|
Berdzor
Lachin ( az, Laçın, , ; hy, Բերձոր, translit=Berdzor; ku, Laçîn) is a town in Azerbaijan and the administrative center of the Lachin District. It is located within the strategic Lachin corridor, which links the disputed region of Nagorno-Karabakh with Armenia. The town was occupied by Armenian forces in 1992, during the First Nagorno-Karabakh War, and its local Azerbaijani and Kurdish population was expelled, while Armenians settled in. The town came under the ''de facto'' control of the breakaway Republic of Artsakh, administrated as part of its Kashatagh Province. It came under the supervision of the Russian peacekeeping force following the ceasefire agreement that ended the 2020 Nagorno-Karabakh war. Lachin and the villages of Sus and Zabukh returned under Azerbaijan's control on 26 August 2022. History Early history Cuneiform inscriptions dating back to the Urartian period have been found in the caves surrounding the town. The area was first mentioned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kashatagh Province
Kashatagh Province ( hy, Քաշաթաղի շրջան) was a province of the Republic of Artsakh. It was the largest province by area (3,376.60 km2). The population as of 2013 was 9,656. Its capital was Berdzor. Territorial entities Kashatagh Region had 54 communities of which 3 were considered urban and 51 were rural. Geography Kashtagh bordered the Shahumyan Province in the north, Martakert Province in the north-east, Askeran Province, Shushi Province and Hadrut Province in the east. Iran in the south and Armenia to the west. History The territory of the Kashatagh Province was part of the Syunik Province of the Kingdom of Armenia. It was one of the many Caucasian areas administrated by a local melikdom known as the Melikdom of Kashatagh under the Persian Empire ( Safavid, Afsharid, Zand and Qajar Iran). It was later included in the Nakhichevan Khanate. The territory remained predominantly Armenian up until the Russo-Persian wars and the South Caucasus invasion of the Ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zabukh
Zabukh ( az, Zabux) is a village in the Lachin District of Azerbaijan. The village came under the control of the breakaway Republic of Artsakh after 1992 and was renamed Aghavno ( hy, Աղավնո) and settled by Armenians. Following the 2020 Nagorno-Karabakh war, Zabukh came under the control of the Russian peacekeeping forces in Nagorno-Karabakh. On 26 August 2022, Azerbaijan regained control of Zabukh along with other settlements located along the former route of the Lachin corridor, including Lachin and Sus. Toponymy Zabukh (also rendered Zabuk in Armenian) is also the name of a tributary of the Hakari River that runs by the village. After coming under Armenian control in 1992, the village was renamed Aghavno, which is one of the Armenian names of the Hakari River. The village is also known as ''Ariavan'' ( hy, Արիավան). History Several Armenian authors identify Zabukh with the village of Shabaki or Shapoki mentioned by the medieval Armenian historian Stephen Or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peacekeeping Operations In Nagorno-Karabakh
Peacekeeping mission in Nagorno-Karabakh refers to the ongoing Peacekeeping, peacekeeping operations by Russia in the Nagorno-Karabakh, Nagorno-Karabakh region, in the aftermath of the 2020 Nagorno-Karabakh war. The operation is intended to monitor the ceasefire between the Armenian and Azerbaijani forces. Separate from the Russian operation, Turkey also has personnel working in a joint Russian–Turkish monitoring centre. After the war, in accordance to the 2020 Nagorno-Karabakh ceasefire agreement, ceasefire agreement signed on 10 November 2020, Russia sent a peacekeeping contingent of 1,960 servicemen, provided by the 15th Separate Motor Rifle Brigade of the Russian Ground Forces, and led by Lieutenant General Rustam Muradov, to the region. The peacekeeping forces, headquartered near Stepanakert, established observation posts along the contact line in Nagorno-Karabakh and along the Lachin corridor. The Russian peacekeeping forces started to assist the International Committee o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sus, Lachin
Sus ( arm, Սուս; az, Sus) is a village within the strategic Lachin corridor, which links the disputed region of Nagorno-Karabakh with Armenia. It was formerly under the supervision of the Russian peacekeeping force following the ceasefire agreement that ended the 2020 Nagorno-Karabakh war. The village came under the ''de facto'' control of the breakaway Republic of Artsakh from 1992–2022, administrated as part of its Kashatagh Province, and is ''de jure'' part of the Lachin District of Azerbaijan. As of 26 August 2022, Azerbaijan regained control of villages in the Lachin corridor, including Lachin, Sus, and Zabukh. Geography Sus sits on the Hakari (Aghavno) river, opposite of Ashaghy Sus (Nerkin Sus). It is 1.8 km (1.1 mi) from Ashaghy Sus (Nerkin Sus), 3.1 km (1.9 mi) from Lachin (Berdzor), 4.8 km (3.0 mi) from Zabukh (Aghavno), 8.4 km (5.2 mi) from Tegh, Armenia, 19.6 km (12.2 mi) from Goris, Armenia, and 30.9 km (19.2 mi) from Stepanakert (Khankendi). At its close ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republic Of Artsakh
Artsakh, officially the Republic of Artsakh () or the Nagorno-Karabakh Republic (),, is a list of states with limited recognition, breakaway state in the South Caucasus whose territory is internationally recognised as part of Azerbaijan. Artsakh controls a part of the former Nagorno-Karabakh Autonomous Oblast, including the capital of Stepanakert. It is an Enclave and exclave, enclave within Azerbaijan. Its only overland access route to Armenia is via the wide Lachin corridor which is under the control of Russian peacekeepers. The predominantly Armenian-populated region of Nagorno-Karabakh was claimed by both the Azerbaijan Democratic Republic and the First Republic of Armenia when both countries became independent in 1918 after the fall of the Russian Empire, and a brief war over the region broke out in 1920. The dispute was largely shelved after the Soviet Union established control over the area, and created the Nagorno-Karabakh Autonomous Oblast (NKAO) within the Aze ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2020 Nagorno-Karabakh War
The Second Nagorno-Karabakh War was an armed conflict in 2020 that took place in the disputed region of Nagorno-Karabakh and Armenian-occupied territories surrounding Nagorno-Karabakh, the surrounding territories. It was a major escalation of an unresolved Nagorno-Karabakh conflict, conflict over the region, involving Azerbaijan, Armenia and the Political status of Nagorno-Karabakh, self-declared Armenian breakaway state of Republic of Artsakh, Artsakh. The war lasted for more than a month and resulted in Azerbaijani victory, with Armenia ceding the Armenian-occupied territories surrounding Nagorno-Karabakh, territories it had occupied in 1994 surrounding Nagorno-Karabakh. The defeat ignited 2020–2021 Armenian protests, anti-government protests in Armenia. Post-war skirmishes continued in the region, including September 2022 Armenia–Azerbaijan clashes, substantial clashes in 2022. Fighting began on the morning of 27 September, with an Azerbaijani offensive along the Nagorn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethnography
Ethnography (from Greek ''ethnos'' "folk, people, nation" and ''grapho'' "I write") is a branch of anthropology and the systematic study of individual cultures. Ethnography explores cultural phenomena from the point of view of the subject of the study. Ethnography is also a type of social research that involves examining the behavior of the participants in a given social situation and understanding the group members' own interpretation of such behavior. Ethnography in simple terms is a type of qualitative research where a person puts themselves in a specific community or organization in attempt to learn about their cultures from a first person point-of-view. As a form of inquiry, ethnography relies heavily on participant observation—on the researcher participating in the setting or with the people being studied, at least in some marginal role, and seeking to document, in detail, patterns of social interaction and the perspectives of participants, and to understand these i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymath
A polymath ( el, πολυμαθής, , "having learned much"; la, homo universalis, "universal human") is an individual whose knowledge spans a substantial number of subjects, known to draw on complex bodies of knowledge to solve specific problems. In Western Europe, the first work to use the term polymathy in its title () was published in 1603 by Johann von Wowern, a Hamburg philosopher. Von Wowern defined polymathy as "knowledge of various matters, drawn from all kinds of studies ... ranging freely through all the fields of the disciplines, as far as the human mind, with unwearied industry, is able to pursue them". Von Wowern lists erudition, literature, philology, philomathy, and polyhistory as synonyms. The earliest recorded use of the term in the English language is from 1624, in the second edition of ''The Anatomy of Melancholy'' by Robert Burton; the form ''polymathist'' is slightly older, first appearing in the ''Diatribae upon the first part of the late History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armenian Apostolic Church
, native_name_lang = hy , icon = Armenian Apostolic Church logo.svg , icon_width = 100px , icon_alt = , image = Էջմիածնի_Մայր_Տաճար.jpg , imagewidth = 250px , alt = , caption = Etchmiadzin Cathedral, the mother church of the Armenian Apostolic Church , abbreviation = , type = , main_classification = Eastern Christian , orientation = Oriental Orthodox , scripture = Septuagint, New Testament, Armenian versions , theology = Miaphysitism , polity = Episcopal , governance = Mother See of Holy Etchmiadzin , structure = , leader_title = Head , leader_name = Catholicos of All Armenians Karekin II , leader_title1 = , leader_name1 = , leader_title2 = , leader_name2 = , leader_title3 = , leader_name3 = , associations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Movses Kaghankatvatsi
Movses Kaghankatvatsi ( hy, Մովսէս Կաղանկատուացի ''Movses Kaġankatvac’i''), or Movses Daskhurantsi ( ''Movses Dasxuranc’i'') is the reputed author (or authors) of a tenth-century Classical Armenian historiographical work on Caucasian Albania and eastern provinces of Armenia, known as ''The History of the Country of Albania'' (, ). Authorship The first historian to mention Movses' work was medieval Armenian legal scholar Mkhitar Gosh, referring to him as "Movses Daskhurantsi." A later historian, Kirakos Gandzaketsi, author of the ''History of Armenia'', referred to a statement in the ''History'' itself, to attribute the name of the author as ''Movses Kaghankatvatsi''. The statement in question (Book II, ch. 11) says: Movses narrates the Khazar invasion of Transcaucasia and other events up to the seventh century in Book I and II of ''History''. Book III of his ''History'' differs from the previous ones in style of writing and date. It deals with the Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
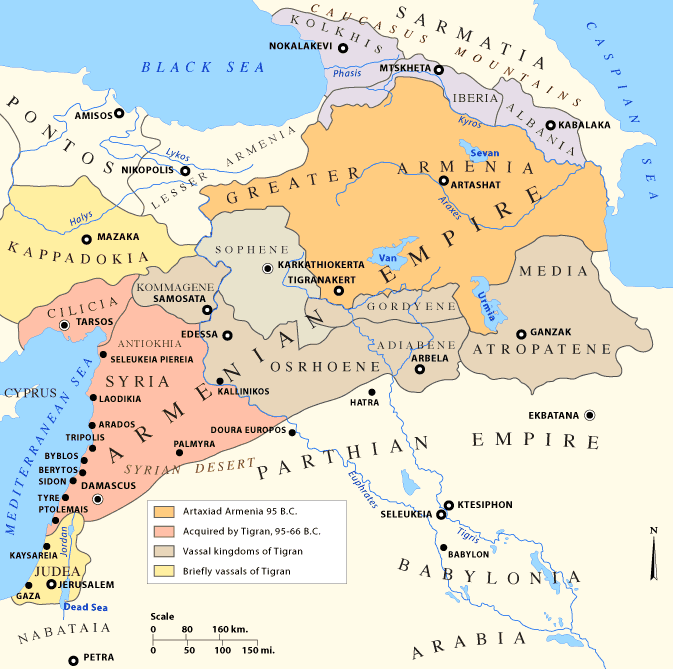
Greater Armenia
Greater Armenia ( hy, Մեծ Հայք, translit=Mets Hayk) is the name given to the Armenian state that emerged on the Armenian Highlands during the reign of King Artaxias I at the turn of the 2nd century BC. The term was used to refer principally to the fifteen provinces that made up Armenian kingdoms throughout the classical, late antique, and medieval periods by contemporary Armenian and non-Armenian authors alike. Extent Though its borders were never exactly defined, Greater Armenia usually referred to the stretch of land beginning from the Euphrates River to the west, the region of Artsakh and parts of what are now Azerbaijan and Iranian Azerbaijan to the east, parts of the modern state of Georgia to the north, with its southern boundary rounding the northern tip of Mesopotamia. The Romans referred to it in Latin as ''Armenia Maior'' while the Greek-speaking peoples called it ''Armenia Megale'' (), to differentiate it from Lesser Armenia (''Pok'r Hayk′'', in Latin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)