamilaraay, and the language is taught in some schools. Wirray Wirray, Guyinbaraay, Yuwaalayaay, Waalaraay and Gawambaraay are dialects; Yuwaalaraay/Euahlayi is a closely related language. Name The name Gamilaraay means '-having', with being the word for 'no'. Other dialects and languages are similarly named after their respective words for 'no'. (Compare the division between ''langues d'oïl'' and ''langues d'oc'' in France, distinguished by their respective words for 'yes'.) Spellings of the name, pronounced in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kwiambal Language
Gujambal (Guyambal, Kwiambal) is a possible extinct Australian Aboriginal language. It is undocumented. ' Gambuwal' may have been the same language. References External links Bibliography of Gujambal people and language resources at the Australian Institute of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Studies The Australian Institute of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Studies (AIATSIS), established as the Australian Institute of Aboriginal Studies (AIAS) in 1964, is an independent Australian Government statutory authority. It is a collecting, ... Unclassified languages of Australia Extinct languages of Queensland {{ia-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gambuwal Language
Gujambal (Guyambal, Kwiambal) is a possible extinct Australian Aboriginal language. It is undocumented. ' Gambuwal' may have been the same language. References External links Bibliography of Gujambal people and language resources at the Australian Institute of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Studies The Australian Institute of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Studies (AIATSIS), established as the Australian Institute of Aboriginal Studies (AIAS) in 1964, is an independent Australian Government statutory authority. It is a collecting, ... Unclassified languages of Australia Extinct languages of Queensland {{ia-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Library Of Queensland
The State Library of Queensland is the main reference and research library provided to the people of the State of Queensland, Australia, by the state government. Its legislative basis is provided by the Queensland Libraries Act 1988. It contains a significant portion of Queensland's documentary heritage, major reference and research collections, and is an advocate of and partner with public libraries across Queensland. The library is at Kurilpa Point, within the Queensland Cultural Centre on the Brisbane River at South Bank. History The Brisbane Public Library was established by the government of the Colony of Queensland in 1896, and was renamed the Public Library of Queensland in 1898. The library was opened to the public in 1902. In 1934, the Oxley Memorial Library (now the John Oxley Library), named for the explorer John Oxley, opened as a centre for research and study relating specifically to Queensland. The Libraries Act of 1943 established the Library Board of Queen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pama–Nyungan Languages
The Pama–Nyungan languages are the most widespread family of Australian Aboriginal languages, containing 306 out of 400 Aboriginal languages in Australia. The name "Pama–Nyungan" is a merism: it derived from the two end-points of the range: the Pama languages of northeast Australia (where the word for "man" is ) and the Nyungan languages of southwest Australia (where the word for "man" is ). The other language families indigenous to the continent of Australia are occasionally referred to, by exclusion, as non-Pama–Nyungan languages, though this is not a taxonomic term. The Pama–Nyungan family accounts for most of the geographic spread, most of the Aboriginal population, and the greatest number of languages. Most of the Pama–Nyungan languages are spoken by small ethnic groups of hundreds of speakers or fewer. The vast majority of languages, either due to disease or elimination of their speakers, have become extinct, and almost all remaining ones are endangered in some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Millmerran, Queensland
Millmerran , known as Domville between 1 June 1889 and 16 November 1894, is a town and a locality in the Toowoomba Region, Queensland, Australia. In the , the locality of Millmerran had a population of 1,563 people. Geography The town is on the Darling Downs, west of the state capital, Brisbane. The Gore Highway passes through the locality from the north-east (Yandilla) to the west ( Captains Mountain). The Millmerran–Inglewood Road (State Route 82) runs to the south. State Route 82 enters Millmerran from the north-east concurrent with the Gore Highway. The Millmerran–Cecil Plains Road exits to the north. History Bigambul (also known as Bigambal, Bigumbil, Pikambul, Pikumbul) is an Australian Aboriginal language spoken by the Bigambul people. The Bigambul language region includes the landscape within the local government boundaries of the Goondiwindi Regional Council, including the towns of Goondiwindi, Yelarbon and Texas extending north towards Moonie and Millmerran. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |