|
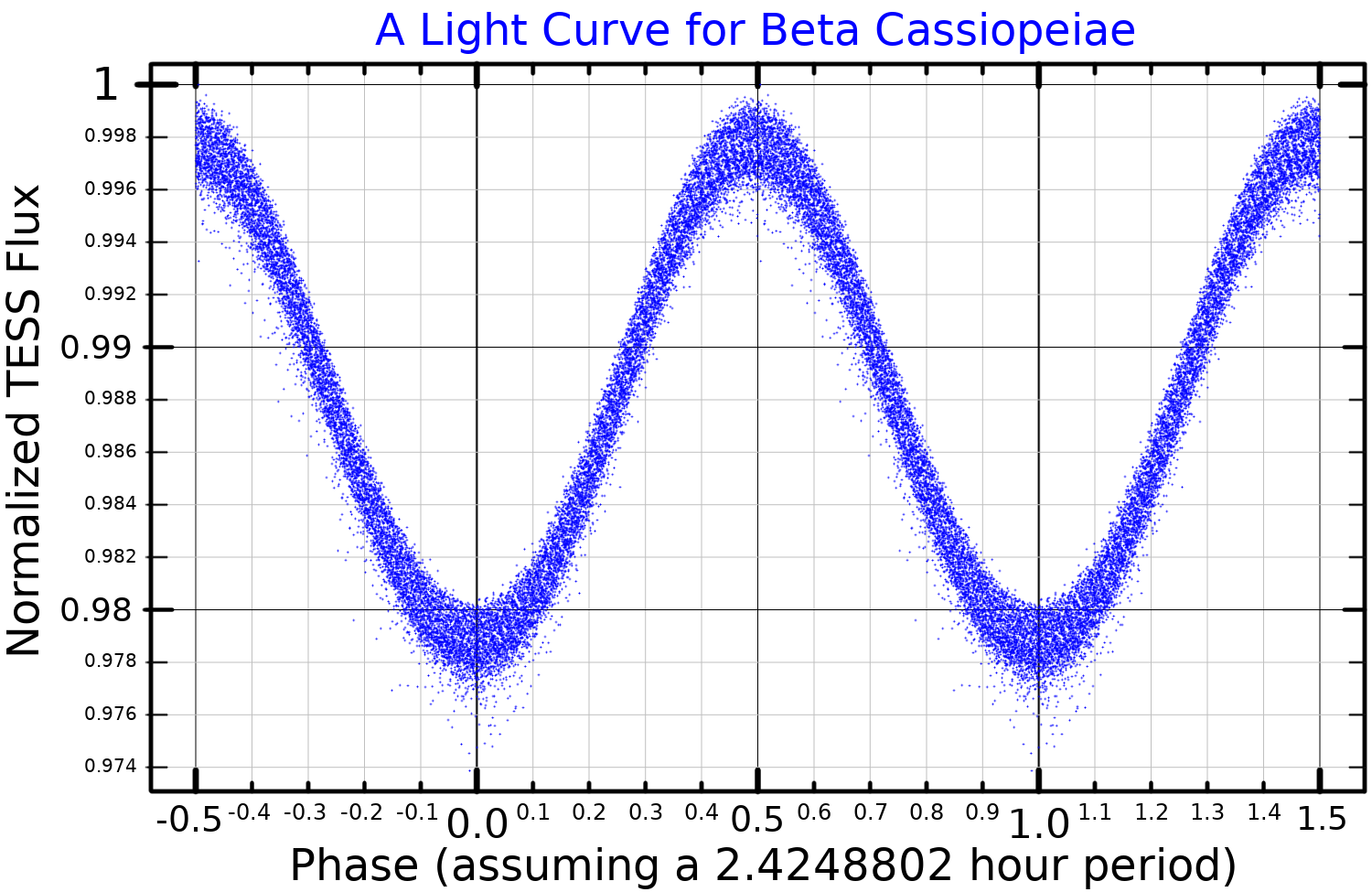
Beta Cassiopeiae
Beta Cassiopeiae (β Cassiopeiae, abbreviated Beta Cas or β Cas), officially named Caph , is a Delta Scuti variable star in the constellation of Cassiopeia. It is a giant star belonging to the spectral class F2. The white star of second magnitude (+2.28 mag, variable) has an absolute magnitude of +1.3 mag. Nomenclature ''Beta Cassiopeiae'' is the star's Bayer designation. It also bore the traditional names ''Caph'' (from the Arabic word ', "palm" - ''i.e.'' reaching from the Pleiades), ''Chaph'' and ''Kaff'', as well as ''al-Sanam al-Nakah'' "the Camel's Hump". In 2016, the International Astronomical Union organized a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) to catalog and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN's first bulletin of July 2016 included a table of the first two batches of names approved by the WGSN; which included ''Caph'' for this star. Originally, the pre-Islamic Arabic term ''al-Kaff al-Khadib'' "the stained hand" referred to the five stars comprisin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cassiopeia (constellation)
Cassiopeia () is a constellation in the northern sky named after the vain queen Cassiopeia, mother of Andromeda, in Greek mythology, who boasted about her unrivaled beauty. Cassiopeia was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. It is easily recognizable due to its distinctive ' W' shape, formed by five bright stars. Cassiopeia is located in the northern sky and from latitudes above 34°N it is visible year-round. In the (sub)tropics it can be seen at its clearest from September to early November, and at low southern, tropical, latitudes of less than 25°S it can be seen, seasonally, low in the North. At magnitude 2.2, Alpha Cassiopeiae, or Schedar, is generally the brightest star in Cassiopeia, though it is occasionally outshone by the variable Gamma Cassiopeiae, which has reached magnitude 1.6. The constellation hosts some of the most luminous stars known, including the yello ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giant Star
A giant star is a star with substantially larger radius and luminosity than a main sequence, main-sequence (or ''dwarf'') star of the same effective temperature, surface temperature.Giant star, entry in ''Astronomy Encyclopedia'', ed. Patrick Moore, New York: Oxford University Press, 2002. . They lie above the main sequence (luminosity class V in the Spectral classification#Yerkes spectral classification, Yerkes spectral classification) on the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram and correspond to luminosity classes II and III.giant, entry in ''The Facts on File Dictionary of Astronomy'', ed. John Daintith and William Gould, New York: Facts On File, Inc., 5th ed., 2006. . The terms ''giant'' and ''dwarf'' were coined for stars of quite different luminosity despite similar temperature or spectral type by Ejnar Hertzsprung about 1905. Giant stars have radii up to a few hundred times the solar radii, Sun and luminosities between 10 and a few thousand times that of the Sun. Stars still mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Star Names
Chinese star names (Chinese: , ''xīng míng'') are named according to ancient Chinese astronomy and astrology. The sky is divided into star mansions (, ''xīng xiù'', also translated as "lodges") and asterisms (, ''xīng guān''). The system of 283 asterisms under Three Enclosures and Twenty-eight Mansions was established by Chen Zhuo of the Three Kingdoms period, who synthesized ancient constellations and the asterisms created by early astronomers Shi Shen, Gan De and Wuxian. Since the Han and Jin Dynasties, stars have been given reference numbers within their asterisms in a system similar to the Bayer or Flamsteed designations, so that individual stars can be identified. For example, Deneb (α Cyg) is referred to as (''Tiān Jīn Sì'', the Fourth Star of Celestial Ford). In the Qing Dynasty, Chinese knowledge of the sky was improved by the arrival of European star charts. ''Yixiang Kaocheng'', compiled in mid-18th century by then deputy Minister of Rites Ignaz Kögler, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lambda Cassiopeiae
Lambda Cassiopeiae, Latinisation of names, Latinized from λ Cassiopeiae, is a binary star system, in the northern constellation of Cassiopeia (constellation), Cassiopeia. The system has a combined apparent magnitude of +4.74, making it faintly visible to the naked eye. With an annual stellar parallax, parallax shift of 8.64 milliarcsecond, mass, it is approximately 380 light years from Earth. The system is moving closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of −12 km/s. Both components are blue-white B-type main-sequence stars. The brighter member, component A, has an apparent magnitude of +5.5, while its companion, component B, has an apparent magnitude of +5.8. The two stars are separated by 0.6 arcseconds and complete one orbit around their common centre of mass about once every 250 years. The primary displays an infrared excess, possibly due to a debris disk or other orbiting material. References {{Stars of Cassiopeia B-type main-sequence stars Bina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Cassiopeiae
Alpha Cassiopeiae or α Cassiopeiae, also named Schedar (), is a second magnitude star in the northern constellation of Cassiopeia. Though listed as the " alpha star" by Johann Bayer, α Cas's visual brightness closely matches the ' beta' (β) star in the constellation ( Beta Cassiopeiae) and it may appear marginally brighter or dimmer, depending on which passband is used. However, recent calculations from NASA's WISE telescope confirm that α Cas is the brightest in Cassiopeia, with an apparent magnitude of 2.240. Its absolute magnitude is 18 times greater than β Cas, and it is located over four times farther away from the Sun. Nomenclature ''α Cassiopeiae'' ( Latinised to ''Alpha Cassiopeiae'') is the star's Bayer designation. It bore the traditional name ''Schedar'', which was first encountered in the Alfonsine tables of the thirteenth century. It derives from the Arabic word صدر ''şadr'', meaning "breast", a word which is derived from its relative po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eta Cassiopeiae
Eta Cassiopeiae (η Cassiopeiae, abbreviated Eta Cas, η Cas) is a binary star system in the northern constellation of Cassiopeia. Its binary nature was first discovered by William Herschel in August 1779. Based upon parallax measurements, the distance to this system is from the Sun. The two components are designated Eta Cassiopeiae A (officially named Achird , the traditional name for the system) and B. Nomenclature ''η Cassiopeiae'' ( Latinised to ''Eta Cassiopeiae'') is the system's Bayer designation. The designations of the two constituents as ''Eta Cassiopeiae A'' and ''B'' derive from the convention used by the Washington Multiplicity Catalog (WMC) for star systems, and adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). The proper name ''Achird'' was apparently first applied to Eta Cassiopeiae in the Skalnate Pleso Atlas of the Heavens published in 1950, but is not known prior to that. Richard Hinckley Allen gives no historical names for the star ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kappa Cassiopeiae
Kappa Cassiopeiae (κ Cas, κ Cassiopeiae) is a star in the constellation Cassiopeia. κ Cassiopeiae has an unusual spectrum that has anomalously weak nitrogen lines, taken as an actual nitrogen deficiency in the atmosphere. This is indicated by the modified letter C on the assumption that it is also carbon-rich, although this might not actually be the case. It is also interpolated to BC0.7, being slightly hotter than a standard B1 star. κ Cassiopeiae is assumed to be a member of the Cassiopeia OB14 stellar association (Cas OB14) and treated as being at a distance of about , while its distance found from the Hipparcos parallax is about 1,400 parsecs. Its Gaia parallaxes are somewhat uncertain due to the brightness of the star, but a modern determination of the distance to Cas OB14 is . It is classified as an Alpha Cygni type variable star and its brightness varies by a few hundredths of a magnitude. Periods of two hours, 2.65 days, and nine days have been report ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spring And Autumn Period
The Spring and Autumn period was a period in Chinese history from approximately 770 to 476 BC (or according to some authorities until 403 BC) which corresponds roughly to the first half of the Eastern Zhou period. The period's name derives from the ''Spring and Autumn Annals'', a chronicle of the state of Lu between 722 and 479 BCE, which tradition associates with Confucius (551–479 BCE). During this period, the Zhou royal authority over the various feudal states eroded as more and more dukes and marquesses obtained ''de facto'' regional autonomy, defying the king's court in Luoyi and waging wars amongst themselves. The gradual Partition of Jin, one of the most powerful states, marked the end of the Spring and Autumn period and the beginning of the Warring States period. Background In 771 BCE, a Quanrong invasion in coalition with the states of Zeng and Shen — the latter polity being the fief of the grandfather of the disinherited crown prince Yijiu — destroyed the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legs (Chinese Constellation)
The Legs mansion (奎宿, pinyin: Kuí Xiù) is one of the Twenty-eight mansions of the Chinese constellations. It is one of the western mansions of the White Tiger The white tiger or bleached tiger is a leucistic pigmentation variant of the Mainland tiger. It is reported in the wild from time to time in the Indian states of Madhya Pradesh, Assam, West Bengal, Bihar, Odisha, in the Sunderbans region and .... Cultural significance In East Asian cultures, the Legs mansion (Kuí Xiù) represents wisdom, scholarship and literature. A notable example is a structure known as "Kuiwen Pavilion" (奎文閣) in the many Confucius temples in China and other East Asian countries. Asterisms See also * Kui Xing {{Chinese constellation Chinese constellations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Astronomy
Astronomy in China has a long history stretching from the Shang dynasty, being refined over a period of more than 3,000 years. The ancient Chinese people have identified stars from 1300 BCE, as Chinese star names later categorized in the twenty-eight mansions have been found on oracle bones unearthed at Anyang, dating back to the mid-Shang dynasty. The core of the "mansion" (宿 ''xiù'') system also took shape around this period, by the time of King Wu Ding (1250–1192 BCE). Detailed records of astronomical observations began during the Warring States period (fourth century BCE) and flourished from the Han period onward. Chinese astronomy was equatorial, centered on close observation of circumpolar stars, and was based on different principles from those in traditional Western astronomy, where heliacal risings and settings of zodiac constellations formed the basic ecliptic framework. Joseph Needham has described the ancient Chinese as the most persistent and accurate obser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IAU Working Group On Star Names
The International Astronomical Union (IAU) established a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) in May 2016 to catalog and standardize proper names for stars for the international astronomical community. It operates under Division C – Education, Outreach and Heritage. The IAU states that it is keen to make a distinction between the terms ''name'' and ''designation''. To the IAU, ''name'' refers to the (usually colloquial) term used for a star in everyday conversation, while ''designation'' is solely alphanumerical, and used almost exclusively in official catalogues and for professional astronomy. (The WGSN notes that transliterated Bayer designations (e.g., Tau Ceti) are considered a special historical case and are treated as designations.) Terms of reference The terms of reference for the WGSN for the period 2016–2018 were approved by the IAU Executive Committee at its meeting on 6 May 2016. In summary, these are to: * establish IAU guidelines for the proposal and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Astronomical Union
The International Astronomical Union (IAU; french: link=yes, Union astronomique internationale, UAI) is a nongovernmental organisation with the objective of advancing astronomy in all aspects, including promoting astronomical research, outreach, education, and development through global cooperation. It was founded in 1919 and is based in Paris, France. The IAU is composed of individual members, who include both professional astronomers and junior scientists, and national members, such as professional associations, national societies, or academic institutions. Individual members are organised into divisions, committees, and working groups centered on particular subdisciplines, subjects, or initiatives. As of 2018, the Union had over 13,700 individual members, spanning 90 countries, and 82 national members. Among the key activities of the IAU is serving as a forum for scientific conferences. It sponsors nine annual symposia and holds a triannual General Assembly that sets policy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |