|
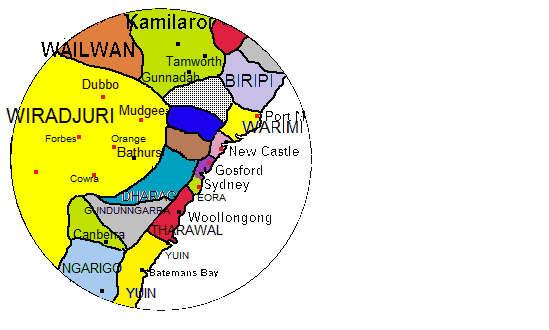
Wiradhuric Languages
The Wiradhuric languages or Central (Inland) New South Wales, are a family of Pama–Nyungan languages of Australia. There are three languages: *Gamilaraay (northeast) *Wiradhuri–Ngiyambaa ** Wiradhuri (south) **Ngiyambaa (west) All are now moribund Moribund refers to a literal or figurative state near death. Moribund may refer to: * ''Moribund'' (album), a 2006 album by the Norwegian black metal band Koldbrann * " Le Moribond", a song by Jacques Brel known in English as "Seasons in the Sun .... Wiradhuri and Ngiyambaa appear to be more closely related to each other than to Gamilaraay, as they show some common features that Gamilaraay lacks. The languages are close enough to be accepted as related in the conservative classification of Dixon (2002). Bowern (2011) lists the Yuwaaliyaay and Yuwaalaraay varieties of Gamilaraay as separate languages.Bowern, Claire. 2011.How Many Languages Were Spoken in Australia?, ''Anggarrgoon: Australian languages on the web'', December 23, 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New South Wales
) , nickname = , image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg , map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates: , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Australia , established_title = Before federation , established_date = Colony of New South Wales , established_title2 = Establishment , established_date2 = 26 January 1788 , established_title3 = Responsible government , established_date3 = 6 June 1856 , established_title4 = Federation , established_date4 = 1 January 1901 , named_for = Wales , demonym = , capital = Sydney , largest_city = capital , coordinates = , admin_center = 128 local government areas , admin_center_type = Administration , leader_title1 = Monarch , leader_name1 = Charles III , leader_title2 = Governor , leader_name2 = Margaret Beazley , leader_title3 = Premier , leader_name3 = Dominic Perrottet (Liberal) , national_representation = Parliament of Australia , national_representation_type1 = Senat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pama–Nyungan Languages
The Pama–Nyungan languages are the most widespread family of Australian Aboriginal languages, containing 306 out of 400 Aboriginal languages in Australia. The name "Pama–Nyungan" is a merism: it derived from the two end-points of the range: the Pama languages of northeast Australia (where the word for "man" is ) and the Nyungan languages of southwest Australia (where the word for "man" is ). The other language families indigenous to the continent of Australia are occasionally referred to, by exclusion, as non-Pama–Nyungan languages, though this is not a taxonomic term. The Pama–Nyungan family accounts for most of the geographic spread, most of the Aboriginal population, and the greatest number of languages. Most of the Pama–Nyungan languages are spoken by small ethnic groups of hundreds of speakers or fewer. The vast majority of languages, either due to disease or elimination of their speakers, have become extinct, and almost all remaining ones are endangered in some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamilaraay Language
The Gamilaraay or Kamilaroi language is a Pama–Nyungan languages, Pama–Nyungan language of the Wiradhuric languages, Wiradhuric subgroup found mostly in south-eastern Australia. It is the traditional language of the Gamilaraay, Gamilaraay (Kamilaroi), an Aboriginal Australian people. It has been noted as endangered, but the number of speakers grew from 87 in the 2011 Australian Census to 105 in the 2016 Australian Census. Thousands of Australians identify as Gamilaraay, and the language is taught in some schools. Wirray Wirray, Guyinbaraay, Yuwaalayaay, Waalaraay and Gawambaraay are dialects; Yuwaalaraay/Euahlayi is a closely related language. Name The name Gamilaraay means '-having', with being the word for 'no'. Other dialects and languages are similarly named after their respective words for 'no'. (Compare the division between ''langues d'oïl'' and ''langues d'oc'' in France, distinguished by their respective words for 'yes'.) Spellings of the name, pronounced in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wiradhuri Language
Wiradjuri (; many other spellings, see Wiradjuri) is a Pama–Nyungan language of the Wiradhuric subgroup. It is the traditional language of the Wiradjuri people of Australia. A progressive revival is underway, with the language being taught in schools. Wiraiari and Jeithi may have been dialects. Reclamation The Wiradjuri language is taught in primary schools, secondary schools and at TAFE in the towns of Parkes and Forbes & Condobolin. Northern Wiradjuri schools such as Peak Hill, Dubbo (several schools), Narromine, Wellington, Gilgandra, Trangie, Geurie are taught Wiradjuri by AECG Language & Culture Educators. All lessons include both indigenous and non-indigenous Australians. As of 2017 the language is also being taught in Young, where it has been observed as having a positive impact on the number of pupils self-identifying as Aboriginal. Charles Sturt University also offers a two-year course in Wiradjuri language, heritage, and culture, focusing on language reclamatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ngiyambaa Language
The Ngiyambaa language, also spelt Ngiyampaa, Ngempa, Ngemba and other variants, is a Pama–Nyungan language of the Wiradhuric subgroup. It was the traditional language of the Wangaibon and Weilwan peoples of New South Wales, Australia, but is now moribund; according to Donaldson by the 1970s there were only about ten people fluent in Wangaibon, whilst there were only a couple of Weilwan speakers left. Ngiyambaa (meaning language), or Ngiyambaambuwali, was also used by the Wangaibon and Weilwan The Weilwan (also known as Wayilwan, Wailwan, Ngiyampaa Wailwan and Ngemba Wailwan) are an Aboriginal Australian people of the state of New South Wales. They are a clan of the Ngiyampaa nation. Name The Weilwan ethnonym is derived from their wor ... to describe themselves, whilst 'Wangaibon' and 'Weilwan' (meanining 'With Wangai/Weil' (for 'no') were used to distinguish both the language and the speakers from others who did not have ''wangai'' or ''weil'' for ''no''. Other Names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ngiyambaa
The Ngiyambaa language, also spelt Ngiyampaa, Ngempa, Ngemba and other variants, is a Pama–Nyungan languages, Pama–Nyungan language of the Wiradhuric languages, Wiradhuric subgroup. It was the traditional language of the Wangaibon and Weilwan Indigenous Australians, peoples of New South Wales, Australia, but is now moribund; according to Tamsin Donaldson, Donaldson by the 1970s there were only about ten people fluent in Wangaibon, whilst there were only a couple of Weilwan speakers left. Ngiyambaa (meaning language), or Ngiyambaambuwali, was also used by the Wangaibon and Weilwan to describe themselves, whilst 'Wangaibon' and 'Weilwan' (meanining 'With Wangai/Weil' (for 'no') were used to distinguish both the language and the speakers from others who did not have ''wangai'' or ''weil'' for ''no''. Other Names Other names for Ngiyambaa are: Giamba, Narran, Noongaburrah, Ngampah, Ngemba, Ngeumba, Ngiamba, Ngjamba, Ngiyampaa and Ngumbarr; Wangaibon is also called Wangaaybuwan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moribund Language
An endangered language or moribund language is a language that is at risk of disappearing as its speakers die out or shift to speaking other languages. Language loss occurs when the language has no more native speakers and becomes a "dead language". If no one can speak the language at all, it becomes an "extinct language". A dead language may still be studied through recordings or writings, but it is still dead or extinct unless there are fluent speakers. Although languages have always become extinct throughout human history, they are currently dying at an accelerated rate because of globalization, imperialism, neocolonialism and linguicide (language killing). Language shift most commonly occurs when speakers switch to a language associated with social or economic power or spoken more widely, the ultimate result being language death. The general consensus is that there are between 6,000 and 7,000 languages currently spoken. Some linguists estimate that between 50% and 90% of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bigambal Language
Bigambal (also ''Bigambul'', ''Bigumbil'', ''Pikambul'', or ''Pikumbul'') is an extinct and unclassified Australian Aboriginal language from the Pama–Nyungan language family. The Bigambul language region includes the landscape within the local government boundaries of the Goondiwindi Regional Council, including the towns of Goondiwindi, Yelarbon and Texas extending north towards Moonie and Millmerran. The AUSTLANG database maintained by the Australian Institute of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Studies states that the Bigambal language was spoken by the Bigambul people, with Gambuwal and Kwiambal (or Gujambal) known dialects. However, it is likely that the Gamilaraay (or Yuwaaliyaay) language was used by those peoples living in southern Bigambul territory. Classification Dixon (2002) groups Bigambal together with the Bundjalung languages while O'Grady, Voegelin and Voegelin classify it as a 'Wiradjuric' language. Glottolog states that Wafer and Lissarrague (2008) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gujambal Language
Gujambal (Guyambal, Kwiambal) is a possible extinct Australian Aboriginal language. It is undocumented. ' Gambuwal' may have been the same language. References External links Bibliography of Gujambal people and language resources at the Australian Institute of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Studies The Australian Institute of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Studies (AIATSIS), established as the Australian Institute of Aboriginal Studies (AIAS) in 1964, is an independent Australian Government statutory authority. It is a collecting, ... Unclassified languages of Australia Extinct languages of Queensland {{ia-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baagandji Language
The Paakantyi language, also spelt Paakantji, Barkindji, Barkandji, and Baagandji, and also known as the Darling language, is a nearly extinct Australian Aboriginal language spoken along the Darling River in New South Wales from present-day Bourke to Wentworth and including much of the back country around the Paroo River and Broken Hill. The people's and language name refers to the ''Paaka'' (Darling River) with the suffix ''-ntyi'' meaning "belonging to".Luise Hercus. ''Baagandji Grammar'', ANU 1960; ''Paakantyi Dictionary'' (published with the assistance of AIATSIS, 1993) The speakers of the language are known as the Paakantyi (or variant spelling). The major work on the Paakantyi language has been that of linguist Luise Hercus.Luise Hercus. ''Baagandji Grammar'', ANU 1960; ''Paakantyi Dictionary'' (published with the assistance of AIATSIS, 1993) Dialects Dialects of Paakantyi include Southern Paakantyi (Baagandji, Bagundji), Kurnu (Kula), Wilyakali (Wiljagali), and Pant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central New South Wales Languages
The Central New South Wales languages (Central NSW) are a largely geographic grouping of Australian Aboriginal languages within the traditional Pama–Nyungan family, partially overlapping the Kuri subgroup of the Yuin–Kuric languages. The languages most often included are: * Wiradhuric ( Wiradhuri, Ngiyambaa, Gamilaraay) * Dyangadi ( Dyangadi, Nganyaywana) *Worimi (Worimi, Awabakal) *'' Muruwarri'' *'' Barranbinja'' Bowern and Atkinson use the term Central NSW to group the Wiradhuric languages The Wiradhuric languages or Central (Inland) New South Wales, are a family of Pama–Nyungan languages of Australia. There are three languages: *Gamilaraay (northeast) *Wiradhuri–Ngiyambaa ** Wiradhuri (south) **Ngiyambaa (west) All are now mor ... with Muruwaric. Elsewhere it is known as ''Central Inland NSW''. References * * {{ia-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)