|
Benny Moré
Bartolomé Maximiliano Moré Gutiérrez (24 August 1919 – 19 February 1963), better known as Benny Moré (also spelled Beny Moré), was a Cuban singer, bandleader and songwriter. Due to his fluid tenor voice and his great expressivity, he was known variously as ''El Bárbaro del Ritmo'' and ''El Sonero Mayor''. Moré was a master of the – the art of vocal improvisation in son cubano – and many of his tunes developed this way. He often took part in ''controversias'' (vocal duels) with other singers like Cheo Marquetti and Joseíto Fernández. Apart from ''son cubano'', Moré was a popular singer of guarachas, cha cha cha, mambo, son montuno, and boleros. Moré started his career with the Trío Matamoros in the 1940s and after a tour in Mexico he decided to stay in the country. Both Moré and dancer Ninón Sevilla made their cinematic debut in 1946's ''Carita de cielo'', but Moré focused on his music career. In the late 1940s, he sang guaracha-mambos with Pérez Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santa Isabel De Las Lajas
Lajas, known historically and culturally as Santa Isabel de las Lajas, is a municipality and town in the Cienfuegos Province of Cuba. It is located in the northern part of the province, west of Santa Clara and immediately south of the A1 motorway. Demographics In 2004, the municipality of Lajas had a population of 22,602. With a total area of , it has a population density of . See also *Municipalities of Cuba The provinces of Cuba are divided into 168 municipalities or ''municipios''. They were defined by Cuban Law Number 1304 of July 3, 1976Fifth United Nations Conference on the Standardization of Geographical Names, Vol. II, published by the United N ... * List of cities in Cuba References External links * Lajason EcuRed Populated places in Cienfuegos Province {{Cuba-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
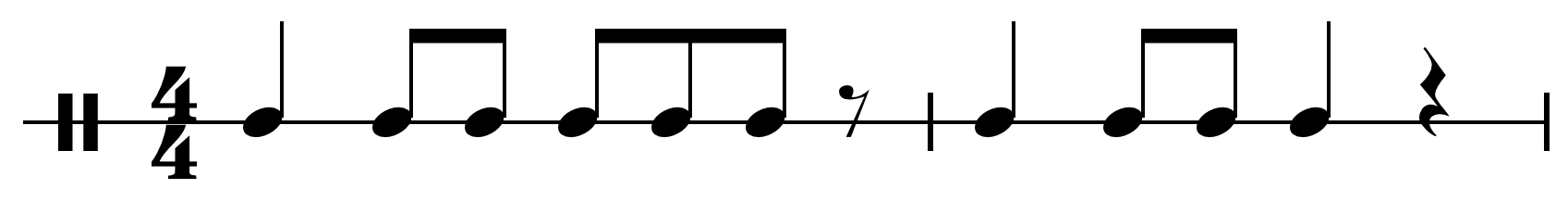
Cha-cha-chá (music)
Cha-cha-chá () is a genre of Cuban music. It has been a popular dance music which developed from the Danzón-mambo in the early 1950s, and became widely popular throughout the entire world. Origin The creation of cha-cha-chá has been traditionally attributed to Cuban composer and violinist Enrique Jorrín, who began his career playing for the charanga band Orquesta América. According to the testimony of Enrique Jorrín, he composed some '' danzones'' in which musicians of the orchestra had to sing short refrains, and this style was very successful. In the danzón "Constancia", he introduced some montunos and the audience was motivated to join in singing the refrains. Jorrín also asked the members of the orchestra to sing in unison so the lyrics might be heard more clearly and achieve a greater impact in the audience. That way of singing also helped to mask the poor singing skills of the orchestra members. In 1948, Jorrín changed the style of a Mexican song by Guty Cár ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
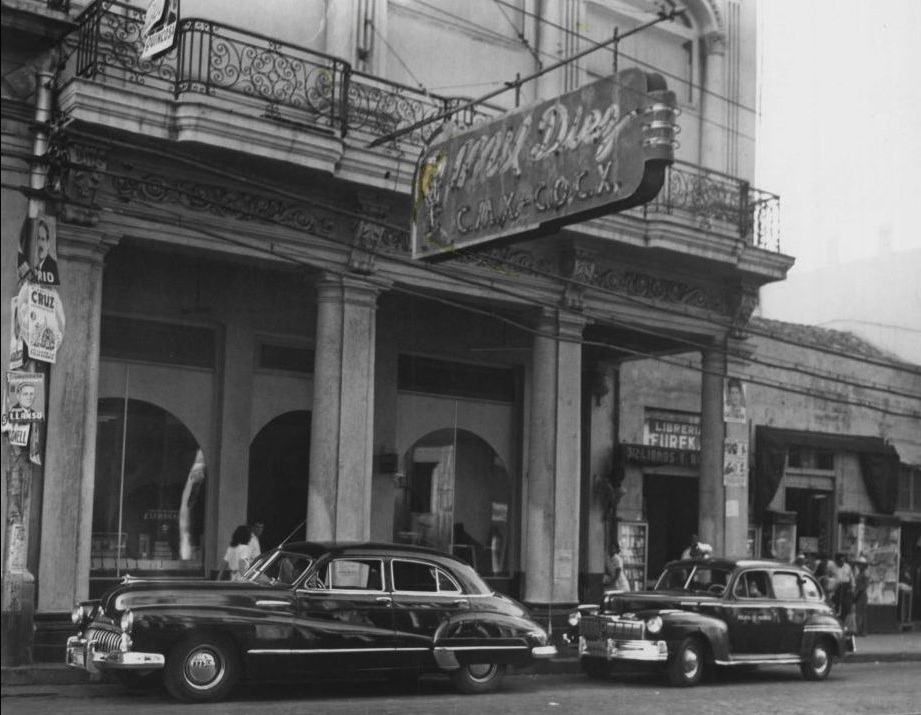
Radio Mil Diez
Radio Mil Diez (or Radio 1010) was a radio station broadcasting from Havana, Cuba, owned by the Popular Socialist Party (PSP). Radio Mil Diez broadcast for five years, between 1943-1948, and played an important role in shaping contemporary Cuban music. Emergence Following the entry of the Soviet Union in the war against Germany the Cuban communists re-emerged as a legal political party, the PSP. The party purchased Radio Lavín and converted it into Radio Mil Diez in 1943. The first broadcast was made on April 1, 1943. The name reflected the dial sign (1010). Radio Mil Diez became an important propaganda weapon of the party, and one of the foremost communist media outlets in the Caribbean at the time. The slogans of the radio station were ''La emisora del pueblo'' ('The Broadcaster of the People') and ''Todo lo bueno al servicio del pueblo'' ('All the Best to Serve the People'). Frequency Radio Mil Diez had the most powerful shortwave radio transmitter in Havana. It broadcast on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CMQ (Cuba)
CMQ was a Cuban radio and television station located in Havana, Cuba, reaching an audience in the 1940s and 1950s, attracting viewers and listeners with a program that ranged from music and news dissemination. It later expanded into radio and television networks. As a radio network it was a heated competitor of the RHC-Cadena Azul network. Founding The company was founded on March 12, 1933, by Miguel Gabriel and Ángel Cambó. Ten years later, on August 1, 1943, half of it was acquired by the business group of Goar Mestre. In the beginning, it transmitted only in the capital expanding later to the rest of the country. Pre-revolutionary Cuba was an early adopter of new technology, including TV. Cuba was the first Latin American country to have television. In December 1946, station CM-21P conducted an experimental multi-point live broadcast. Regular commercial broadcasting began in October 1950 with Gaspar Pumarejo's Unión Radio TV. This was followed by Goar Mestre Espinosa's CMQ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morón, Cuba
Morón is a city and a municipality in Ciego de Ávila Province in central Cuba. It is one of ten municipalities in the province, and is the second in importance and the oldest. Morón is the closest city to the tourist resorts on Cayo Coco and Cayo Guillermo. Geography The municipality is located north of the city of Ciego de Ávila, bordering the Bolivia municipality to the east, Chambas to the west, the Bay of Buena Vista and the Jardines del Rey to the north and the Ciro Redondo municipality to the south. The terrain is mostly plain, with small hills to the north, made up of salt domes. The north shore is covered by marshes. Morón has the largest natural water mirror in Cuba, Laguna de Leche, of . Cayo Coco and Cayo Guillermo, two of the cays of Jardines del Rey archipelago is located north of Morón, across the Bay of Dogs (''Bahia Perros''). Previously the municipality was much larger, being one of nine in the previous province of Camagüey. In 1943, it was divide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Kongo
The Kingdom of Kongo ( kg, Kongo dya Ntotila or ''Wene wa Kongo;'' pt, Reino do Congo) was a kingdom located in central Africa in present-day northern Angola, the western portion of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, and the Republic of the Congo. At its greatest extent it reached from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Kwango River in the east, and from the Congo River in the north to the Kwanza River in the south. The kingdom consisted of several core provinces ruled by the ''Manikongo'', the Portuguese version of the Kongo title ''Mwene Kongo'', meaning "lord or ruler of the Kongo kingdom", but its sphere of influence extended to neighbouring kingdoms, such as Ngoyo, Kakongo, Loango, Ndongo and Matamba, the latter two located in what is Angola today. From c. 1390 to 1862 it was an independent state. From 1862 to 1914 it functioned intermittently as a vassal state of the Kingdom of Portugal. In 1914, following the Portuguese suppression of a Kongo revolt, Portugal abol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cienfuegos Province
Cienfuegos () is one of the provinces of Cuba. The capital city of the province is also called Cienfuegos and was founded by French settlers in 1819. Overview Until 2011 Cienfuegos was the smallest province in Cuba (excluding the city of Havana and the Isla de la Juventud) with an economy almost entirely dedicated to the growing and processing of sugar. Sugar mills and sugarcane plantations dot the landscape. There are waterfalls in the sierra of the province. Scuba diving off Cienfuegos province is extremely popular both with tourists and locals. There are numerous underwater caves, and well over 50 dive sites in the province. The provinces of Cienfuegos, Sancti Spíritus Sancti Spíritus () is a municipality and capital city of the province of Sancti Spíritus Province, Sancti Spíritus in central Cuba and one of the oldest Cuban European settlements. Sancti Spíritus is the genitive case of Latin language, Lat ..., and Villa Clara were once all part of the now defu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santa Clara Province
Santa Clara (also known as Las Villas after 1940) was a historical province of Cuba and its capital was Santa Clara. After 1976, its territory was divided into the modern Cuban provinces of Villa Clara, Cienfuegos and Sancti Spíritus Sancti Spíritus () is a municipality and capital city of the province of Sancti Spíritus Province, Sancti Spíritus in central Cuba and one of the oldest Cuban European settlements. Sancti Spíritus is the genitive case of Latin language, Lat .... Overview The province was split up in 1976, with the administrative re-adjustment proclaimed by Cuban Law Number 1304 of July 3, 1976.Fifth United Nations Conference on the Standardization of Geographical Names, Vol. II, published by the United Nations, New York, 1991 References Further reading * External links Province webpage Former provinces of Cuba 1900s establishments in Cuba 1976 disestablishments in Cuba Cienfuegos Province Sancti Spíritus Province Villa Clara Province Sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuba Cienfuegos BennyMore (www
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribbean Sea, Gulf of Mexico, and Atlantic Ocean meet. Cuba is located east of the Yucatán Peninsula (Mexico), south of both the American state of Florida and the Bahamas, west of Hispaniola (Haiti/Dominican Republic), and north of both Jamaica and the Cayman Islands. Havana is the largest city and capital; other major cities include Santiago de Cuba and Camagüey. The official area of the Republic of Cuba is (without the territorial waters) but a total of 350,730 km² (135,418 sq mi) including the exclusive economic zone. Cuba is the second-most populous country in the Caribbean after Haiti, with over 11 million inhabitants. The territory that is now Cuba was inhabited by the Ciboney people from the 4th millennium BC with the Guanahatabey ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis, also known as liver cirrhosis or hepatic cirrhosis, and end-stage liver disease, is the impaired liver function caused by the formation of scar tissue known as fibrosis due to damage caused by liver disease. Damage causes tissue repair and subsequent formation of scar tissue, which over time can replace normal functioning tissue, leading to the impaired liver function of cirrhosis. The disease typically develops slowly over months or years. Early symptoms may include tiredness, weakness, loss of appetite, unexplained weight loss, nausea and vomiting, and discomfort in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen. As the disease worsens, symptoms may include itchiness, swelling in the lower legs, fluid build-up in the abdomen, jaundice, bruising easily, and the development of spider-like blood vessels in the skin. The fluid build-up in the abdomen may become spontaneously infected. More serious complications include hepatic encephalopathy, bleeding from dilated veins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcoholism
Alcoholism is, broadly, any drinking of alcohol (drug), alcohol that results in significant Mental health, mental or physical health problems. Because there is disagreement on the definition of the word ''alcoholism'', it is not a recognized diagnostic entity. Predominant diagnostic classifications are alcohol use disorder (DSM-5) or alcohol dependence (ICD-11); these are defined in their respective sources. Excessive alcohol use can damage all organ systems, but it particularly affects the brain, heart, liver, pancreas and immune system. Alcoholism can result in mental illness, delirium tremens, Wernicke–Korsakoff syndrome, Heart arrhythmia, irregular heartbeat, an impaired immune response, liver cirrhosis and alcohol and cancer, increased cancer risk. Drinking during pregnancy can result in fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Women are generally more sensitive than men to the harmful effects of alcohol, primarily due to their smaller body weight, lower capacity to metaboli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernesto Duarte Brito
Ernesto Duarte Brito (Jovellanos (Cuba), November 7, 1922 – Madrid, Spain, March 4, 1988) was a Cuban musician, author of the bolero ''Cómo fue'', whose performance by Benny Moré became very famous. There are many versions of this bolero all over the world. He was the father of the multi-instrumentalist, composer and arranger Tito Duarte. Artistic career He was a composer and producer, conductor and arranger. Among the many songs he composed, the most outstanding are ''Nicolasa'', ''El baile del pingüino'', ''Bájate de esa nube'', ''Anda dilo ya'', ''Cicuta tibia'', ''Arrímate cariñito'', ''Dónde estabas tú'', ''Qué chiquitico es el mundo'', etc. As a producer, he launched to fame, first with the record label "Gema", founded with Guillermo Alvarez Guedes, and later with his own label "Duarte",Díaz Ayala, Cristóbal. Música cubana, del Areyto a la Nueva Trova. Edit. Cubanacán, 1981, p.224. artists like the afore mentioned Benny Moré, Rolando Laserie, Rolo Martínez ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)