|
Berladnici
The Berladnici ( pl, Berładnicy; ro, Berladnici; russian: Берладники; uk, Берладники) were a supposed medieval people living along the northeastern Black Sea coast. While their ethnicity is unclear, it included runaways from Kievan Rus' who left those lands due to feudal oppression. Peasants as well as boyars dissatisfied with the rulers purportedly settled in the vicinity of the city of Bârlad as well as the river of the same name in eastern Romania, as well as on the lower Don River. History The Berladnici are first mentioned in the Ipatiev Chronicle. The text recounts the 1159 war between Prince Yaroslav of Halych and his cousin Ivan Berladnic, during which the latter fled to "the Cumans in towns near the Danube and allied with him many Cumans and Berladnici being over 6,000 people". In 1161, The Berladnici captured the port of Oles at the mouth of the Dnieper river, which caused severe damage to Rus' merchants. They were occupied mainly with fishing, hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
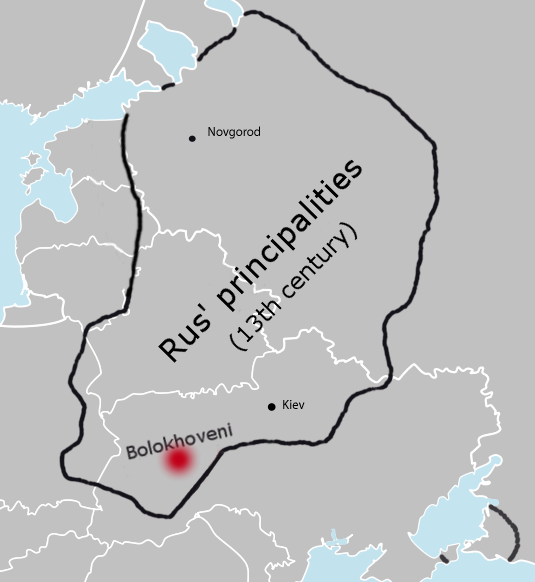
Bolohoveni Land From A
Bolokhovians, Bolokhoveni, also Bolokhovens ( ro, Bolohoveni; Old Slavic: Болоховци, Bolokhovtsy), were a 13th-century ethnic group that resided in the vicinity of the Rus' principalities of Halych, Volhynia and Kiev, in the territory known as the "" centered at the city of Bolokhov or Bolokhovo (not identified yet). Their ethnic identity is uncertain; although Romanian scholars, basing on their ethnonym identify them as Romanians (who were called Vlachs in the Middle Ages), archeological evidence and the ''Hypatian Chronicle'' (which is the only primary source that documents their history) suggest that they were a Slavic people. Their princes, or ''knyazes'', were in constant conflict with Daniel of Galicia, Prince of Halych and Volhynia, between 1231 and 1257. After the Mongols sacked Kiev in 1240, the Bolokhovians supplied them with troops, but the Bolokhovian princes fled to Poland. The Bolokhovians disappeared after Daniel defeated them in 1257. Etymology Roman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fishing
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch fish. Fish are often caught as wildlife from the natural environment, but may also be caught from stocked bodies of water such as ponds, canals, park wetlands and reservoirs. Fishing techniques include hand-gathering, spearing, netting, angling, shooting and trapping, as well as more destructive and often illegal techniques such as electrocution, blasting and poisoning. The term fishing broadly includes catching aquatic animals other than fish, such as crustaceans ( shrimp/ lobsters/crabs), shellfish, cephalopods (octopus/squid) and echinoderms ( starfish/ sea urchins). The term is not normally applied to harvesting fish raised in controlled cultivations ( fish farming). Nor is it normally applied to hunting aquatic mammals, where terms like whaling and sealing are used instead. Fishing has been an important part of human culture since hunter-gatherer times, and is one of the few food production activities that have persisted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foundation Of Moldavia
The founding of Moldavia ( ro, Descălecatul Moldovei) began with the arrival of a Vlach (Romanian) voivode (military leader), Dragoș, soon followed by his people from Maramureș, then a voivodeship, to the region of the Moldova River. Dragoș established a polity there as a vassal to the Kingdom of Hungary in the 1350s. The independence of the Principality of Moldavia was gained when Bogdan I, another Vlach voivode from Maramureș who had fallen out with the Hungarian king, crossed the Carpathians in 1359 and took control of Moldavia, wresting the region from Hungary. It remained a principality until 1859, when it united with Wallachia, initiating the development of the modern Romanian state. Competing cultures in the future region of Moldavia Moldavia developed in the lands between the Carpathian Mountains and the Dniester River, which had been dominated by nomadic Turkic peoples—the Pechenegs, Ouzes and Cumans—from around 900. The neighboring Principality of Halyc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brodnici
The Brodnici (russian: Бродники, ukr, Бродники) were a tribe of disputed origin. Etymology In some opinions, the name, as used by foreign chronicles, means a person in charge of a ford (water crossing) in Slavic language (cf. Slavic ''brodŭ''). The probable reason for the name is that the territory of the Brodniks constituted the link between the mountain passes in the Carpathians and the mouths of the Danube, having a major economical importance, assuring the access to the Genovese colonies. According to other opinions, their name is related to Slavic ''бродить'' ("to wander"), probably referring to the nomadic way of life of this population.Victor Spinei, ''Moldavia in the 11th–14th centuries'', Editura Academiei Republicii Socialiste România 1986. Other opinions claim that the name came from the river Prut or from its purportedly old name Brutus. Territory The territory of Brodnici consisted of the southwestern part of today's Republic of Moldov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolokhoveni
Bolokhovians, Bolokhoveni, also Bolokhovens ( ro, Bolohoveni; Old Slavic: Болоховци, Bolokhovtsy), were a 13th-century ethnic group that resided in the vicinity of the Rus' principalities of Halych, Volhynia and Kiev, in the territory known as the "" centered at the city of Bolokhov or Bolokhovo (not identified yet). Their ethnic identity is uncertain; although Romanian scholars, basing on their ethnonym identify them as Romanians (who were called Vlachs in the Middle Ages), archeological evidence and the ''Hypatian Chronicle'' (which is the only primary source that documents their history) suggest that they were a Slavic people. Their princes, or '' knyazes'', were in constant conflict with Daniel of Galicia, Prince of Halych and Volhynia, between 1231 and 1257. After the Mongols sacked Kiev in 1240, the Bolokhovians supplied them with troops, but the Bolokhovian princes fled to Poland. The Bolokhovians disappeared after Daniel defeated them in 1257. Etymology Roma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blakumen
''Blakumen'' or ''Blökumenn'' were a people mentioned in Scandinavian sources dating from the 11th through 13th centuries. The name of their land, ''Blokumannaland'', has also been preserved. Victor Spinei, Florin Curta, Florin Pintescu and other historians identify them as Romanians (variation of the exonym Vlach), while Omeljan Pritsak argues that they were Cumans. Judith Jesch adds the possibility that the terms meant "black men", the meaning of which is unclear. Historians identify ''Blokumannaland'' as the lands south of the Lower Danube which were inhabited by Vlachs in the Middle Ages, adding that the term may refer to either Wallachia (to the north of the Danube) or Africa in the modern Icelandic language. ''Blakumen'' on runestone G134 The only preserved example of the variant ''Blakumen'' of the ethnonym was an inscription on a runestone in the Sjonhem cemetery in Gotland in Sweden. The forms of the runes on the memorial stone suggest that it was raised in approximate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ukrainian Cossacks
The Zaporozhian Cossacks, Zaporozhian Cossack Army, Zaporozhian Host, (, or uk, Військо Запорізьке, translit=Viisko Zaporizke, translit-std=ungegn, label=none) or simply Zaporozhians ( uk, Запорожці, translit=Zaporozhtsi, translit-std=ungegn) were Cossacks who lived beyond (that is, downstream from) the Dnieper Rapids, the land also known historically as the Wild Fields in what is today Central Ukraine, central and eastern Ukraine. Much of this territory is now flooded by the waters of the Kakhovka Reservoir. The Zaporozhian Sich grew rapidly in the 15th century from serfdom, serfs fleeing the more controlled parts of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. It became established as a well-respected political entity with a parliamentary system of government. During the course of the 16th, 17th and well into the 18th century, the Zaporozhian Cossacks were a strong political and military force that challenged the authority of the Polish–Lithuanian Common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of The Kalka River
The Battle of the Kalka River (russian: Битва на реке Калке; uk, Битва на річці Калка) was fought between the Mongol Empire, whose armies were led by Jebe and Subutai, and a coalition of several Rus' principalities, including Kiev and Halych, and the Cumans under Köten. They were under the joint command of Mstislav the Bold and Mstislav III of Kiev. The battle was fought on May 31, 1223 on the banks of the Kalka River in present-day Donetsk Oblast, Ukraine, and ended in a decisive Mongol victory. Following the Mongol invasion of Central Asia and the subsequent collapse of the Khwarezmian Empire, a Mongol force under the command of generals Jebe and Subutai advanced into Iraq-i Ajam. Jebe requested permission from the Mongolian emperor, Genghis Khan, to continue his conquests for a few years before returning to the main army via the Caucasus. While waiting for Genghis Khan's reply, the duo set out on a raid in which they attacked the Kingdom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voivode
Voivode (, also spelled ''voievod'', ''voevod'', ''voivoda'', ''vojvoda'' or ''wojewoda'') is a title denoting a military leader or warlord in Central, Southeastern and Eastern Europe since the Early Middle Ages. It primarily referred to the medieval rulers of the Romanian-inhabited states and of governors and military commanders of Hungarian, Balkan or some Slavic-speaking populations. In the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, ''voivode'' was interchangeably used with ''palatine''. In the Tsardom of Russia, a voivode was a military governor. Among the Danube principalities, ''voivode'' was considered a princely title. Etymology The term ''voivode'' comes from two roots. is related to warring, while means 'leading' in Old Slavic, together meaning 'war leader' or 'warlord'. The Latin translation is for the principal commander of a military force, serving as a deputy for the monarch. In early Slavic, ''vojevoda'' meant the , the military leader in battle. The term has als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principality Of Halych
The Principality of Halych ( uk, Галицьке князівство, translit=Halytske kniazivstvo; rus, Галицкое княжество; orv, Галицкоє кънѧжьство; ro, Cnezatul Galiția), or Principality of Halychian Rus, was a medieval East Slavic principality, and one of main regional states within the political scope of Kievan Rus', established by members of the oldest line of Yaroslav the Wise descendants. A characteristic feature of Halych principality was an important role of the nobility and citizens in political life, consideration a will of which was the main condition for the princely rule. Halych as the capital mentioned in around 1124 as a seat of Ivan Vasylkovych the grandson of Rostislav of Tmutarakan. According to Mykhailo Hrushevsky the realm of Halych was passed to Rostyslav upon the death of his father Vladimir Yaroslavich, but he was banished out of it later by his uncle to Tmutarakan. The realm was then passed to Yaropolk Izyaslavich ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victor Spinei
Victor Spinei (born 26 October 1943 in Lozova, Lăpușna County, Romania) is Emeritus Professor of history and archaeology at the Alexandru Ioan Cuza University, member and vice president of the Romanian Academy. He is a specialist on the history of Romania and the Romanian people in the Early and High Middle Ages, the history of migratory peoples in Eastern and Southeastern Europe during this period, and the production and circulation of cult objects in Eastern and Southeastern Europe during the Middle Ages. Education In 1961 Spinei graduated from the Costache Negruzzi National College. In 1966 he received a Bachelor of Science in History and Philosophy from the Alexandru Ioan Cuza University, after which he specialised at the Institute for Prehistory and Historical Archaeology from Saarland University (1973–1974). In 1977 he earned a PhD from the Nicolae Iorga Institute of History in Bucharest, under Ștefan Ștefănescu (initially under Ion Nestor at the University of Bucha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , passing through or bordering Austria, Slovakia, Hungary, Croatia, Serbia, Romania, Bulgaria, Moldova, and Ukraine before draining into the Black Sea. Its drainage basin extends into nine more countries. List of cities and towns on Danube river, The largest cities on the river are Vienna, Budapest, Belgrade and Bratislava, all of which are the capitals of their respective countries; the Danube passes through four capital cities, more than any other river in the world. Five more capital cities lie in the Danube's basin: Bucharest, Sofia, Zagreb, Ljubljana and Sarajevo. The fourth-largest city in its basin is Munich, the capital of Bavaria, standing on the Isar River. The Danube is the List of rivers of Europe#Longest rivers, second-longest riv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)
.png)
