|
Bicton Woodland Railway
The Bicton Woodland Railway is a narrow-gauge railway running in Bicton Park Botanical Gardens in the grounds of Bicton House near Budleigh Salterton in Devon. The line was built in 1962 as a tourist attraction for visitors to the house. Most of the rolling stock was acquired from the Royal Arsenal Railway, Woolwich, with two locomotives, ''Woolwich'' and ''Carnegie'' coming from that source, as well as seven goods wagons which were reduced to their frames and converted to passenger carriages. It opened to passengers in 1963. Originally locomotives and carriages had royal blue livery. Additional rolling stock was acquired from the RAF Fauld railway and the internal railway of the LNWR Wolverton works. In 1998, the Bicton Gardens were put up for sale and the railway put into hiatus. The new owners sold the line's existing stock, and in 2000 took delivery of a 5.5-tonne diesel-powered replica tank engine. The line's original equipment was purchased by the Waltham Abbey Royal Gu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe by the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south. The country covers five-eighths of the island of Great Britain, which lies in the North Atlantic, and includes over 100 smaller islands, such as the Isles of Scilly and the Isle of Wight. The area now called England was first inhabited by modern humans during the Upper Paleolithic period, but takes its name from the Angles, a Germanic tribe deriving its name from the Anglia peninsula, who settled during the 5th and 6th centuries. England became a unified state in the 10th century and has had a significant cultural and legal impact on the wider world since the Age of Discovery, which began during the 15th century. The English language, the Anglican Church, and Engli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waltham Abbey Royal Gunpowder Mills
The Royal Gunpowder Mills are a former industrial site in Waltham Abbey, England. It was one of three Royal Gunpowder Mills in the United Kingdom (the others being at Ballincollig and Faversham). Waltham Abbey is the only site to have survived virtually intact. The Royal Gunpowder Mills, Waltham Abbey, were in operation for over 300 years. Starting in the mid-1850s the site became involved in the development of revolutionary nitro-based explosives and propellants known as "smokeless powder". The site grew in size, and black powder became less important. Shortly after the Second World War it became solely a Defence Research Establishment – firstly the Explosives Research and Development Establishment, then the Propellants, Explosives and Rocket Motor Establishment Waltham Abbey; and finally the Royal Armament Research and Development Establishment Waltham Abbey. The Mills are an ''Anchor Point'' of the European Route of Industrial Heritage, set in of parkland and contain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
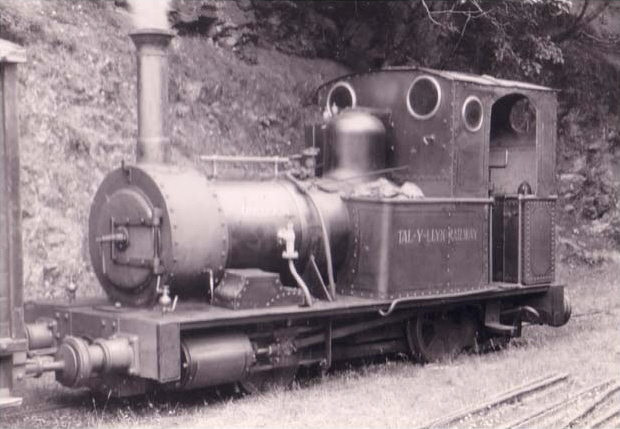
British Narrow Gauge Railways
There were more than a thousand British narrow-gauge railways ranging from large, historically significant common carriers to small, short-lived industrial railways. Many notable events in British railway history happened on narrow-gauge railways including the first use of steam locomotives, the first public railway and the first heritage railway, preserved railway. History Early railways: before 1865 The earliest narrow-gauge railways were crude wooden trackways used in coal mines to guide wooden Quarry tub, tubs. Because of the restricted loading gauge of the tunnels and the need for the tubs to be small enough to be pushed by one man, these railways were almost all narrow gauge. These underground lines often had short above-ground sections as well. After the start of the Industrial Revolution it became possible to create railways with iron tracks and wheels, which reduced the friction involved in moving wagons and made longer horse-hauled trains possible. These could mov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alan Keef
Alan Keef Ltd is a British narrow gauge railway engineering company which manufactures, overhauls, and deals in narrow gauge locomotives, rolling stock and associated equipment. The Limited Company was formed in 1975 at Cote, Bampton, Oxon, continuing what Alan Keef had already been doing for some years as an individual. In 1986 the company moved to larger premises at Lea, near Ross-on-Wye in Herefordshire. The first new loco was built in 1976. To date (2008) over eighty locos have been built – steam, diesel and electric. Most have been miniature or narrow gauge except for two standard gauge steam locos for Beamish Museum – the replicas of " Steam Elephant" and " Puffing Billy". In 2008 Alan Keef Ltd built the frames, running gear and mechanical parts for two Parry People Mover railcars for use on the Stourbridge Town branch (139001 and 139002). A number of Alan Keef's locomotives are replicas of steam locomotives but with diesel power. These are referred to as ''stea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hunslet Engine Company
The Hunslet Engine Company is a locomotive-building company, founded in 1864 in Hunslet, England. It manufactured steam locomotives for over 100 years and currently manufactures diesel shunting locomotives. The company is part of Ed Murray & Sons. History The early years 1864–1901 The company was founded in 1864 at Jack Lane in Hunslet by John Towlerton Leather, a civil engineering contractor, who appointed James Campbell (son of Alexander Campbell, a Leeds engineer) as his works manager. The first engine was completed in 1865. It was ''Linden'', a standard gauge delivered to Brassey and Ballard, a railway civil engineering contractor as were several of the firm's early customers. Other customers included collieries. This basic standard gauge shunting and short haul "industrial" engine was to be the main-stay of Hunslet production for many years. In 1871, James Campbell bought the company for £25,000 (payable in five instalments over two years) and the firm remained ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scalford
Scalford is a village and civil parish in the Melton borough of Leicestershire, England. It lies to the north of Melton Mowbray at the southern end of the Vale of Belvoir. In the 2011 census the parish (including Chadwell and Wycomb) had a population of 608. Etymology The name of the village is derived from Old English and originally meant shallow ford. It has retained its current spelling for at least 440 years, being shown as 'Scalford' on the map of Warwickshire and Leicestershire produced (in Latin) in 1576 by Christopher Saxton as part of his ''Atlas of England and Wales''. The name is partly due to Old Norse influence, as the village lies in the former Danelaw; it is identical in meaning to Shalford and Shelford. Churches The Scalford parish church, which is on a small hill in the centre of the village, is named after St Egelwin the Martyr (alias St Ethelwin) and is believed to be the only one in the country dedicated to this saint. It was built circa 1100 AD. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruston And Hornsby
Ruston & Hornsby was an industrial equipment manufacturer in Lincoln, England founded in 1918. The company is best known as a manufacturer of narrow and standard gauge diesel locomotives and also of steam shovels. Other products included cars, steam locomotives and a range of internal combustion engines, and later gas turbines. It is now a subsidiary of Siemens. Background Proctor & Burton was established in 1840, operating as millwrights and engineers. It became Ruston, Proctor and Company in 1857 when Joseph Ruston joined them, acquiring limited liability status in 1899. From 1866 it built a number of four and six-coupled tank locomotives, one of which was sent to the Paris Exhibition in 1867. In 1868 it built five 0-6-0 tank engines for the Great Eastern Railway to the design of Samuel Waite Johnson. Three of these were converted to crane tanks, two of which lasted until 1952, aged eighty-four. Among the company's output were sixteen for Argentina and some for T. A. Walk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statfold Barn Railway
The Statfold Barn Railway is a narrow gauge railway based near Tamworth, Staffordshire and partially in Warwickshire, England. Founded by engineering entrepreneur Graham Lee and his wife Carol at their farm-based home, they originally designed what is still termed the garden railway, in which Graham could run his trains and Carol could design an extensive English country garden around a lake. Graham Lee chaired the family-owned Wabtec, LH Group, with its main focus on railway engineering services. After LH Group acquired what remained of the Hunslet Engine Company in 2005, Graham pursued the opportunity to acquire the last steam locomotive built by Hunslet. Commissioned in 1971, it had been ordered by Leeds-based Robert Hudson & Co Ltd, who supplied and installed a complete railway system for the Trangkil sugar mill estate in Indonesia. As he pursued the Hunslet, Graham noticed a number of other interesting but defunct steam locomotives of European origin in Indonesia, and set abo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avonside Engine Company
The Avonside Engine Company was a locomotive manufacturer in Avon Street, St. Philip's, Bristol, England between 1864 and 1934. However the business originated with an earlier enterprise Henry Stothert and Company. Origins The firm was originally started by Henry Stothert in 1837 as Henry Stothert and Company. Henry was the son of George Stothert (senior), founder of the nearby Bath engineering firm of Stothert & Pitt. Henry's brother, also named George, was manager of the same firm. The company was given an order for two broad gauge () Firefly class express passenger engines ''Arrow'' and ''Dart'', with driving wheels, delivered for the opening of the Great Western Railway (GWR) from Bristol to Bath on 31 August 1840. This was soon followed by an order for eight smaller Sun class engines with driving wheels. Stothert, Slaughter and Company Edward Slaughter joined the company in 1841, when it became known as Stothert, Slaughter and Company. By 1844 their works were n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waltham Abbey (town)
Waltham Abbey is a town and civil parish in the Epping Forest District of Essex, within the metropolitan and urban area of London, England, north-east of Charing Cross. It lies on the Greenwich Meridian, between the River Lea in the west and Epping Forest in the east, with large sections forming part of the Metropolitan Green Belt. The town borders Nazeing and Epping Upland to the north, Chingford to the south, Loughton, Theydon Bois and Buckhurst Hill to the east and south-east, and Waltham Cross, Cheshunt and Enfield to the west. Historically an ancient parish named Waltham Holy Cross in the Waltham hundred of Essex, it became a local government district in 1850, and was granted urban district status in 1894. Whilst the use of the name Waltham Abbey for the town dates back to the 16th century at the earliest, the parish itself was not renamed until 1974, when the Waltham Holy Cross Urban District was abolished and succeeded by Waltham Abbey Town Council. The town council ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London And North Western Railway
The London and North Western Railway (LNWR, L&NWR) was a British railway company between 1846 and 1922. In the late 19th century, the L&NWR was the largest joint stock company in the United Kingdom. In 1923, it became a constituent of the London, Midland and Scottish (LMS) railway, and, in 1948, the London Midland Region of British Railways: the LNWR is effectively an ancestor of today's West Coast Main Line. History The company was formed on 16 July 1846 by the amalgamation of the Grand Junction Railway, London and Birmingham Railway and the Manchester and Birmingham Railway. This move was prompted, in part, by the Great Western Railway's plans for a railway north from Oxford to Birmingham. The company initially had a network of approximately , connecting London with Birmingham, Crewe, Chester, Liverpool and Manchester. The headquarters were at Euston railway station. As traffic increased, it was greatly expanded with the opening in 1849 of the Great Hall, designed by P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narrow-gauge Railway
A narrow-gauge railway (narrow-gauge railroad in the US) is a railway with a track gauge narrower than standard-gauge railway, standard . Most narrow-gauge railways are between and . Since narrow-gauge railways are usually built with Minimum railway curve radius, tighter curves, smaller structure gauges, and lighter rails, they can be less costly to build, equip, and operate than standard- or broad-gauge railways (particularly in mountainous or difficult terrain). Lower-cost narrow-gauge railways are often used in mountainous terrain, where engineering savings can be substantial. Lower-cost narrow-gauge railways are often built to serve industries as well as sparsely populated communities where the traffic potential would not justify the cost of a standard- or broad-gauge line. Narrow-gauge railways have specialised use in mines and other environments where a small structure gauge necessitates a small loading gauge. In some countries, narrow gauge is the standard; Japan, Indone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)


