|
Benzotriyne
Benzotriyne or cyclo arbon is a hypothetical compound, an allotrope of carbon with molecular formula . The molecule is a ring of six carbon atoms, connected by alternating triple and single bonds. It is, therefore, a potential member of the cyclo 'n''arbon family. There have been a few attempts to synthesize benzotriyne, e.g. by pyrolysis of mellitic anhydride, but without success . Recent investigations have concluded that benzotriyne is unlikely to exist due to the large angle strain. A likely alternative isomer would be a cyclic cumulene called cyclohexahexaene, which should itself be a metastable species. The name ''cracatene'' was suggested for this compound (after Karel Čapek's Krakatit ''Krakatit'' is a 1948 Czechoslovak science fiction mystery film directed by Otakar Vávra, starring Karel Höger as a chemist who suffers from delirium and regret after inventing a powerful explosive. The film is based on Karel Čapek's novel wit ..., a hypothetical explosive). Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclocarbons
In organic chemistry, a cyclo 'n''arbon (or simply cyclocarbon) is a chemical compound consisting solely of a number ''n'' of carbon atoms covalently linked in a ring. Since the compounds are composed only of carbon atoms, they are allotropes of carbon. Possible bonding patterns include all double bonds (a cyclic cumulene) or alternating single bonds and triple bonds (a cyclic polyyne). As of 2020, the only cyclocarbon that has been synthesized is cyclo 8arbon. Cyclo arbon The (hypothetical) three-carbon member of this family () is also called cyclopropatriene. Cyclo arbon The (hypothetical) six-carbon member of this family () is also called benzotriyne. Cyclo 8arbon The smallest cyclo 'n''arbon predicted to be thermodynamically stable is C18, with a computed strain energy of 72 kilocalories per mole. An IBM/Oxford team claimed to synthesize its molecules in solid state in 2019: According to these IBM researchers, the synthesized cyclocarbon has alternating triple a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclocarbon
In organic chemistry, a cyclo 'n''arbon (or simply cyclocarbon) is a chemical compound consisting solely of a number ''n'' of carbon atoms covalently linked in a ring. Since the compounds are composed only of carbon atoms, they are allotropes of carbon. Possible bonding patterns include all double bonds (a cyclic cumulene) or alternating single bonds and triple bonds (a cyclic polyyne). As of 2020, the only cyclocarbon that has been synthesized is cyclo 8arbon. Cyclo arbon The (hypothetical) three-carbon member of this family () is also called cyclopropatriene. Cyclo arbon The (hypothetical) six-carbon member of this family () is also called benzotriyne. Cyclo 8arbon The smallest cyclo 'n''arbon predicted to be thermodynamically stable is C18, with a computed strain energy of 72 kilocalories per mole. An IBM/Oxford team claimed to synthesize its molecules in solid state in 2019: According to these IBM researchers, the synthesized cyclocarbon has alternating triple a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypothetical Compound
A hypothetical chemical compound is a chemical compound that has been conceived of, but is not known to have been synthesized, observed, or isolated (identified or shown to exist). Some hypothetical compounds cannot form at all. Others might turn out to be highly unstable, decomposing, isomerizing, polymerizing, rearranging, or disproportionating. Some are thought to exist only briefly as reactive intermediates, or in vacuum (e.g. helium hydride ion). Some cannot hold together due to steric hindrance (e.g. tetra-''tert''-butylmethane) or bond stress (e.g. tetrahedrane). Some have no known pathway for synthesis (e.g. hypercubane). Some compounds of radioactive elements have never been synthesized due to their radioactive decay and short half-lives (e.g. francium hydroxide) Some "parent compounds" have not been or cannot be isolated, even though stable structural analogs with substituents have been discovered or synthesized (e.g. borole). Hypothetical compounds are oft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isomer
In chemistry, isomers are molecules or polyatomic ions with identical molecular formulae – that is, same number of atoms of each element – but distinct arrangements of atoms in space. Isomerism is existence or possibility of isomers. Isomers do not necessarily share similar chemical or physical properties. Two main forms of isomerism are structural or constitutional isomerism, in which ''bonds'' between the atoms differ; and stereoisomerism or spatial isomerism, in which the bonds are the same but the ''relative positions'' of the atoms differ. Isomeric relationships form a hierarchy. Two chemicals might be the same constitutional isomer, but upon deeper analysis be stereoisomers of each other. Two molecules that are the same stereoisomer as each other might be in different conformational forms or be different isotopologues. The depth of analysis depends on the field of study or the chemical and physical properties of interest. The English word "isomer" () is a back-for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypothetical Chemical Compounds
A hypothesis (plural hypotheses) is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon. For a hypothesis to be a scientific hypothesis, the scientific method requires that one can test it. Scientists generally base scientific hypotheses on previous observations that cannot satisfactorily be explained with the available scientific theories. Even though the words "hypothesis" and "theory" are often used interchangeably, a scientific hypothesis is not the same as a scientific theory. A working hypothesis is a provisionally accepted hypothesis proposed for further research in a process beginning with an educated guess or thought. A different meaning of the term ''hypothesis'' is used in formal logic, to denote the antecedent of a proposition; thus in the proposition "If ''P'', then ''Q''", ''P'' denotes the hypothesis (or antecedent); ''Q'' can be called a consequent. ''P'' is the assumption in a (possibly counterfactual) ''What If'' question. The adjective ''hypothetical'', meaning "havin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krakatit
''Krakatit'' is a 1948 Czechoslovak science fiction mystery film directed by Otakar Vávra, starring Karel Höger as a chemist who suffers from delirium and regret after inventing a powerful explosive. The film is based on Karel Čapek's novel with the same title, written in 1922. The name is derived from the volcano Krakatoa. Plot A barely conscious, unidentified man is given intensive care by a doctor and a nurse. The man's hands are badly burned and cut. The doctor tells the nurse to give the man oxygen. A sequence begins where the man walks along a street in delirium. An old classmate, Jiří Tomeš, greets him and we learn that the man's name is Prokop. He speaks incoherently about an explosion and something he calls krakatit. Jiří brings him home and puts him in bed. In a dream, a university professor asks Prokop about krakatit. He answers that it is a powerful explosive, named after the volcano Krakatoa, and explains its formula. As the dream ends we see that Jiří has w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karel Čapek
Karel Čapek (; 9 January 1890 – 25 December 1938) was a Czech writer, playwright and critic. He has become best known for his science fiction, including his novel ''War with the Newts'' (1936) and play ''R.U.R.'' (''Rossum's Universal Robots'', 1920), which introduced the word ''robot''.Oxford English Dictionary: robot n2 He also wrote many politically charged works dealing with the social turmoil of his time. Influenced by American pragmatic liberalism, he campaigned in favor of free expression and strongly opposed the rise of both fascism and communism in Europe. Though nominated for the Nobel Prize in Literature seven times, Čapek never received it. However, several awards commemorate his name, such as the Karel Čapek Prize, awarded every other year by the Czech PEN Club for literary work that contributes to reinforcing or maintaining democratic and humanist values in society. He also played a key role in establishing the Czechoslovak PEN Club as a part of Internatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
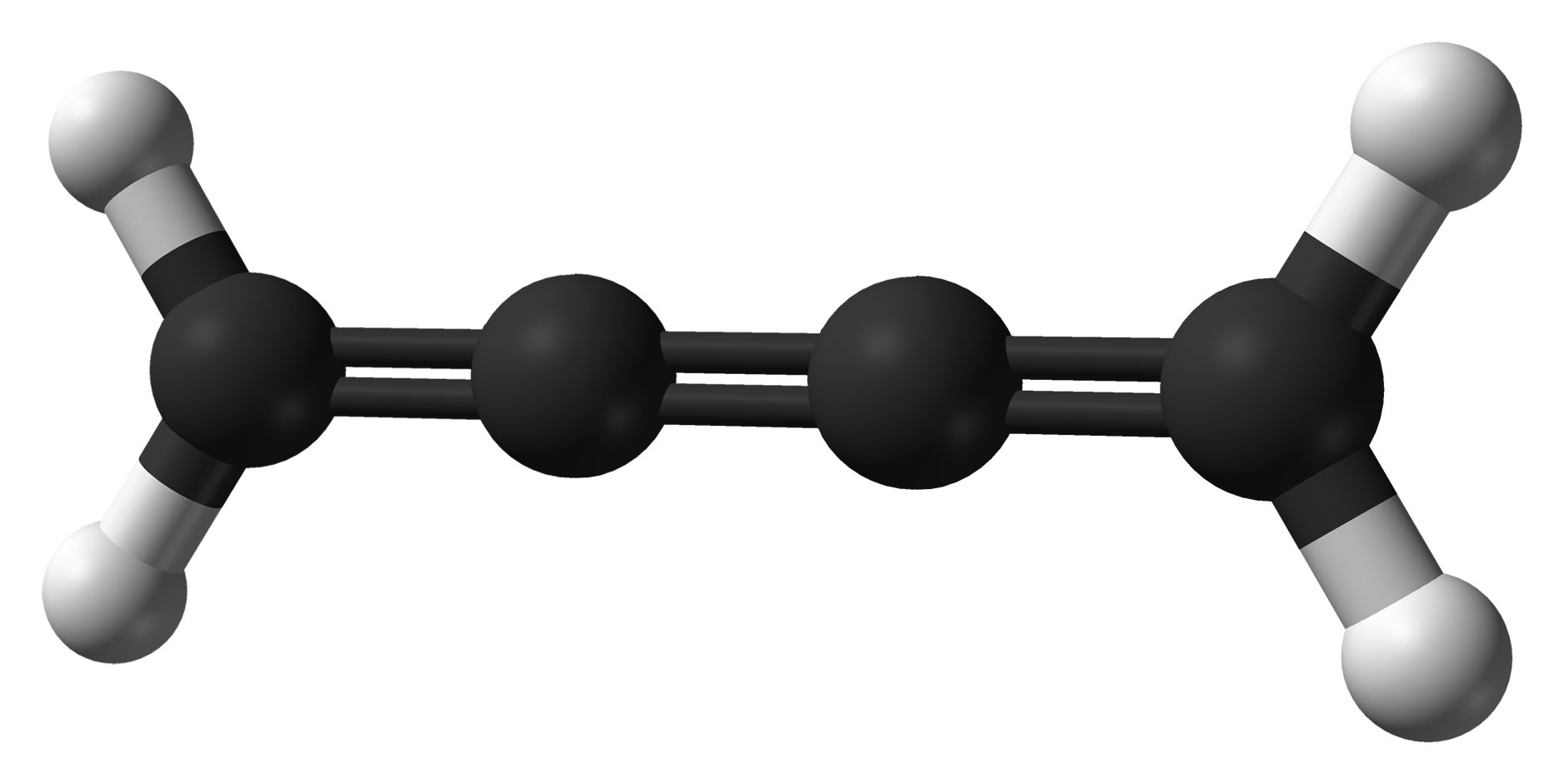
Cumulene
In organic chemistry, a cumulene is a compound having three or more ''cumulative'' (consecutive) double bonds. They are analogous to allenes, only having a more extensive chain. The simplest molecule in this class is butatriene (), which is also called simply ''cumulene''. Unlike most alkanes and alkenes, cumulenes tend to be rigid, comparable to polyynes. Cumulene carbenes for ''n'' from 3 to 6 have been observed in interstellar molecular clouds and in laboratory experiments by using microwave and infrared spectroscopy. (The more stable cumulenes are difficult to detect optically because they lack an electric dipole moment.) Cumulenes containing heteroatoms are called heterocumulenes; an example is carbon suboxide. Synthesis The first reported synthesis of a butatriene is that of tetraphenylbutatriene in 1921. The most common synthetic method for butatriene synthesis is based on reductive coupling of a geminal dihalovinylidene. Tetraphenylbutatriene was reported synthesized ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclic Molecule
A cyclic compound (or ring compound) is a term for a chemical compound, compound in the field of chemistry in which one or more series of atoms in the compound is connected to form a Ring (chemistry), ring. Rings may vary in size from three to many atoms, and include examples where all the atoms are carbon (i.e., are carbocycles), none of the atoms are carbon (inorganic cyclic compounds), or where both carbon and non-carbon atoms are present (heterocyclic compounds). Depending on the ring size, the bond order of the individual links between ring atoms, and their arrangements within the rings, carbocyclic and heterocyclic compounds may be aromatic compound, aromatic or non-aromatic; in the latter case, they may vary from being fully saturated compound, saturated to having varying numbers of multiple bonds between the ring atoms. Because of the tremendous diversity allowed, in combination, by the Valence (chemistry), valences of common atoms and their ability to form rings, the number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mellitic Anhydride
Mellitic anhydride, the anhydride of mellitic acid, is an organic compound with the formula C12O9. Containing no other elements (e.g., hydrogen) besides carbon and oxygen, mellitic anhydride is an oxide of carbon (oxocarbon), and, along with CO2, CO, and C3O2, is one of the only four that are reasonably stable under standard conditions. It is a white sublimable solid, apparently obtained by Justus Liebig and Friedrich Wöhler in 1830 in their study of mellite ("honey stone") and has the empirical formula In chemistry, the empirical formula of a chemical compound is the simplest whole number ratio of atoms present in a compound. A simple example of this concept is that the empirical formula of sulfur monoxide, or SO, would simply be SO, as is th ... C4O3. The substance was properly characterized in 1913 by H. Meyer and K. Steiner. It retains the aromatic character of the benzene ring. References Phthalic anhydrides Oxocarbons {{aromatic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angle Strain
In organic chemistry, ring strain is a type of instability that exists when bonds in a molecule form angles that are abnormal. Strain is most commonly discussed for small rings such as cyclopropanes and cyclobutanes, whose internal angles are substantially smaller than the idealized value of approximately 109°. Because of their high strain, the heat of combustion for these small rings is elevated. Ring strain results from a combination of angle strain, conformational strain or Pitzer strain (torsional eclipsing interactions), and transannular strain, also known as van der Waals strain or Prelog strain. The simplest examples of angle strain are small cycloalkanes such as cyclopropane and cyclobutane. Ring strain energy can be attributed to the energy required for the distortion of bond and bond angles in order to close a ring. Ring strain energy is believed to be the cause of accelerated rates in altering ring reactions. Its interactions with traditional bond energies chan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allotropes Of Carbon
Carbon is capable of forming many allotropy, allotropes (structurally different forms of the same element) due to its Valence (chemistry), valency. Well-known forms of carbon include diamond and graphite. In recent decades, many more allotropes have been discovered and researched, including ball shapes such as buckminsterfullerene and sheets such as graphene. Larger-scale structures of carbon include carbon nano tube, nanotubes, Carbon nanobud, nanobuds and Graphene nanoribbon, nanoribbons. Other unusual forms of carbon exist at very high temperatures or extreme pressures. Around 500 hypothetical 3‑periodic allotropes of carbon are known at the present time, according to the Samara Carbon Allotrope Database (SACADA). Diamond Diamond is a well-known allotrope of carbon. The hardness, extremely high refractive index, and high Dispersion (optics), dispersion of light make diamond useful for industrial applications and for jewelry. Diamond is the hardest known natural min ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |