|
Bermuda-Azores High
The Azores High also known as North Atlantic (Subtropical) High/Anticyclone or the Bermuda-Azores High, is a large subtropical semi-permanent centre of high atmospheric pressure typically found south of the Azores in the Atlantic Ocean, at the Horse latitudes. It forms one pole of the North Atlantic oscillation, the other being the Icelandic Low. The system influences the weather and climatic patterns of vast areas of North Africa and Southern Europe, and to a lesser extent, eastern North America. The aridity of the Sahara Desert and the summer drought of the Mediterranean Basin is due to the large-scale subsidence and sinking motion of air in the system. In its summer position, the high is centered near Bermuda, and creates a southwest flow of warm tropical air toward the East Coast of the United States. In summer, the Azores-Bermuda High is strongest. The central pressure hovers around 1024 mbar ( hPa). This high-pressure block exhibits anticyclonic behaviour, circulating th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subtropics
The subtropical zones or subtropics are geographical and climate zones to the north and south of the tropics. Geographically part of the temperate zones of both hemispheres, they cover the middle latitudes from to approximately 35° north and south. The horse latitudes lie within this range. Subtropical climates are often characterized by hot summers and mild winters with infrequent frost. Most subtropical climates fall into two basic types: humid subtropical (Koppen climate Cfa), where rainfall is often concentrated in the warmest months, for example Southeast China and the Southeastern United States, and dry summer or Mediterranean climate (Koppen climate Csa/Csb), where seasonal rainfall is concentrated in the cooler months, such as the Mediterranean Basin or Southern California. Subtropical climates can also occur at high elevations within the tropics, such as in the southern end of the Mexican Plateau and in Da Lat of the Vietnamese Central Highlands. The six climate cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric Pressure
Atmospheric pressure, also known as barometric pressure (after the barometer), is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as , which is equivalent to 1013.25 millibars, 760mm Hg, 29.9212 inchesHg, or 14.696psi.International Civil Aviation Organization. ''Manual of the ICAO Standard Atmosphere'', Doc 7488-CD, Third Edition, 1993. . The atm unit is roughly equivalent to the mean sea-level atmospheric pressure on Earth; that is, the Earth's atmospheric pressure at sea level is approximately 1 atm. In most circumstances, atmospheric pressure is closely approximated by the hydrostatic pressure caused by the weight of air above the measurement point. As elevation increases, there is less overlying atmospheric mass, so atmospheric pressure decreases with increasing elevation. Because the atmosphere is thin relative to the Earth's radius—especially the dense atmospheric layer at low altitudes—the Earth's gravi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Global Warming
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to Earth's climate. The current rise in global average temperature is more rapid than previous changes, and is primarily caused by humans burning fossil fuels. Fossil fuel use, deforestation, and some agricultural and industrial practices increase greenhouse gases, notably carbon dioxide and methane. Greenhouse gases absorb some of the heat that the Earth radiates after it warms from sunlight. Larger amounts of these gases trap more heat in Earth's lower atmosphere, causing global warming. Due to climate change, deserts are expanding, while heat waves and wildfires are becoming more common. Increased warming in the Arctic has contributed to melting permafrost, glacial retreat and sea ice loss. Higher temperatures are also causing m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
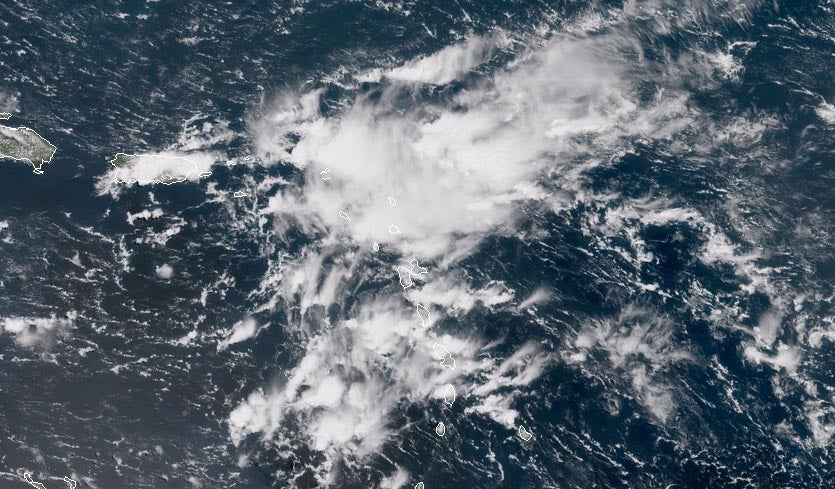
Tropical Waves
A tropical wave (also called easterly wave, tropical easterly wave, and African easterly wave), in and around the Atlantic Ocean, is a type of atmospheric trough, an elongated area of relatively low air pressure, oriented north to south, which moves from east to west across the tropics, causing areas of cloudiness and thunderstorms. Tropical waves form in the easterly flow along the equatorial side of the subtropical ridge or belt of high air pressure which lies north and south of the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ). Tropical waves are generally carried westward by the prevailing easterly winds along the tropics and subtropics near the equator. They can lead to the formation of tropical cyclones in the north Atlantic and northeastern Pacific basins. A tropical wave study is aided by Hovmöller diagrams, a graph of meteorological data. West-moving waves can also form from the tail end of frontal zones in the subtropics and tropics, and may be referred to as easterly wave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
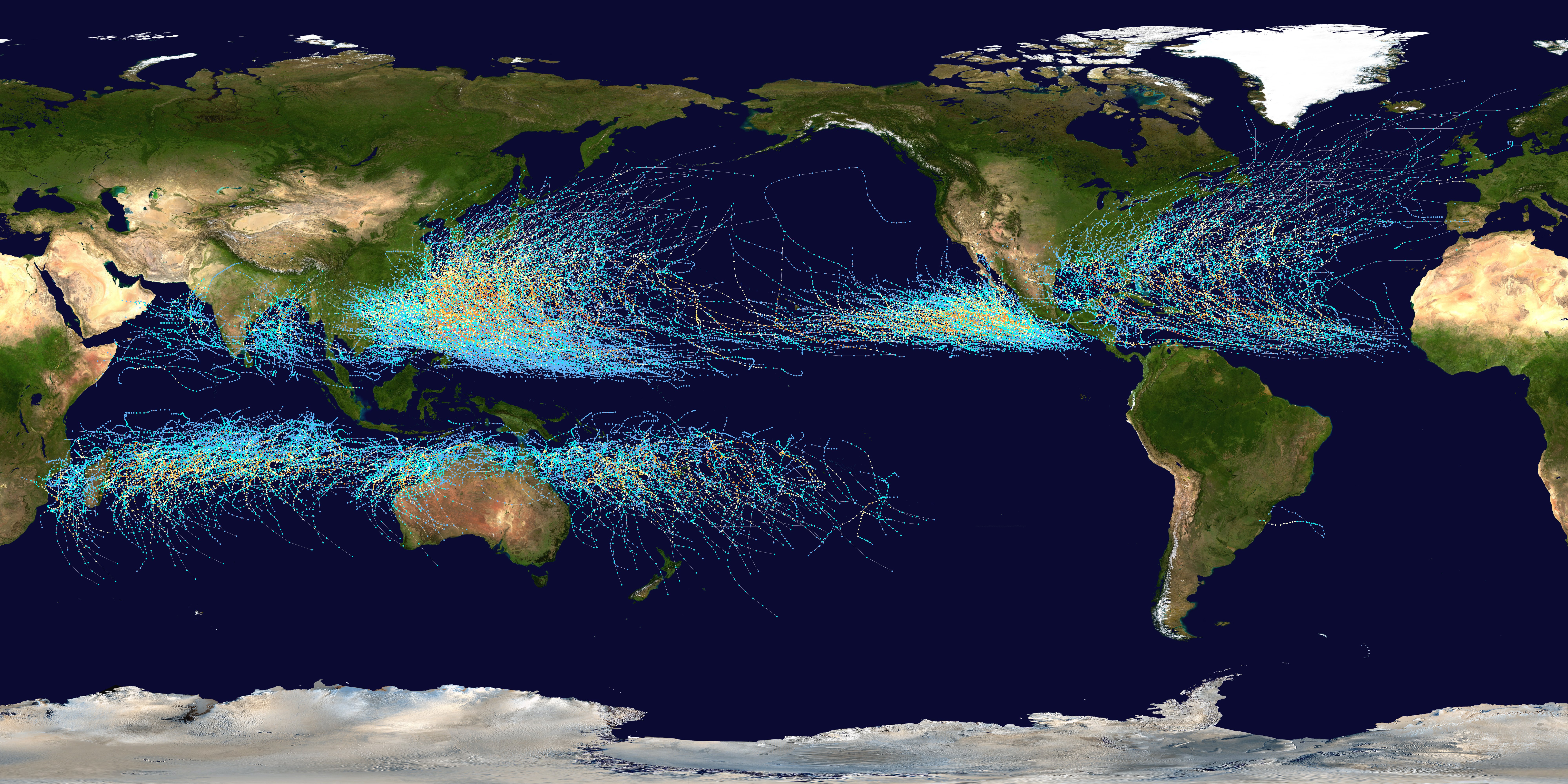
Atlantic Hurricane Season
The Atlantic hurricane season is the period in a year from June through November when tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic Ocean, referred to in North American countries as hurricanes, tropical storms, or tropical depressions. In addition, there have been several storms over the years that have not been fully tropical and are categorized as subtropical depressions and subtropical storms. Even though subtropical storms and subtropical depressions are not technically as strong as tropical cyclones, the damages can still be devastating. Worldwide, tropical cyclone activity peaks in late summer, when the difference between temperatures aloft and sea surface temperatures is the greatest. However, each tropical cyclone basin has its own seasonal patterns. On a worldwide scale, May is the least active month, while September is the most active. In the Northern Atlantic Ocean, a distinct hurricane season occurs from June 1 to November 30, sharply peaking from late August through Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Cyclogenesis
Tropical cyclogenesis is the development and strengthening of a tropical cyclone in the atmosphere. The mechanisms through which tropical cyclogenesis occurs are distinctly different from those through which temperate cyclogenesis occurs. Tropical cyclogenesis involves the development of a warm-core cyclone, due to significant convection in a favorable atmospheric environment. Tropical cyclogenesis requires six main factors: sufficiently warm sea surface temperatures (at least ), atmospheric instability, high humidity in the lower to middle levels of the troposphere, enough Coriolis force to develop a low-pressure center, a pre-existing low-level focus or disturbance, and low vertical wind shear. Tropical cyclones tend to develop during the summer, but have been noted in nearly every month in most basins. Climate cycles such as ENSO and the Madden–Julian oscillation modulate the timing and frequency of tropical cyclone development. There is a limit on tropical cyclone i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bahamas
The Bahamas (), officially the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is an island country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the West Indies in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic. It takes up 97% of the Lucayan Archipelago's land area and is home to 88% of the archipelago's population. The archipelagic state consists of more than 3,000 islands, cays, and islets in the Atlantic Ocean, and is located north of Cuba and northwest of the island of Hispaniola (split between the Dominican Republic and Haiti) and the Turks and Caicos Islands, southeast of the U.S. state of Florida, and east of the Florida Keys. The capital is Nassau, Bahamas, Nassau on the island of New Providence. The Royal Bahamas Defence Force describes The Bahamas' territory as encompassing of ocean space. The Bahama Islands were inhabited by the Lucayan people, Lucayans, a branch of the Arawakan-Taino language, speaking Taíno, for many centuries. Christopher Columbus was the first European to see the islands, making hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central America
Central America ( es, América Central or ) is a subregion of the Americas. Its boundaries are defined as bordering the United States to the north, Colombia to the south, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. Central America consists of eight countries: Belize, Costa Rica, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua, and Panama. Within Central America is the Mesoamerican biodiversity hotspot, which extends from northern Guatemala to central Panama. Due to the presence of several active geologic faults and the Central America Volcanic Arc, there is a high amount of seismic activity in the region, such as volcanic eruptions and earthquakes which has resulted in death, injury, and property damage. In the pre-Columbian era, Central America was inhabited by the indigenous peoples of Mesoamerica to the north and west and the Isthmo-Colombian peoples to the south and east. Following the Spanish expedition of Christopher Columbus' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caribbean
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean) and the surrounding coasts. The region is southeast of the Gulf of Mexico and the North American mainland, east of Central America, and north of South America. Situated largely on the Caribbean Plate, the region has more than 700 islands, islets, reefs and cays (see the list of Caribbean islands). Island arcs delineate the eastern and northern edges of the Caribbean Sea: The Greater Antilles and the Lucayan Archipelago on the north and the Lesser Antilles and the on the south and east (which includes the Leeward Antilles). They form the West Indies with the nearby Lucayan Archipelago (the Bahamas and Turks and Caicos Islands), which are considered to be part of the Caribbean despite not bordering the Caribbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, Mauritania, Niger, Nigeria, Senegal, Sierra Leone, and Togo, as well as Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha ( United Kingdom Overseas Territory).Paul R. Masson, Catherine Anne Pattillo, "Monetary union in West Africa (ECOWAS): is it desirable and how could it be achieved?" (Introduction). International Monetary Fund, 2001. The population of West Africa is estimated at about million people as of , and at 381,981,000 as of 2017, of which 189,672,000 are female and 192,309,000 male. The region is demographically and economically one of the fastest growing on the African continent. Early history in West Africa included a number of prominent regional powers that dominated different parts of both the coastal and internal trade networks, suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Waves
A tropical wave (also called easterly wave, tropical easterly wave, and African easterly wave), in and around the Atlantic Ocean, is a type of atmospheric trough, an elongated area of relatively low air pressure, oriented north to south, which moves from east to west across the tropics, causing areas of cloudiness and thunderstorms. Tropical waves form in the easterly flow along the equatorial side of the subtropical ridge or belt of high air pressure which lies north and south of the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ). Tropical waves are generally carried westward by the prevailing easterly winds along the tropics and subtropics near the equator. They can lead to the formation of tropical cyclones in the north Atlantic and northeastern Pacific basins. A tropical wave study is aided by Hovmöller diagrams, a graph of meteorological data. West-moving waves can also form from the tail end of frontal zones in the subtropics and tropics, and may be referred to as easterly wave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clockwise
Two-dimensional rotation can occur in two possible directions. Clockwise motion (abbreviated CW) proceeds in the same direction as a clock's hands: from the top to the right, then down and then to the left, and back up to the top. The opposite sense of rotation or revolution is (in Commonwealth English) anticlockwise (ACW) or (in North American English) counterclockwise (CCW). Terminology Before clocks were commonplace, the terms " sunwise" and "deasil", "deiseil" and even "deocil" from the Scottish Gaelic language and from the same root as the Latin "dexter" ("right") were used for clockwise. "Widdershins" or "withershins" (from Middle Low German "weddersinnes", "opposite course") was used for counterclockwise. The terms clockwise and counterclockwise can only be applied to a rotational motion once a side of the rotational plane is specified, from which the rotation is observed. For example, the daily rotation of the Earth is clockwise when viewed from above the South Pole, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |