|
Besselian Elements
The Besselian elements are a set of values used to calculate and predict the local circumstances of occultations for an observer on Earth. This method is particularly used for solar eclipses, but is also applied for occultations of stars or planets by the Moon and transits of Venus or Mercury. In addition, for lunar eclipses a similar method is used, in which the shadow is cast on the Moon instead of the Earth. For solar eclipses, the Besselian elements are used to calculate the path of the umbra and penumbra on the Earth's surface, and hence the circumstances of the eclipse at a specific location. This method was developed in the 1820s by the German mathematician and astronomer, Friedrich Wilhelm Bessel, and later improved by William Chauvenet. The basic concept is that Besselian elements describe the movement of the shadow cast by the occulting body – for solar eclipses this is the shadow of the Moon – on a specifically chosen plane, called the ''fundamental plane' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Chauvenet
William Chauvenet (24 May 1820 in Milford, Pennsylvania – 13 December 1870 in St. Paul, Minnesota) was a professor of mathematics, astronomy, navigation, and surveying who was instrumental in the establishment of the U.S. Naval Academy at Annapolis, Maryland, and later the second chancellor of Washington University in St. Louis. Early life William Chauvenet was born on a farm near Milford, Pennsylvania to Guillaume Marc Chauvenet, a former soldier of Napoleon's army reconverted in silk trade after the Emperor's fall, and Mary B. Kerr and was raised in Philadelphia. He entered Yale University at age 16, and graduated in 1840 with high honors. While at Yale, Chauvenet contributed to the school newspaper and was a pianist with the Beethoven Society. He was one of eight founding members of the Skull and Bones Society. United States Navy In 1841, he was appointed a professor of mathematics in the United States Navy, and for a while served on the USS ''Mississippi'' teaching math ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eclipses
An eclipse is an astronomical event that occurs when an astronomical object or spacecraft is temporarily obscured, by passing into the shadow of another body or by having another body pass between it and the viewer. This alignment of three celestial objects is known as a syzygy. Apart from syzygy, the term eclipse is also used when a spacecraft reaches a position where it can observe two celestial bodies so aligned. An eclipse is the result of either an occultation (completely hidden) or a transit (partially hidden). The term eclipse is most often used to describe either a solar eclipse, when the Moon's shadow crosses the Earth's surface, or a lunar eclipse, when the Moon moves into the Earth's shadow. However, it can also refer to such events beyond the Earth–Moon system: for example, a planet moving into the shadow cast by one of its moons, a moon passing into the shadow cast by its host planet, or a moon passing into the shadow of another moon. A binary star system can a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ΔT (timekeeping)
In precise timekeeping, Δ''T'' (Delta ''T'', delta-''T'', delta''T'', or D''T'') is a measure of the cumulative effect of the departure of the Earth's rotation period from the fixed-length day of International Atomic Time (86,400 seconds). Formally, Δ''T'' is the time difference between Universal Time (UT, defined by Earth's rotation) and Terrestrial Time (TT, independent of Earth's rotation). The value of ΔT for the start of 1902 was approximately zero; for 2002 it was about 64 seconds. So Earth's rotations over that century took about 64 seconds longer than would be required for days of atomic time. As well as this long-term drift in the length of the day there are short-term fluctuations in the length of day () which are dealt with separately. Since 2017, the length of the day has happened to be very close to the conventional value, and ΔT has remained within a second of 69 seconds. Calculation Earth's rotational speed is , and a day corresponds to one period . A ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
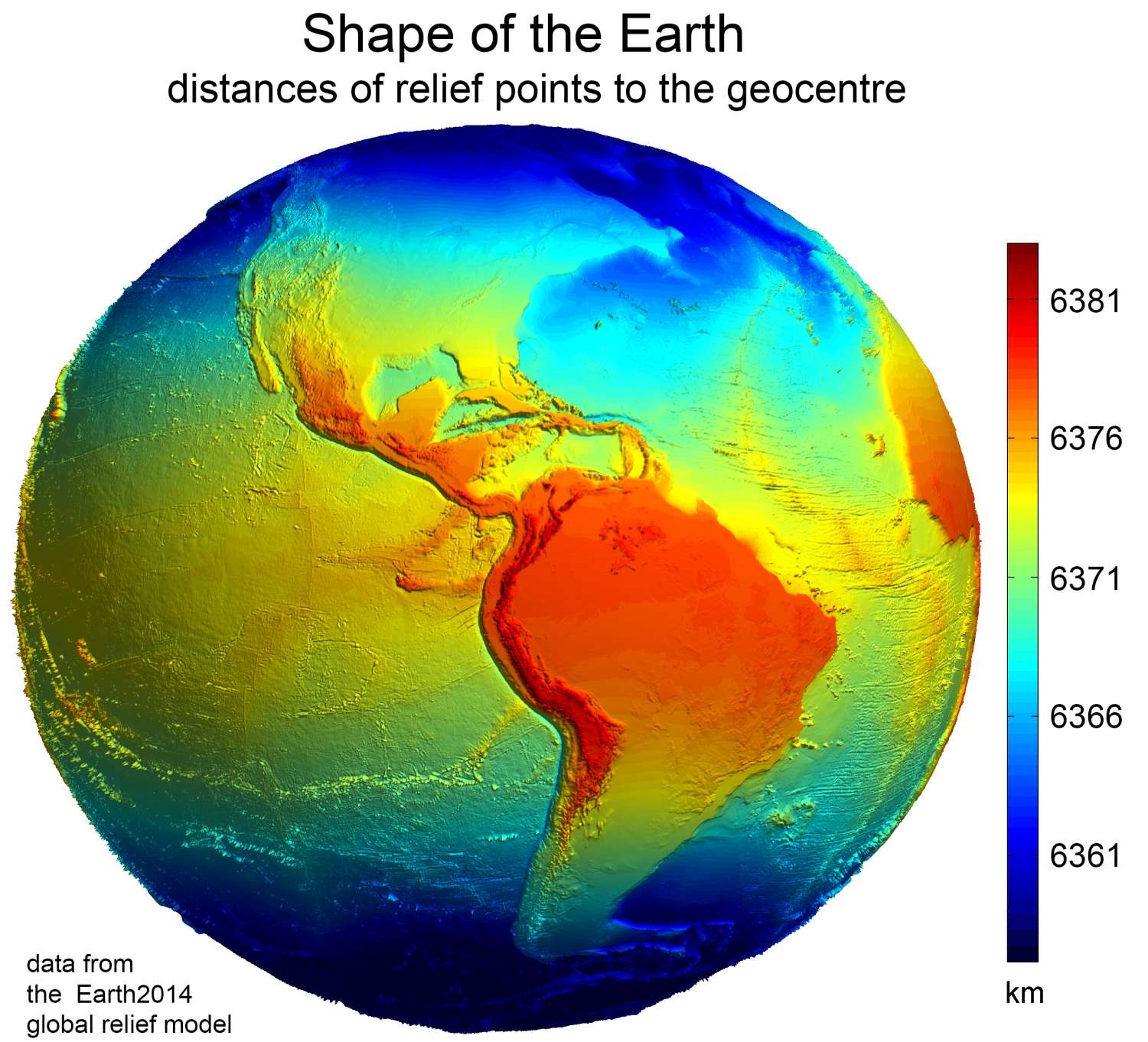
Elevation
The elevation of a geographic location is its height above or below a fixed reference point, most commonly a reference geoid, a mathematical model of the Earth's sea level as an equipotential gravitational surface (see Geodetic datum § Vertical datum). The term ''elevation'' is mainly used when referring to points on the Earth's surface, while ''altitude'' or ''geopotential height'' is used for points above the surface, such as an aircraft in flight or a spacecraft in orbit, and '' depth'' is used for points below the surface. Elevation is not to be confused with the distance from the center of the Earth. Due to the equatorial bulge, the summits of Mount Everest and Chimborazo have, respectively, the largest elevation and the largest geocentric distance. Aviation In aviation the term elevation or aerodrome elevation is defined by the ICAO as the highest point of the landing area. It is often measured in feet and can be found in approach charts of the aerodrome. It is n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longitude
Longitude (, ) is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east–west position of a point on the surface of the Earth, or another celestial body. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek letter lambda (λ). Meridians are semicircular lines running from pole to pole that connect points with the same longitude. The prime meridian defines 0° longitude; by convention the International Reference Meridian for the Earth passes near the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, England on the island of Great Britain. Positive longitudes are east of the prime meridian, and negative ones are west. Because of the Earth's rotation, there is a close connection between longitude and time measurement. Scientifically precise local time varies with longitude: a difference of 15° longitude corresponds to a one-hour difference in local time, due to the differing position in relation to the Sun. Comparing local time to an absolute measure of time allows ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pole, with 0° at the Equator. Lines of constant latitude, or ''parallels'', run east–west as circles parallel to the equator. Latitude and ''longitude'' are used together as a coordinate pair to specify a location on the surface of the Earth. On its own, the term "latitude" normally refers to the ''geodetic latitude'' as defined below. Briefly, the geodetic latitude of a point is the angle formed between the vector perpendicular (or ''normal'') to the ellipsoidal surface from the point, and the plane of the equator. Background Two levels of abstraction are employed in the definitions of latitude and longitude. In the first step the physical surface is modeled by the geoid, a surface which approximates the mean sea level over the ocean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth's Rotation
Earth's rotation or Earth's spin is the rotation of planet Earth around its own Rotation around a fixed axis, axis, as well as changes in the orientation (geometry), orientation of the rotation axis in space. Earth rotates eastward, in retrograde and prograde motion, prograde motion. As viewed from the northern polar star Polaris, Earth turns counterclockwise. The North Pole, also known as the Geographic North Pole or Terrestrial North Pole, is the point in the Northern Hemisphere where Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface. This point is distinct from Earth's North Magnetic Pole. The South Pole is the other point where Earth's axis of rotation intersects its surface, in Antarctica. Earth rotates once in about 24 hours with respect to the Sun, but once every 23 hours, 56 minutes and 4 seconds with respect to other distant stars (#Stellar and sidereal day, see below). Earth's rotation is slowing slightly with time; thus, a day was shorter in the past. This is due to the tida ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Figure Of The Earth
Figure of the Earth is a Jargon, term of art in geodesy that refers to the size and shape used to model Earth. The size and shape it refers to depend on context, including the precision needed for the model. A Spherical Earth, sphere is a well-known historical approximation of the figure of the Earth that is satisfactory for many purposes. Several models with greater accuracy (including Earth ellipsoid, ellipsoid) have been developed so that Geographic coordinate system, coordinate systems can serve the precise needs of navigation, surveying, cadastre, land use, and various other concerns. Motivation Earth's Topography, topographic surface is apparent with its variety of land forms and water areas. This topographic surface is generally the concern of topographers, Hydrography, hydrographers, and Geophysics, geophysicists. While it is the surface on which Earth measurements are made, mathematically modeling it while taking the irregularities into account would be extremely compl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphical Projection
A 3D projection (or graphical projection) is a design technique used to display a three-dimensional (3D) object on a two-dimensional (2D) surface. These projections rely on visual perspective and aspect analysis to project a complex object for viewing capability on a simpler plane. 3D projections use the primary qualities of an object's basic shape to create a map of points, that are then connected to one another to create a visual element. The result is a graphic that contains conceptual properties to interpret that the figure or image as not actually flat (2D), but rather, as a solid object (3D) being viewed on a 2D display. 3D objects are largely displayed on two-dimensional mediums (i.e. paper and computer monitors). As such, graphical projections are a commonly used design element; notably, in engineering drawing, drafting, and computer graphics. Projections can be calculated through employment of mathematical analysis and formulae, or by using various geometric and op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perspective Projection Distortion
Perspective may refer to: Vision and mathematics * Perspectivity, the formation of an image in a picture plane of a scene viewed from a fixed point, and its modeling in geometry ** Perspective (graphical), representing the effects of visual perspective in graphic arts ** Aerial perspective, the effect the atmosphere has on the appearance of an object as it is viewed from a distance ** Perspective distortion (photography), the way that viewing a picture from the wrong position gives a perceived distortion ** Perspective (geometry), a relation between geometric figures ** Vue d'optique or perspective view, a genre of etching popular during the second half of the 18th century and into the 19th. Entertainment * ''Perspective'' (P-Model album), 1982 * ''Perspective'' (America album), 1984 * ''Perspective'' (Jason Becker album), 1996 * ''Perspective'' (Lawson album), 2016 * ''Perspective'', a 2010 album by Prague * Perspective (EP), an EP by Tesseract * ''Perspectives'' (album), t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Wilhelm Bessel
Friedrich Wilhelm Bessel (; 22 July 1784 – 17 March 1846) was a German astronomer, mathematician, physicist, and geodesist. He was the first astronomer who determined reliable values for the distance from the sun to another star by the method of parallax. A special type of mathematical functions were named Bessel functions after Bessel's death, though they had originally been discovered by Daniel Bernoulli and then generalised by Bessel. Life and family Bessel was born in Minden, Westphalia, then capital of the Prussian administrative region Minden-Ravensberg, as second son of a civil servant into a large family. At the age of 14 Bessel was apprenticed to the import-export concern Kulenkamp at Bremen. The business's reliance on cargo ships led him to turn his mathematical skills to problems in navigation. This in turn led to an interest in astronomy as a way of determining longitude. Bessel came to the attention of a major figure of German astronomy at the time, Heinrich Wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |