|
Benz Plane
In mathematics, a Benz plane is a type of 2-dimensional geometrical structure, named after the German mathematician Walter Benz. The term was applied to a group of objects that arise from a common axiomatization of certain structures and split into three families, which were introduced separately: Möbius planes, Laguerre planes, and Minkowski planes. F. Buekenhout (ed.), ''Handbook of Incidence Geometry'', Elsevier (1995) Möbius plane Starting from the real Euclidean plane and merging the set of lines with the set of circles to form a set of blocks results in an inhomogeneous incidence structure: three distinct points determine one block, but lines are distinguishable as a set of blocks that pairwise mutually intersect at one point without being tangent (or no points when parallel). Adding to the point set the new point \infty, defined to lie on every line results in every block being determined by exactly three points, as well as the intersection of any two blocks follow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline. Most mathematical activity involves the discovery of properties of abstract objects and the use of pure reason to prove them. These objects consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicsentities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. A ''proof'' consists of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction from naturesome basic properties that are considered true starting points of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incidence Structure
In mathematics, an incidence structure is an abstract system consisting of two types of objects and a single relationship between these types of objects. Consider the points and lines of the Euclidean plane as the two types of objects and ignore all the properties of this geometry except for the relation of which points are on which lines for all points and lines. What is left is the incidence structure of the Euclidean plane. Incidence structures are most often considered in the geometrical context where they are abstracted from, and hence generalize, planes (such as affine, projective, and Möbius planes), but the concept is very broad and not limited to geometric settings. Even in a geometric setting, incidence structures are not limited to just points and lines; higher-dimensional objects (planes, solids, -spaces, conics, etc.) can be used. The study of finite structures is sometimes called finite geometry. Formal definition and terminology An incidence structure is a triple ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopedia Of Mathematics
The ''Encyclopedia of Mathematics'' (also ''EOM'' and formerly ''Encyclopaedia of Mathematics'') is a large reference work in mathematics. Overview The 2002 version contains more than 8,000 entries covering most areas of mathematics at a graduate level, and the presentation is technical in nature. The encyclopedia is edited by Michiel Hazewinkel and was published by Kluwer Academic Publishers until 2003, when Kluwer became part of Springer. The CD-ROM contains animations and three-dimensional objects. The encyclopedia has been translated from the Soviet ''Matematicheskaya entsiklopediya'' (1977) originally edited by Ivan Matveevich Vinogradov and extended with comments and three supplements adding several thousand articles. Until November 29, 2011, a static version of the encyclopedia could be browsed online free of charge online. This URL now redirects to the new wiki incarnation of the EOM. ''Encyclopedia of Mathematics'' wiki A new dynamic version of the encyclopedia is now ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laguerre Transformations
Edmond Nicolas Laguerre (9 April 1834, Bar-le-Duc – 14 August 1886, Bar-le-Duc) was a French mathematician and a member of the Académie des sciences (1885). His main works were in the areas of geometry and complex analysis. He also investigated orthogonal polynomials (see Laguerre polynomials). Laguerre's method is a root-finding algorithm tailored to polynomials. He laid the foundations of a geometry of oriented spheres (Laguerre geometry and Laguerre plane), including the Laguerre transformation or transformation by reciprocal directions. Works Selection * * * * Théorie des équations numériques', Paris: Gauthier-Villars. 1884 on Google Books * * Oeuvres de Laguerrepubl. sous les auspices de l'Académie des sciences par MM. Charles Hermite, Henri Poincaré, et Eugène Rouché.'' (Paris, 1898-1905) (reprint: New York : Chelsea publ., 1972 ) Extensive lists More than 80 articleson Nundam.org.p See also * Isotropic line * ''q''-Laguerre polynomials * Big ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Projective Plane
In mathematics, a projective plane is a geometric structure that extends the concept of a plane. In the ordinary Euclidean plane, two lines typically intersect in a single point, but there are some pairs of lines (namely, parallel lines) that do not intersect. A projective plane can be thought of as an ordinary plane equipped with additional "points at infinity" where parallel lines intersect. Thus ''any'' two distinct lines in a projective plane intersect at exactly one point. Renaissance artists, in developing the techniques of drawing in perspective, laid the groundwork for this mathematical topic. The archetypical example is the real projective plane, also known as the extended Euclidean plane. This example, in slightly different guises, is important in algebraic geometry, topology and projective geometry where it may be denoted variously by , RP2, or P2(R), among other notations. There are many other projective planes, both infinite, such as the complex projective plane, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
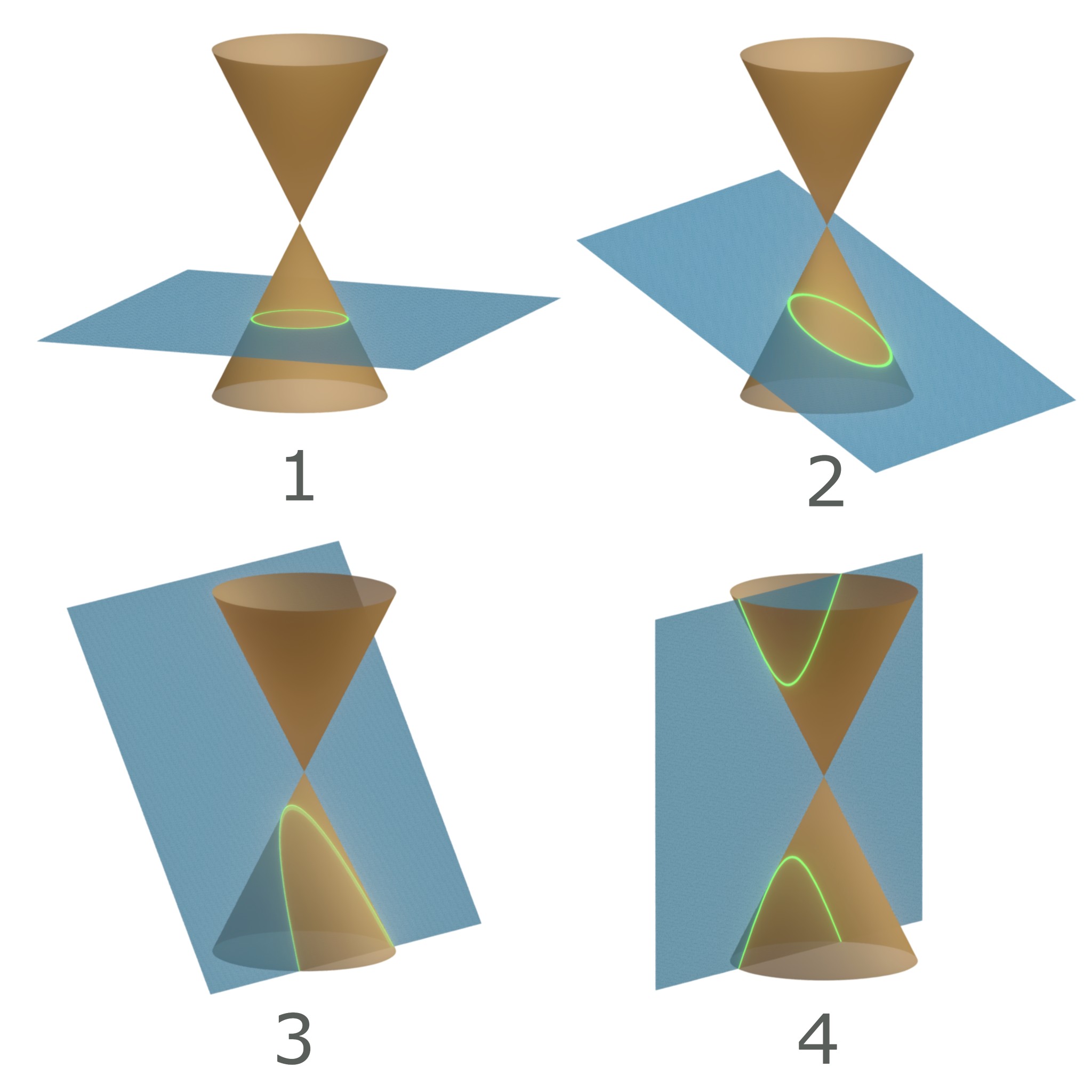
Quadric
In mathematics, a quadric or quadric surface (quadric hypersurface in higher dimensions), is a generalization of conic sections (ellipses, parabolas, and hyperbolas). It is a hypersurface (of dimension ''D'') in a -dimensional space, and it is defined as the zero set of an irreducible polynomial of degree two in ''D'' + 1 variables; for example, in the case of conic sections. When the defining polynomial is not absolutely irreducible, the zero set is generally not considered a quadric, although it is often called a ''degenerate quadric'' or a ''reducible quadric''. In coordinates , the general quadric is thus defined by the algebraic equationSilvio LevQuadricsin "Geometry Formulas and Facts", excerpted from 30th Edition of ''CRC Standard Mathematical Tables and Formulas'', CRC Press, from The Geometry Center at University of Minnesota : \sum_^ x_i Q_ x_j + \sum_^ P_i x_i + R = 0 which may be compactly written in vector and matrix notation as: : x Q x^\mathrm + P x^\mathrm + ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conformal Geometry
In mathematics, conformal geometry is the study of the set of angle-preserving ( conformal) transformations on a space. In a real two dimensional space, conformal geometry is precisely the geometry of Riemann surfaces. In space higher than two dimensions, conformal geometry may refer either to the study of conformal transformations of what are called "flat spaces" (such as Euclidean spaces or spheres), or to the study of conformal manifolds which are Riemannian or pseudo-Riemannian manifolds with a class of metrics that are defined up to scale. Study of the flat structures is sometimes termed Möbius geometry, and is a type of Klein geometry. Conformal manifolds A conformal manifold is a pseudo-Riemannian manifold equipped with an equivalence class of metric tensors, in which two metrics ''g'' and ''h'' are equivalent if and only if :h = \lambda^2 g , where ''λ'' is a real-valued smooth function defined on the manifold and is called the conformal factor. An equivalence cla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conic
In mathematics, a conic section, quadratic curve or conic is a curve obtained as the intersection of the surface of a cone with a plane. The three types of conic section are the hyperbola, the parabola, and the ellipse; the circle is a special case of the ellipse, though historically it was sometimes called a fourth type. The ancient Greek mathematicians studied conic sections, culminating around 200 BC with Apollonius of Perga's systematic work on their properties. The conic sections in the Euclidean plane have various distinguishing properties, many of which can be used as alternative definitions. One such property defines a non-circular conic to be the set of those points whose distances to some particular point, called a ''focus'', and some particular line, called a ''directrix'', are in a fixed ratio, called the ''eccentricity''. The type of conic is determined by the value of the eccentricity. In analytic geometry, a conic may be defined as a plane algebraic curve of deg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Field (mathematics)
In mathematics, a field is a set on which addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division are defined and behave as the corresponding operations on rational and real numbers do. A field is thus a fundamental algebraic structure which is widely used in algebra, number theory, and many other areas of mathematics. The best known fields are the field of rational numbers, the field of real numbers and the field of complex numbers. Many other fields, such as fields of rational functions, algebraic function fields, algebraic number fields, and ''p''-adic fields are commonly used and studied in mathematics, particularly in number theory and algebraic geometry. Most cryptographic protocols rely on finite fields, i.e., fields with finitely many elements. The relation of two fields is expressed by the notion of a field extension. Galois theory, initiated by Évariste Galois in the 1830s, is devoted to understanding the symmetries of field extensions. Among other results, thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Projective Plane
In mathematics, a projective plane is a geometric structure that extends the concept of a plane. In the ordinary Euclidean plane, two lines typically intersect in a single point, but there are some pairs of lines (namely, parallel lines) that do not intersect. A projective plane can be thought of as an ordinary plane equipped with additional "points at infinity" where parallel lines intersect. Thus ''any'' two distinct lines in a projective plane intersect at exactly one point. Renaissance artists, in developing the techniques of drawing in perspective, laid the groundwork for this mathematical topic. The archetypical example is the real projective plane, also known as the extended Euclidean plane. This example, in slightly different guises, is important in algebraic geometry, topology and projective geometry where it may be denoted variously by , RP2, or P2(R), among other notations. There are many other projective planes, both infinite, such as the complex projective plane, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |