|
Beowa
Beowa, Beaw, Bēow , Beo or Bedwig is a figure in Anglo-Saxon paganism associated with barley and agriculture. The figure is attested in the Anglo-Saxon royal genealogies as they were extended in the age of Alfred, where Beowa is inserted as the son of Scyld and the grandson of Sceafa, in lineages carried back to Adam. Connections have been proposed between the figure of Beowa and the hero Beowulf of the poem of the same name and English folk song figure John Barleycorn. Etymology ''Beoƿ'' is an Old English word for barley. In the Anglo-Saxon genealogies, Beoƿa is the son or grandson of Sceafa, the Old English word for sheaf. The noun ''beoƿ'' has an Old Norse parallel in ''Bygg'', the word for "grain." Related comparisons have been made between the figure of Beoƿ and Byggvir, attested in the ''Prose Edda'' as a servant of the god Freyr.Alexander (2002:28). Theories Some scholars posit a connection between the mythical figure of Beowa and the legendary Beowulf. As the two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Barleycorn
"John Barleycorn" is an English and Scottish folk song listed as number 164 in the Roud Folk Song Index. John Barleycorn, the song's protagonist, is a personification of barley and of the alcoholic beverages made from it: beer and whisky. In the song, he suffers indignities, attacks, and death that correspond to the various stages of barley cultivation, such as reaping and malting. The song may have its origins in ancient English or Scottish folklore, with written evidence of the song dating it at least as far back as the Elizabethan era. The oldest versions are Scottish and include the Scots poem " Quhy Sowld Nocht Allane Honorit Be". In 1782, the Scottish poet Robert Burns published his own version of the song, which influenced subsequent versions. The song survived into the twentieth century in the oral folk tradition, primarily in England, and many popular folk revival artists have recorded versions of the song. In most traditional versions, including the sixteent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Saxon Royal Genealogies
A number of royal genealogies of the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, collectively referred to as the Anglo-Saxon royal genealogies, have been preserved in a manuscript tradition based in the 8th to 10th centuries. The genealogies trace the succession of the early Anglo-Saxon kings, back to the semi-legendary kings of the Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, notably named as Hengest and Horsa in Bede's '' Historia ecclesiastica gentis Anglorum'', and further to legendary kings and heroes of the pre-migration period, usually including an eponymous ancestor of the respective lineage and converging on Woden. In their fully elaborated forms as preserved in the '' Anglo-Saxon Chronicles'' and the ''Textus Roffensis'', they continue the pedigrees back to the biblical patriarchs Noah and Adam. They also served as the basis for pedigrees that would be developed in 13th century Iceland for the Scandinavian royalty. Documentary tradition The Anglo-Saxons, uniquely among the early Germanic peoples, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beowulf (hero)
Beowulf (; ang, Bēowulf ) is a legendary Geatish hero in the eponymous epic poem, one of the oldest surviving pieces of English literature. Etymology and origins of the character A number of origins have been proposed for the name ''Beowulf''. Beowulf Henry Sweet, a philologist and linguist specializing in Germanic languages, proposed that the name ''Bēowulf'' literally means in Old English "bee-wolf" or "bee-hunter" and that it is a kenning for "bear".Sweet, Henry. (1884) ''Anglo-Saxon Reader in Prose and Verse'' The Clarendon Press, p. 202. Recorded instances of similar names mirror this etymology. The AD 1031 ''Liber Vitae'' records the name ''Biuuuwulf''. The name is attested to a monk from Durham and means ''bee wolf'' in the Old Northumbrian dialect.Chadwick, Hector Munro (1983) ''The Origin of the English Nation'', p. 294. The 11th century English ''Domesday Book'' contains a recorded instance of the name ''Beulf''. The scholar suggested that the name ''Beowulf'' de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byggvir
Byggvir is a figure in Norse mythology. The only surviving mention of Byggvir appears in the prose beginning of ''Lokasenna'', and stanzas 55 through 56 of the same poem, where he is referred to as one of Freyr's servants and as the husband of Beyla. ''Bygg'' is the Old Norse word for barley. Subsequently, Byggvir is often identified with this etymology of his name and connections have been placed with the mentioning of Byggvir's described involvement with mill-grinding as being potential references to barley processing.Lindow (2001:90-91) Comparisons to the Anglo-Saxon figure of Beowa (Old English "barley") have been put forth.Bruce (2002:28). ''Lokasenna'' In ''Lokasenna'', Loki is depicted as degrading Byggvir for being of slight stature and as a gossiper: Stanza 43: Stanza 44: Stanza 45: Stanza 46: Interpretation In relation to Loki's comments in ''Lokasenna'', proposals have been made that Beyla and her husband are personifications of agriculture associated with Fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Norse
Old Norse, Old Nordic, or Old Scandinavian, is a stage of development of North Germanic languages, North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and their Viking expansion, overseas settlements and chronologically coincides with the Viking Age, the Christianization of Scandinavia and the consolidation of Scandinavian kingdoms from about the 7th to the 15th centuries. The Proto-Norse language developed into Old Norse by the 8th century, and Old Norse began to develop into the modern North Germanic languages in the mid-to-late 14th century, ending the language phase known as Old Norse. These dates, however, are not absolute, since written Old Norse is found well into the 15th century. Old Norse was divided into three dialects: Old West Norse, ''Old West Norse'' or ''Old West Nordic'' (often referred to as ''Old Norse''), Old East Norse, ''Old East Norse'' or ''Old East Nordic'', and ''Ol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Routledge
Routledge () is a British multinational publisher. It was founded in 1836 by George Routledge, and specialises in providing academic books, journals and online resources in the fields of the humanities, behavioural science, education, law, and social science. The company publishes approximately 1,800 journals and 5,000 new books each year and their backlist encompasses over 70,000 titles. Routledge is claimed to be the largest global academic publisher within humanities and social sciences. In 1998, Routledge became a subdivision and imprint of its former rival, Taylor & Francis Group (T&F), as a result of a £90-million acquisition deal from Cinven, a venture capital group which had purchased it two years previously for £25 million. Following the merger of Informa and T&F in 2004, Routledge became a publishing unit and major imprint within the Informa "academic publishing" division. Routledge is headquartered in the main T&F office in Milton Park, Abingdon, Oxfordshire and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
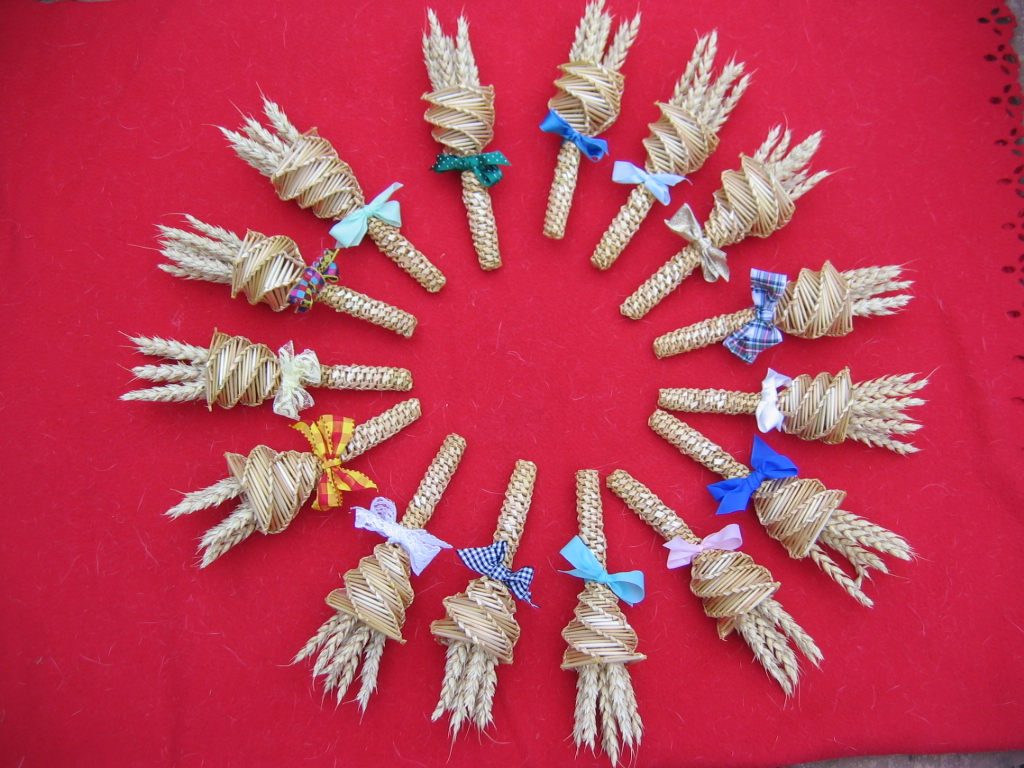
Corn Dolly
Corn dollies or corn mothers are a form of straw work made as part of harvest customs of Europe before mechanization. Before Christianisation, in traditional pagan European culture it was believed that the spirit of the corn (in American English, "corn" would be "grain") lived amongst the crop, and that the harvest made it effectively homeless. James Frazer devotes chapters in ''The Golden Bough'' to "Corn-Mother and Corn-Maiden in Northern Europe" (chs. 45–48) and adduces European folkloric examples collected in great abundance by the folklorist Wilhelm Mannhardt. Among the customs attached to the last sheaf of the harvest were hollow shapes fashioned from the last sheaf of wheat or other cereal crops. The corn spirit would then spend the winter in this home until the "corn dolly" was ploughed into the first furrow of the new season. Background James George Frazer discusses the Corn-mother and the Corn-maiden in Northern Europe, and the harvest rituals that were being practised ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beyla
Beyla (Old Norse: ) is one of Freyr's servants along with her husband, Byggvir, in Norse mythology. Beyla is mentioned in stanzas 55, 66, and the prose introduction to the Poetic Edda poem ''Lokasenna''. Since this is the only mention of Beyla, scholars have turned to the etymology of Beyla's name for additional information about her. However, the meaning of her name is unclear and her name has been proposed as related to "cow," "bean," or "bee." ''Lokasenna'' In the prose introduction to ''Lokasenna'', Beyla and Byggvir are cited as attending In stanza 55 of ''Lokasenna'', after his verses with Sif, Loki accuses Beyla of being filthy but the reason for this is unclear.Lindow (2001:78). Stanza 55: Stanza 56: In relation to Loki's comments in ''Lokasenna'', proposals have been made that Beyla and her husband are personifications of agriculture associated with Freyr: Beyla as the manure that softens the earth and develops the seed, Byggvir as the refuse of the mill, chaff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kathleen Herbert
Kathleen may refer to: People * Kathleen (given name) * Kathleen (singer), Canadian pop singer Places * Kathleen, Alberta, Canada * Kathleen, Georgia, United States * Kathleen, Florida, United States * Kathleen High School (Lakeland, Florida), United States * Kathleen, Western Australia, Western Australia * Kathleen Island, Tasmania, Australia * Kathleen Lumley College, South Australia * Mary Kathleen, Queensland, former mining settlement in Australia Other * ''Kathleen'' (film), a 1941 American film directed by Harold S. Bucquet * ''The Countess Kathleen and Various Legends and Lyrics'' (1892), second poetry collection of William Butler Yeats * Kathleen Ferrier Award, competition for opera singers * Kathleen Mitchell Award, Australian literature prize for young authors * Plan Kathleen, plan for a German invasion of Northern Ireland sanctioned by the IRA Chief of Staff in 1940 * Tropical Storm Kathleen (other) * "Kathleen" (song), a song by Catfish and the Bottl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freyr
Freyr (Old Norse: 'Lord'), sometimes anglicized as Frey, is a widely attested god in Norse mythology, associated with kingship, fertility, peace, and weather. Freyr, sometimes referred to as Yngvi-Freyr, was especially associated with Sweden and seen as an ancestor of the Swedish royal house. According to Adam of Bremen, Freyr was associated with peace and pleasure, and was represented with a phallic statue in the Temple at Uppsala. According to Snorri Sturluson, Freyr was "the most renowned of the æsir", and was venerated for good harvest and peace. In the mythological stories in the Icelandic books the ''Poetic Edda'' and the ''Prose Edda'', Freyr is presented as one of the Vanir, the son of the god Njörðr and his sister-wife, as well as the twin brother of the goddess Freyja. The gods gave him Álfheimr, the realm of the Elves, as a teething present. He rides the shining dwarf-made boar Gullinbursti and possesses the ship Skíðblaðnir which always has a favorable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)