|
Bicroft Mine
Bicroft Mine is a decommissioned underground uranium mine, located near Bancroft, Ontario, Canada. It is one of fourteen former uranium mines in Ontario that is monitored by the Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission, and one of twenty in Canada. Aside from uranium, the mine has also produced globally renowned samples of Kainosite-(Y). Location Bicroft Mine is a decommissioned former underground uranium mine located near Highlands East (previously known as Cardiff), southwest of Bancroft, Ontario, Canada. It is one of four former mines near Bancroft - the others being Faraday Mine/Madawaska Mine, Dyno Mine, and Greyhawk Mine). It is also one of fourteen former uranium mines in Ontario that is monitored by the Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission, and one of twenty of such in Canada. Products Aside from uranium, the mine has also produced globally renowned samples of Kainosite-(Y). Discovery of uranium - 1922 to 1953 Uranium was first discovered in the area of Cardiff i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paudash Lake
Paudash Lake is a lake in south central Ontario southwest of Bancroft along Highway 28. The lake is located just north of Silent Lake Provincial Park in Haliburton County, south of the panhandle of Algonquin Provincial Park. The nearest communities to Paudash Lake are the village of Cardiff, close to the lake's Inlet Bay, and the hamlet of Paudash to the northeast of Lower Paudash Lake. Actually two lakes, 'Paudash' and 'Lower Paudash', the lakes are located on the Crowe River, near its head waters, which flows into the Trent River at Crowe Bay north of Campbellford. Geography and geology Paudash Lake has several different sections within it; Lower Paudash Lake (Outlet Bay) to the east, North Bay to the north, Joe Bay to the southwest and Inlet Bay to the northeast. The lake has a surface area of and a maximum depth of . Fish species include largemouth bass, smallmouth bass, walleye, lake trout, perch, pumpkinseed, northern cisco, white sucker, and small bait fish of various ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Underground Mines In Canada
Underground most commonly refers to: * Subterranea (geography), the regions beneath the surface of the Earth Underground may also refer to: Places * The Underground (Boston), a music club in the Allston neighborhood of Boston * The Underground (Stoke concert venue), a club/music venue based in Hanley, Stoke-on-Trent * Underground Atlanta, a shopping and entertainment district in the Five Points neighborhood of downtown Atlanta, Georgia * Buenos Aires Underground, a rapid transit system * London Underground, a rapid transit system Arts, entertainment, and media Films * ''Underground'' (1928 film), a drama by Anthony Asquith * ''Underground'' (1941 film), a war drama by Vincent Sherman * ''Underground'' (1970 film), a war drama starring Robert Goulet * ''Underground'' (1976 film), a documentary about the radical organization the Weathermen * ''Underground'' (1989 film), a film featuring Melora Walters * ''Underground'' (1995 film), a film by Emir Kusturica * ''The Underground'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uranium Mines In Ontario
Uranium is a chemical element with the symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Uranium is weakly radioactive because all isotopes of uranium are unstable; the half-lives of its naturally occurring isotopes range between 159,200 years and 4.5 billion years. The most common isotopes in natural uranium are uranium-238 (which has 146 neutrons and accounts for over 99% of uranium on Earth) and uranium-235 (which has 143 neutrons). Uranium has the highest atomic weight of the primordially occurring elements. Its density is about 70% higher than that of lead, and slightly lower than that of gold or tungsten. It occurs naturally in low concentrations of a few parts per million in soil, rock and water, and is commercially extracted from uranium-bearing minerals such as uraninite. In nature, uranium is found as uranium-238 (99.2739–99.2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Mines In Ontario
This is a list of mines in the Canadian province of Ontario and includes both operating and closed mines. *Adams Mine *Agnew Lake Mine *Amalgamated Larder Mine *Argonaut Mine * Armistice Mine * Associated Goldfields Mine *Barber Larder Mine *Barton Mine *Beanland Mine * Bell Creek Mine *Bidgood Mine *Bicroft Mine (uranium) *Big Dan Mine * Black Fox Mine *Buckles Mine * Campbell Mine *Can-Met Mine * Cheminis Mine *Chesterville Mine *Coleman Mine *Copper Cliff North Mine *Copper Cliff South Mine *Copperfields Mine *Coppersand Mine *Craig Mine *Creighton Mine *Denison Mine *Detour Gold Mine *Dome Mine *Dyno Mine (uranium) * Eagle River Mine *Falconbridge Mine *Faraday Mine (now Madawaska Mine) *Frood Mine *Fraser Mine * Garson Mine * Geco Mine * Goderich Salt Mines - Sifto Canada *Golden Giant Mine * Greyhawk Mine (Uranium) * Hagersville-CGC * Hemlo Mine *Hermiston-McCauley Mine *Hollinger Mines *Holloway Mine *Holt Mine * Hoyle Pond Mine *Hudson Rand Mine *Josephine Mine *Kanichee M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
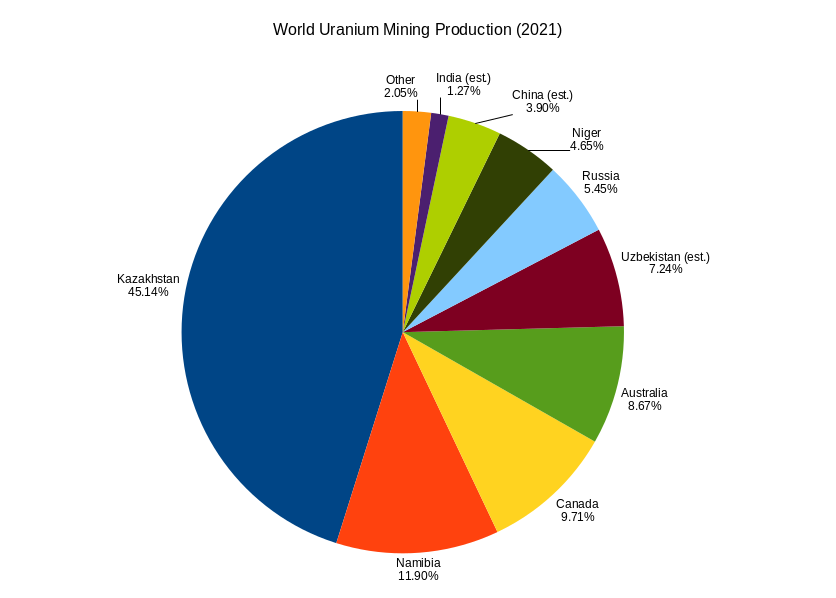
Uranium Mining
Uranium mining is the process of extraction of uranium ore from the ground. Over 50 thousand tons of uranium were produced in 2019. Kazakhstan, Canada, and Australia were the top three uranium producers, respectively, and together account for 68% of world production. Other countries producing more than 1,000 tons per year included Namibia, Niger, Russia, Uzbekistan, the United States, and China. Nearly all of the world's mined uranium is used to power nuclear power plants. Historically uranium was also used in applications such as uranium glass or ferrouranium but those applications have declined due to the radioactivity of uranium and are nowadays mostly supplied with a plentiful cheap supply of depleted uranium which is also used in uranium ammunition. In addition to being cheaper, depleted uranium is also less radioactive due to a lower content of short-lived and than natural uranium. Uranium is mined by in-situ leaching (57% of world production) or by conventional und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Uranium Mines
Uranium production is carried out in about 13 countries around the world, in 2017 producing a cumulative total of 59,462 tonnes of uranium (tU). The international producers were Kazakhstan (39%), Canada (22%), Australia (10%), Namibia (7.1%), Niger (5.8%), Russian Federation (4.9%), Uzbekistan (4.0%), China (3.2%), United States (1.6%), Ukraine (0.9%), India (0.7%), South Africa (0.5%) and Pakistan (0.1%). Since 2009 the in-situ leach (ISL) operations of Kazakhstan have been producing the largest share of world uranium. The largest conventional uranium mines are Cigar Lake and McArthur River (Canada); Ranger and Olympic Dam (Australia); Krasnokamensk (Russia) and Rossing (Namibia). The largest uranium producers are Cameco, Rio Tinto, Areva, KazAtomProm and ARMZ-TVEL. The production methods employed are conventional underground and open cast (50%) and in-situ leaching (50%). About 50 uranium production centers are operational. Viable projects Potentially viable projects N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uranium Ore Deposits
Uranium ore deposits are economically recoverable concentrations of uranium within the Earth's crust. Uranium is one of the more common elements in the Earth's crust, being 40 times more common than silver and 500 times more common than gold. It can be found almost everywhere in rock, soil, rivers, and oceans. The challenge for commercial uranium extraction is to find those areas where the concentrations are adequate to form an economically viable deposit. The primary use for uranium obtained from mining is in fuel for nuclear reactors. Globally, the distribution of uranium ore deposits is widespread on all continents, with the largest deposits found in Australia, Kazakhstan, and Canada. To date, high-grade deposits are only found in the Athabasca Basin region of Canada. Uranium deposits are generally classified based on host rocks, structural setting, and mineralogy of the deposit. The most widely used classification scheme was developed by the International Atomic Energy Agen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uranium Mining In The Bancroft Area
Uranium mining around Bancroft, Ontario, was conducted at four sites, beginning in the early 1950s and concluding by 1982. Bancroft was one of two major uranium-producing areas in Ontario, and one of seven in Canada, all located along the edge of the Canadian Shield. In the context of mining, the "Bancroft area" includes Haliburton, Hastings, and Renfrew counties, and all areas between Minden and Lake Clear. Activity in the mid-1950s was described by engineer A. S. Bayne in a 1977 report as the "greatest uranium prospecting rush in the world". As a result of activities at its four major uranium mines, Bancroft experienced rapid population and economic growth throughout the 1950s. By 1958, Canada had become one of the world's leading producers of uranium; the $274 million of uranium exports that year represented Canada's most significant mineral export. By 1963, the federal government had purchased more than $1.5 billion of uranium from Canadian producers, but soon thereaft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greyhawk Mine
Greyhawk Mine is a decommissioned underground uranium mine located in Faraday Township near Bancroft, Ontario. It operated from 1954 to 1959 and from 1976 to 1982. The mine produced 80,247 tons of uranium ore, of which 0.069% was U3O8 worth $834,899. Aside from uranium, the mine has produced some of the world's best samples of Kainosite-(Y). Uranium discovery - 1922 to 1954 Uranium was first discovered in the nearby area of Cardiff in 1922 by W. M. Richardson. Between 1953 and 1956, one hundred area prospects were opened, including one by one which developed into Greyhawk Mine. Mine operations - 1954 to 1982 In 1954, Goldhawk Porcupine Mines Limited (who later became Goldhawk Uranium Mines Limited) undertook geology surveys, drilling to 450 feet deep. During 1955 and 1956 Greyhawk Uranium Mines Limited sunk a vertical shaft to 361 feet creating three levels at depths of 110 feet, 211 feet, and 333 feet. They then drilled 114 holes (totalling 42,299 feet of drilling). By ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barrick Gold
Barrick Gold Corporation is a mining company that produces gold and copper with 16 operating sites in 13 countries. It is headquartered in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. It has mining operations in Argentina, Canada, Chile, Côte d'Ivoire, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Dominican Republic, Mali, Papua New Guinea, Saudi Arabia, Tanzania, the United States and Zambia. In 2019, it produced 5.5 million ounces of gold at all-in sustaining costs of $894/ounce and 432 million pounds of copper at all-in sustaining costs of $2.52/pound. the company had 71 million ounces of proven and probable gold reserves. Barrick has met or beaten market consensus on its financial and operating results for eleven consecutive quarters as of Q3 2021. Barrick had been the world's largest gold mining company until Newmont Corporation acquired Goldcorp in 2019. Barrick expects to produce between 4.6 and five million ounces of gold and between 440 and 500 million pounds of copper in 2020. Chief executive Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyno Mine
Dyno Mine is a decommissioned underground uranium mine located at Cardiff, near Farrel Lake, approximately 30km southwest of Bancroft, Ontario. It operated from 1958 to 1960. Uranium discovery - 1922 to 1956 Uranium was first discovered in the area of Cardiff (now known as Highlands East) in 1922 by W. M. Richardson. Between 1953 and 1956, one hundred area prospects were opened, including one by Paul Mulliette of Toronto who discovered uranium in 1953, which was developed into Dyno Mine. Mine operations - 1956 to 1960 In 1956, brush was cleared to create 200 houses in Cardiff, some for executives of nearby Bicroft Mine and a settlement called ''Dyno Estates'' was built near Ontario Highway 28 for executives of Dyno Mine. Other construction quickly followed, including, two single-men's bunkhouses, a canteen, an eleven-room school, an ice-curling rink, and a recreation center. In 1957, a swimming pool was started. Mining commenced in 1958 via a 525 meter deep shaft. There wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |