|
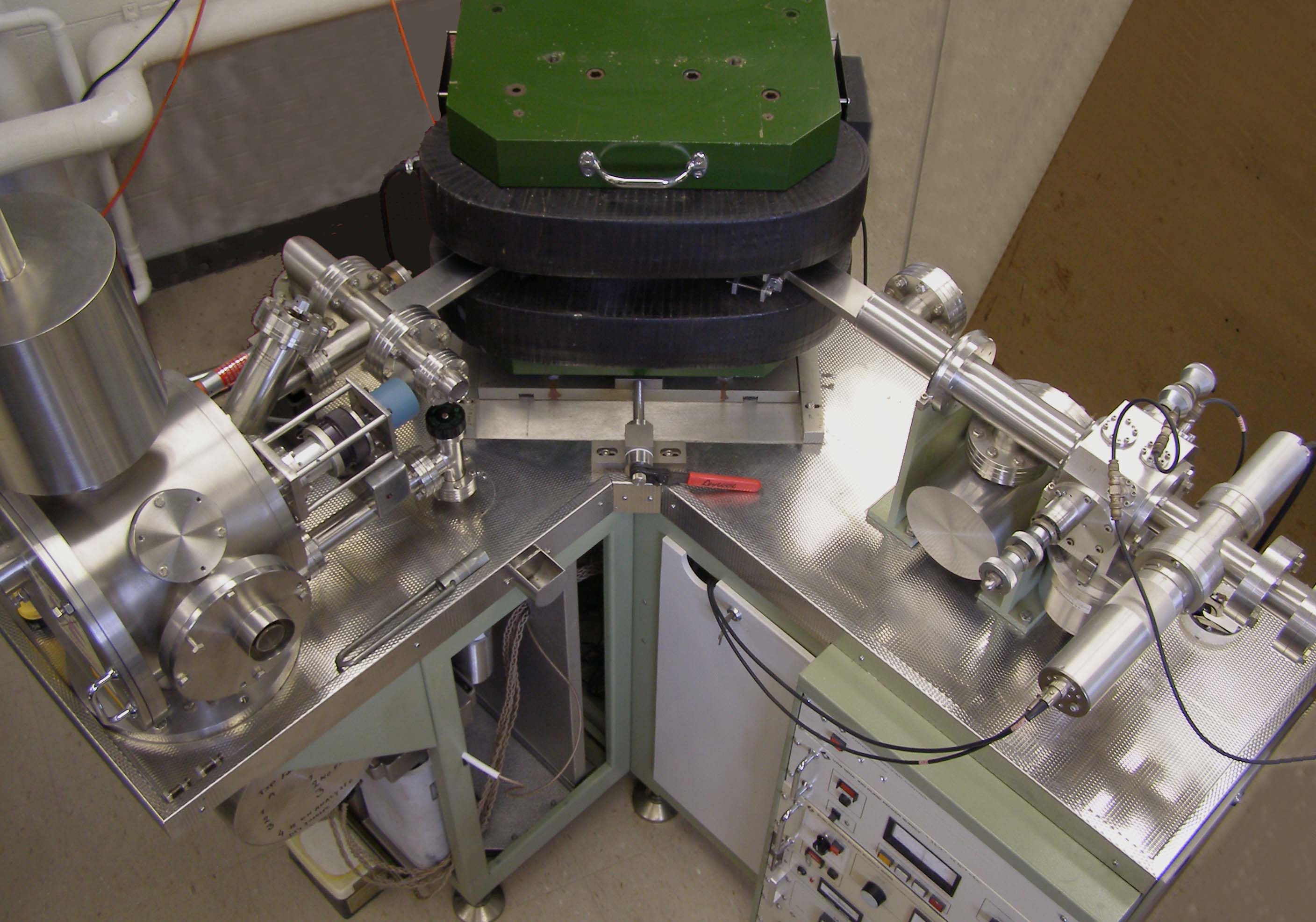
Berkeley Geochronology Center
The Berkeley Geochronology Center (BGC) is a non-profit geochronology research institute in Berkeley, California. It was originally a research group in the laboratory of geochronologist Garniss Curtis at the University of California, Berkeley. The center is now an independent scientific research institute with close Berkeley affiliations and directed by geologist and geochronologist Paul Renne, a professor in residence in the department of earth and planetary science at Berkeley. History In 1985, Curtis, set to retire in 1989, moved the group from his lab at the university to the basement of the independent Institute for Human Origins (IHO), at the suggestion of American anthropologist F. Clark Howell. The geochronologists worked separately from the IHO, although IHO contained their bureaucratic infrastructure, until 1989 when they became officially known as the Institute for Human Origins Geochronology Center. In 1994 the group officially split from the IHO based on different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
501(c) Organization
A 501(c) organization is a nonprofit organization in the Law of the United States#Federal law, federal law of the United States according to Internal Revenue Code (26 U.S.C. § 501(c)) and is one of over 29 types of nonprofit organizations exempt from some Taxation in the United States, federal Income tax in the United States, income taxes. Sections 503 through 505 set out the requirements for obtaining such exemptions. Many states refer to Section 501(c) for definitions of organizations exempt from state taxation as well. 501(c) organizations can receive unlimited contributions from individuals, corporations, and Labor union, unions. For example, a nonprofit organization may be tax-exempt under section 501(c)(3) organization, 501(c)(3) if its primary activities are charitable, religious, educational, scientific, literary, testing for public safety, fostering amateur sports competition, or preventing cruelty to Child abuse, children or Animal cruelty, animals. Types According ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology
Geology () is a branch of natural science concerned with Earth and other astronomical objects, the features or rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth sciences, including hydrology, and so is treated as one major aspect of integrated Earth system science and planetary science. Geology describes the structure of the Earth on and beneath its surface, and the processes that have shaped that structure. It also provides tools to determine the relative and absolute ages of rocks found in a given location, and also to describe the histories of those rocks. By combining these tools, geologists are able to chronicle the geological history of the Earth as a whole, and also to demonstrate the age of the Earth. Geology provides the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and the Earth's past climates. Geologists broadly study the properties and processes of E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geochronological Institutions And Organizations
Geochronology is the science of determining the age of rocks, fossils, and sediments using signatures inherent in the rocks themselves. Absolute geochronology can be accomplished through radioactive isotopes, whereas relative geochronology is provided by tools such as paleomagnetism and stable isotope ratios. By combining multiple geochronological (and biostratigraphic) indicators the precision of the recovered age can be improved. Geochronology is different in application from biostratigraphy, which is the science of assigning sedimentary rocks to a known geological period via describing, cataloging and comparing fossil floral and faunal assemblages. Biostratigraphy does not ''directly'' provide an absolute age determination of a rock, but merely places it within an ''interval'' of time at which that fossil assemblage is known to have coexisted. Both disciplines work together hand in hand, however, to the point where they share the same system of naming strata (rock layers) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BBC News
BBC News is an operational business division of the British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) responsible for the gathering and broadcasting of news and current affairs in the UK and around the world. The department is the world's largest broadcast news organisation and generates about 120 hours of radio and television output each day, as well as online news coverage. The service maintains 50 foreign news bureaus with more than 250 correspondents around the world. Deborah Turness has been the CEO of news and current affairs since September 2022. In 2019, it was reported in an Ofcom report that the BBC spent £136m on news during the period April 2018 to March 2019. BBC News' domestic, global and online news divisions are housed within the largest live newsroom in Europe, in Broadcasting House in central London. Parliamentary coverage is produced and broadcast from studios in London. Through BBC English Regions, the BBC also has regional centres across England and national news c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extraterrestrial Materials
Extraterrestrial material refers to natural objects now on Earth that originated in outer space. Such materials include cosmic dust and meteorites, as well as samples brought to Earth by sample return missions from the Moon, asteroids and comets, as well as solar wind particles. Extraterrestrial materials are of value to science as they preserve the primitive composition of the gas and dust from which the Sun and the Solar System formed. Categories Extraterrestrial material for study on earth can be classified into a few broad categories, namely: # Meteorites too large to vaporize on atmospheric entry but small enough to leave fragments lying on the ground, among which are included likely specimens from the asteroid and Kuiper belts as well as from the moon and from Mars. # Moon rocks brought to Earth by robotic and crewed lunar missions. # Cosmic dust collected on Earth, in the Earth's stratosphere, and in low Earth orbit which likely include particles from the present day i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleomagnetism
Paleomagnetism (or palaeomagnetismsee ), is the study of magnetic fields recorded in rocks, sediment, or archeological materials. Geophysicists who specialize in paleomagnetism are called ''paleomagnetists.'' Certain magnetic minerals in rocks can record the direction and intensity of Earth's magnetic field at the time they formed. This record provides information on the past behavior of the geomagnetic field and the past location of tectonic plates. The record of geomagnetic reversals preserved in volcanic and sedimentary rock sequences (magnetostratigraphy) provides a time-scale that is used as a geochronologic tool. Evidence from paleomagnetism led to the revival of the continental drift hypothesis and its transformation into the modern theory of plate tectonics. Apparent polar wander paths provided the first clear geophysical evidence for continental drift, while marine magnetic anomaly, magnetic anomalies did the same for seafloor spreading. Paleomagnetic data continues t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uranium–lead Dating
Uranium–lead dating, abbreviated U–Pb dating, is one of the oldest and most refined of the radiometric dating schemes. It can be used to date rocks that formed and crystallised from about 1 million years to over 4.5 billion years ago with routine precisions in the 0.1–1 percent range. The method is usually applied to zircon. This mineral incorporates uranium and thorium atoms into its crystal structure, but strongly rejects lead when forming. As a result, newly-formed zircon deposits will contain no lead, meaning that any lead found in the mineral is radiogenic. Since the exact rate at which uranium decays into lead is known, the current ratio of lead to uranium in a sample of the mineral can be used to reliably determine its age. The method relies on two separate decay chains, the uranium series from 238U to 206Pb, with a half-life of 4.47 billion years and the actinium series from 235U to 207Pb, with a half-life of 710 million years. Decay routes Uranium decays to lead via ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argon–argon Dating
Argon–argon (or 40Ar/39Ar) dating is a radiometric dating method invented to supersede potassiumargon (K/Ar) dating in accuracy. The older method required splitting samples into two for separate potassium and argon measurements, while the newer method requires only one rock fragment or mineral grain and uses a single measurement of argon isotopes. 40Ar/39Ar dating relies on neutron irradiation from a nuclear reactor to convert a stable form of potassium (39K) into the radioactive 39Ar. As long as a standard of known age is co-irradiated with unknown samples, it is possible to use a single measurement of argon isotopes to calculate the 40K/40Ar* ratio, and thus to calculate the age of the unknown sample. 40Ar* refers to the radiogenic 40Ar, i.e. the 40Ar produced from radioactive decay of 40K. 40Ar* does not include atmospheric argon adsorbed to the surface or inherited through diffusion and its calculated value is derived from measuring the 36Ar (which is assumed to be of atmosphe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Ionization Mass Spectrometry
Thermal ionization mass spectrometry (TIMS) is also known as surface ionization and is a highly sensitive isotope mass spectrometry characterization technique. The isotopic ratios of radionuclides are used to get an accurate measurement for the elemental analysis of a sample. Singly charged ions of the sample are formed by the thermal ionization effect. A chemically purified liquid sample is placed on a metal filament which is then heated to evaporate the solvent. The removal of an electron from the purified sample is consequently achieved by heating the filament enough to release an electron, which then ionizes the atoms of the sample. TIMS utilizes a magnetic sector mass analyzer to separate the ions based on their mass to charge ratio. The ions gain velocity by an electrical potential gradient and are focused into a beam by electrostatic lenses. The ion beam then passes through the magnetic field of the electromagnet where it is partitioned into separate ion beams based on the io ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Earth
The history of Earth concerns the development of planet Earth from its formation to the present day. Nearly all branches of natural science have contributed to understanding of the main events of Earth's past, characterized by constant geological change and biological evolution. The geological time scale (GTS), as defined by international convention, depicts the large spans of time from the beginning of the Earth to the present, and its divisions chronicle some definitive events of Earth history. (In the graphic, Ma means "million years ago".) Earth formed around 4.54 billion years ago, approximately one-third the age of the universe, by accretion from the solar nebula. Volcanic outgassing probably created the primordial atmosphere and then the ocean, but the early atmosphere contained almost no oxygen. Much of the Earth was molten because of frequent collisions with other bodies which led to extreme volcanism. While the Earth was in its earliest stage (Early Earth), a gia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geobiology
Geobiology is a field of scientific research that explores the interactions between the physical Earth and the biosphere. It is a relatively young field, and its borders are fluid. There is considerable overlap with the fields of ecology, evolutionary biology, microbiology, paleontology, and particularly soil science and biogeochemistry. Geobiology applies the principles and methods of biology, geology, and soil science to the study of the ancient history of the co-evolution of life and Earth as well as the role of life in the modern world. Geobiologic studies tend to be focused on microorganisms, and on the role that life plays in altering the chemical and physical environment of the pedosphere, which exists at the intersection of the lithosphere, Celestial body atmosphere, atmosphere, hydrosphere and/or cryosphere. It differs from biogeochemistry in that the focus is on processes and organisms over space and time rather than on global chemical cycles. Geobiological research synth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gordon Getty
Gordon Peter Getty (born December 20, 1933) is an American businessman and classical music composer, the fourth child of oil tycoon J. Paul Getty. His mother, Ann Rork, was his father's fourth wife. When his father died in 1976, Gordon assumed control of Getty's US$2 billion trust. His net worth was $2.1 billion in September 2020, making him number 391 on the Forbes 400 list of the wealthiest Americans. Early life Getty was raised in San Francisco, California, where he attended St. Ignatius College Preparatory and the University of San Francisco. He would also earn a B.A. in music from the San Francisco Conservatory of Music. Career He joined the oil business to please his father; however, he eventually sold the family's Getty Oil to Texaco in 1986 for US$10 billion. In 1983, ''Forbes'' magazine ranked him the richest person in America with a net worth of a little over $2 billion. His net worth was cited as $2.1 billion in 2020, making him the 391st richest per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |